Introduction: Defining Carbohydrates

Carbohydrates are one of the three macronutrients, along with proteins and fats, that are essential to the human body. Carbohydrates are often referred to as the body’s primary source of energy. When carbohydrates are consumed, they are broken down into glucose, which is then transported to cells throughout the body to provide energy. The body can also convert carbohydrates into glycogen, which is stored in the liver and muscles and used as a fuel source during physical activity.
There are two main types of carbohydrates: simple and complex. Simple carbohydrates, also known as sugars, are made up of one or two sugar molecules and are quickly digested and absorbed by the body. Complex carbohydrates, on the other hand, are made up of three or more sugar molecules and take longer to digest, resulting in a more sustained release of energy.
In addition to providing energy, carbohydrates also play a crucial role in optimal bodily function. For example, carbohydrates are necessary for the proper functioning of the brain and nervous system. Studies have shown that low-carbohydrate diets can lead to decreased cognitive function and mood disturbances.
Carbohydrates are essential for endurance activities, as they provide the necessary energy for muscles to contract and sustain activity over time. This is why athletes and active individuals often consume a higher percentage of carbohydrates in their diets.
It’s important to note that not all carbohydrates are created equal. Simple carbohydrates, such as those found in processed and sugary foods, can lead to spikes in blood sugar and energy crashes. On the other hand, complex carbohydrates, such as those found in whole grains, fruits, and vegetables, provide more stable energy and a host of other nutrients.
Incorporating carbohydrates into a healthy, balanced diet is crucial for maintaining optimal energy levels and overall health. In the following sections, we’ll dive into the different types of carbohydrates and how to incorporate them into your diet for sustained energy.
Benefits of Carbohydrates for Energy

Carbohydrates are one of the three essential macronutrients that our body requires for functioning optimally. They are the primary source of energy for the body and play a crucial role in maintaining normal body functions. Carbohydrates are widely known for their ability to boost energy levels in the body, making it an indispensable part of our diet. In this section, we will discuss the various benefits of carbohydrates for energy, including its role as a primary energy source, its importance for endurance activities, and mental alertness. If you’re looking for ways to increase your energy levels naturally, incorporating carbohydrates into your diet can be a great place to start. To learn more about natural ways to boost energy levels, check out our article on 5 Foods to Boost Energy Levels Naturally.
Carbohydrates as a Primary Energy Source
Carbohydrates are the body’s primary energy source, providing us with the fuel we need to perform daily activities, from walking to thinking to exercising. When consumed, carbohydrates are broken down into glucose, which is then used by the body to produce energy. Glucose is transported through the bloodstream to cells throughout the body, where it is converted into ATP, the molecule our cells use to power nearly all of our biological processes.
It’s important to note that not all carbohydrates are created equal, and their impact on our energy levels can vary depending on their source and other factors. For example, consuming high amounts of simple carbohydrates, such as those found in refined sugars and processed foods, can lead to a rapid spike in blood sugar levels followed by a quick crash, leaving us feeling tired and sluggish. On the other hand, complex carbohydrates, such as those found in whole grains, vegetables, and legumes, are digested more slowly and provide a steady stream of energy over a longer period of time.
Consuming the right types of carbohydrates, in the right amounts, is crucial for maintaining optimal energy levels throughout the day. In addition to providing fuel for physical activity, carbohydrates are also important for mental alertness and focus. Research has shown that consuming carbohydrates can increase levels of serotonin, a neurotransmitter that helps regulate mood, appetite, and sleep.
To ensure that you’re getting enough carbohydrates in your diet, it’s important to focus on whole foods and limit processed and refined carbohydrates. This includes incorporating plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes into your meals. For more information on meal planning for sustained energy, check out our article here.
In addition to providing energy for everyday activities, carbohydrates are also crucial for endurance activities such as running, cycling, and other forms of cardiovascular exercise. During these activities, our bodies rely on carbohydrates as the primary source of fuel, and consuming carbohydrates before, during, and after exercise can help improve performance and reduce fatigue.
To optimize your carbohydrate intake before exercise, it’s recommended to consume a meal containing complex carbohydrates and protein a few hours before your workout. This can help provide sustained energy throughout your exercise routine. For more information on the best pre-workout foods, check out our article here.
During long periods of exercise, consuming carbohydrates in the form of sports drinks, gels, or other easily-digestible sources can help provide a quick source of energy and delay fatigue. After exercise, consuming carbohydrates can help replenish glycogen stores and support muscle recovery.
Carbohydrates play a crucial role in providing energy for both everyday activities and endurance exercise. Incorporating the right types and amounts of carbohydrates into your diet can help support optimal energy levels throughout the day. For more information on incorporating superfoods for energy and gut health, check out our articles here and here, respectively.
Carbohydrates for Endurance Activities
Carbohydrates for endurance activities are crucial for individuals who engage in prolonged periods of physical activity. During endurance exercises such as long-distance running or cycling, carbohydrates are the primary source of fuel for the body. When the body runs out of carbohydrates, it will turn to fat stores for energy, which is a less efficient process and can cause fatigue and decreased performance.
Consuming carbohydrates before endurance activities can help to ensure that the body has enough fuel to sustain the activity. It is recommended to consume a meal that is high in carbohydrates 3-4 hours before the activity. This will give the body enough time to digest the food and convert it into glucose, which will be stored in the muscles and liver as glycogen.
During the activity, consuming carbohydrates in the form of gels, bars, or sports drinks can help to maintain energy levels and delay muscle fatigue. It is recommended to consume 30-60 grams of carbohydrates per hour of activity, depending on the intensity and duration of the activity. It is important to also stay hydrated by drinking water or a sports drink that contains electrolytes.
After the activity, consuming carbohydrates is important to replenish the glycogen stores in the muscles and liver. It is recommended to consume a meal or snack that is high in carbohydrates within 30 minutes of completing the activity. This will help the body to recover faster and prepare for the next endurance activity.
Here is a table that shows some examples of carbohydrates that are good for endurance activities:
| Type of Carbohydrate | Examples |
|---|---|
| Simple | Bananas, dried fruit, sports drinks |
| Complex | Whole grain pasta, brown rice, oatmeal |
| Fiber | Vegetables, beans, whole grain bread |
Consuming carbohydrates before, during, and after endurance activities is important for maintaining energy levels and delaying muscle fatigue. It is recommended to consume a diet that is high in carbohydrates from both simple and complex sources, as well as fiber. By incorporating carbohydrates into your diet, you can enhance your performance and achieve your fitness goals.
Carbohydrates for Mental Alertness
Carbohydrates are not only essential for physical energy, but also for mental alertness. The brain relies heavily on glucose, which is a type of carbohydrate, to function properly. Without enough glucose, brain function can be impaired, leading to sluggishness and difficulty concentrating.
A study published in the journal Nutrients found that consuming carbohydrates can improve cognitive performance, including memory, attention, and processing speed.
To further understand the relationship between carbohydrates and mental alertness, it’s important to consider the glycemic index (GI). The GI is a measure of how quickly carbohydrates are broken down and released into the bloodstream as glucose. Foods with a high GI, such as sugary snacks or white bread, cause a rapid spike in blood sugar levels, followed by a crash. This can lead to feelings of drowsiness or lack of concentration.
On the other hand, foods with a low GI, such as whole grain breads or oatmeal, release glucose into the bloodstream more slowly and steadily, providing sustained energy and promoting mental alertness.
It’s also important to note that combining carbohydrates with protein and healthy fats can help slow down the digestion of carbohydrates, leading to a more sustained release of glucose and better mental function.
Incorporating complex carbohydrates, such as whole grains, fruits, and vegetables, into your diet can help improve mental alertness and cognitive performance. Avoiding simple carbohydrates, like candy and refined sugar, can also help prevent blood sugar crashes and promote sustained mental energy throughout the day.
So, the next time you’re feeling sluggish at work or school, consider reaching for a complex carbohydrate-rich snack, like an apple with almond butter or whole grain crackers with hummus. Your brain will thank you for the sustained mental energy boost.
If you’re looking for more tips on how to boost your energy levels and start your day off right, check out our article on 5 Ways to Boost Your Energy and Start Your Day Off Right.
Types of Carbohydrates
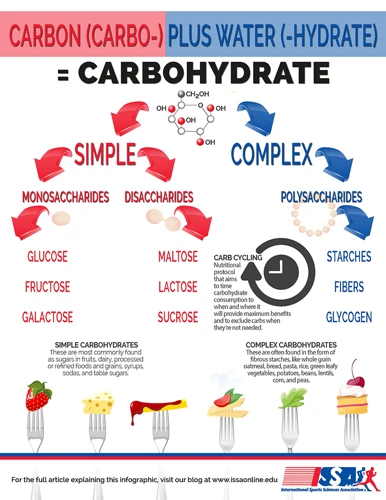
When it comes to carbohydrates, not all foods are created equal. There are various types of carbohydrates, and some are more beneficial for our energy levels than others. It’s important to understand the differences between these types of carbohydrates in order to make informed decisions about what we consume. Let’s take a closer look at the various types of carbohydrates, highlighting their unique properties and benefits.
Simple Carbohydrates: The Good and the Bad
When it comes to carbohydrates, not all sources are created equal. Simple carbohydrates, for example, are often touted as “bad” carbohydrates, but the truth is a little more nuanced. There are both good and bad sources of simple carbohydrates, and it’s important to be able to distinguish between the two.
The Good:
– Fruits: Many fruits, such as bananas, grapes, and oranges, are rich in simple carbohydrates. However, they also contain important nutrients like vitamins and minerals, and are a great source of fiber.
– Milk: Milk contains a simple sugar called lactose, which is an important source of energy for the body. It also provides important nutrients like calcium and vitamin D.
– Honey: Honey is a natural sweetener that also happens to be rich in antioxidants and has antimicrobial properties.
The Bad:
– Added sugars: Many processed foods contain added sugars, which are often listed on ingredient lists under a variety of names, including high fructose corn syrup, corn syrup, and sucrose. These types of simple carbohydrates can cause spikes in blood sugar and should be limited in the diet.
– Refined carbohydrates: Refined carbohydrates, such as white bread and white rice, have had the fiber and many nutrients stripped out, leaving behind a simple carbohydrate that is quickly digested and can cause spikes in blood sugar. These types of carbohydrates should also be limited in the diet.
While it’s important to limit certain sources of simple carbohydrates, such as added sugars and refined carbohydrates, it’s also important to include good sources of simple carbohydrates, such as fruits and milk, in a well-rounded diet.
Complex Carbohydrates: The Key to Sustained Energy
Complex carbohydrates are a type of carbohydrate that consists of long chains of sugar molecules. They are also known as starchy carbohydrates, and they are found in foods such as whole grains, vegetables, and legumes. Complex carbohydrates are essential for providing sustained energy throughout the day.
Benefits of Complex Carbohydrates:
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Slow Release of Energy | Complex carbohydrates take longer to break down, which means they provide a slow release of energy over time. This is beneficial for sustained energy and endurance. |
| Fiber Content | Many complex carbohydrates also contain fiber, which helps to regulate blood sugar levels and promote feelings of fullness. |
| Nutrient Density | Complex carbohydrates are often found in nutrient-dense foods such as whole grains and vegetables, which provide essential vitamins and minerals. |
Additionally, complex carbohydrates are beneficial for weight management as they are typically more filling and satiating than simple carbohydrates. They also provide sustained energy for physical activity, making them an essential component of an athlete’s diet.
Examples of complex carbohydrates include:
– Whole grains such as brown rice, quinoa, and whole wheat bread
– Vegetables such as sweet potatoes, butternut squash, and beets
– Legumes such as lentils, chickpeas, and black beans
It’s important to note that not all carbohydrates are created equal. While complex carbohydrates provide sustained energy, simple carbohydrates such as candy and soda provide a quick burst of energy followed by a crash. Focusing on incorporating complex carbohydrates into your diet can provide numerous benefits for sustained energy and overall health.
Fiber: The Often Overlooked Carbohydrate
Fiber is a type of carbohydrate that is commonly overlooked in the diet. Despite its importance in digestive health and overall well-being, many people do not consume enough fiber on a daily basis.
What is fiber?
Fiber is a type of carbohydrate that cannot be digested by the body. Instead, it passes through the digestive system relatively intact. There are two types of fiber: soluble and insoluble. Soluble fiber dissolves in water and forms a gel-like substance in the digestive system. Insoluble fiber, on the other hand, does not dissolve in water and helps to add bulk to the stool.
The benefits of fiber
Fiber plays an important role in maintaining digestive health. It helps to prevent constipation by adding bulk to the stool and promoting regular bowel movements. Fiber can help to lower cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of heart disease. It may also play a role in reducing the risk of certain types of cancer.
Sources of fiber
Fiber can be found in a variety of foods, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes. Some of the best sources of fiber include:
- Fruits such as apples, bananas, and oranges
- Vegetables such as broccoli, carrots, and sweet potatoes
- Whole grains such as quinoa, brown rice, and oatmeal
- Legumes such as lentils, chickpeas, and black beans
How to incorporate fiber into your diet
Incorporating fiber into your diet is easier than you might think. Simply adding more fruits, vegetables, and whole grains to your meals can help to increase your fiber intake. You can also try swapping out refined grains for whole grains, such as choosing brown rice instead of white rice or whole wheat pasta instead of regular pasta.
The bottom line
Fiber is an important nutrient that plays a key role in digestive health and overall well-being. By incorporating more fiber-rich foods into your diet, you can help to improve your health and increase your energy levels.
How Much Carbohydrate Do You Need?

One of the most common questions when it comes to carbohydrates and energy is how much carbohydrate is actually necessary. It can be confusing to know how to calculate your daily carbohydrate needs, especially when different factors such as activity level and weight loss goals come into play. However, understanding the importance of carbohydrates and the role they play in providing energy can help guide you in determining the right amount for your individual needs. Let’s delve into the details and explore how to effectively incorporate carbohydrates into your diet.
Calculating Your Daily Carbohydrate Needs
Calculating Your Daily Carbohydrate Needs
When it comes to determining how many carbohydrates one should consume daily, there are several factors to consider. These include age, gender, activity level, and overall goals.
| Carbohydrate Intake | |
|---|---|
| Sedentary Adult | 6-10 grams/kg of body weight |
| Active Adult | 10-12 grams/kg of body weight |
| Adult Athlete | 8-12 grams/kg of body weight |
For sedentary adults, a range of 6-10 grams/kg of body weight is generally recommended. This means that someone who weighs 68 kilograms (150 pounds) would need between 408-680 grams of carbohydrates per day.
Active adults, who engage in regular moderate exercise, should aim for a slightly higher carbohydrate intake of 10-12 grams/kg of body weight. For the same person who weighs 68 kilograms (150 pounds), this would equate to 680-816 grams of carbohydrates per day.
For adult athletes who engage in intense training sessions, a range of 8-12 grams/kg of body weight is recommended. So for the same person, this would be between 544-816 grams of carbohydrates per day.
It is important to note that these are just general guidelines and may need to be adjusted based on individual needs and goals. For example, someone who is trying to lose weight may benefit from consuming fewer carbohydrates and more protein, while someone training for a marathon may need a higher carbohydrate intake to support their endurance training.
Incorporating carbohydrates into your daily diet in a balanced way can help increase energy levels and support overall health and fitness goals.
Carbohydrates for Active Individuals
For active individuals, carbohydrates are a key component of their diet to ensure they have enough energy to fuel their physical activities. Here are some tips on how to incorporate carbohydrates in your diet if you have an active lifestyle:
- Choose the right types of carbohydrates: As mentioned earlier, not all carbohydrates are created equal. Complex carbohydrates, such as whole grains and vegetables, will offer you sustained energy for longer periods of time compared to simple carbohydrates, such as candy and soda, which are quickly absorbed and can cause a crash in energy levels.
- Eat the right amount: The amount of carbohydrates an active individual needs will depend on the intensity and duration of their physical activities. Aim to consume 2-3 grams of carbohydrates per pound of body weight if you engage in moderate to high-intensity activities for an hour or more per day.
- Time your carbohydrate intake: Eating too many carbohydrates at once can lead to a spike in blood sugar levels and a consequent crash. To avoid this, spread out your carbohydrate intake throughout the day and try consuming them before, during, and after your workout sessions to maintain your energy levels and aid in recovery.
- Fuel up before endurance activities: Endurance activities, such as long distance running or cycling, require additional fuel in the form of carbohydrates to keep you going. Eat a meal containing complex carbohydrates before such activities and consider consuming glucose gels or sports drinks during the activity to sustain energy levels.
Remember, carbohydrates are an essential macronutrient for active individuals and should not be feared or avoided. By consuming the right types of carbohydrates in the right amounts, you can ensure you have enough energy to power through your physical activities and achieve your fitness goals.
Carbohydrates for Weight Loss
When it comes to weight loss, carbohydrates sometimes get a bad reputation. However, it’s important to recognize that not all carbohydrates are created equal. In fact, incorporating the right types of carbohydrates into your diet can actually support weight loss efforts.
1. Choose Complex Carbohydrates
Instead of cutting carbohydrates entirely, make sure you’re choosing the right types. Complex carbohydrates, found in foods like whole grains, fruits, and vegetables, are the key to sustained energy and can also support weight loss. These foods are high in fiber and take longer for your body to digest, which means they keep you feeling full for longer periods of time.
2. Pay Attention to Portion Sizes
While complex carbohydrates can be beneficial for weight loss, it’s still important to pay attention to portion sizes. Eating too many carbohydrates, even the right kinds, can lead to weight gain. Aim to have a serving of carbohydrates with each meal, but keep portion sizes in check.
3. Limit Simple Carbohydrates and Sugars
While complex carbohydrates are great for weight loss, simple carbohydrates and sugars should be limited. These are the types of carbohydrates found in processed and packaged foods, as well as sugary drinks and snacks. They are low in fiber and can cause blood sugar spikes, which can lead to overeating and weight gain.
4. Time Carbohydrate Intake
Timing your carbohydrate intake can also support weight loss efforts. Eating carbohydrates earlier in the day can give you the energy you need to get through your day and can also support weight loss. Eating carbohydrates in the evening, especially in large quantities, can lead to weight gain.
5. Don’t Cut Carbohydrates Completely
Finally, it’s important to remember that cutting carbohydrates completely is not necessary for weight loss. In fact, it can actually be counterproductive. Carbohydrates are an important source of energy for your body, and not getting enough can lead to fatigue and cravings that can derail weight loss efforts. Instead, focus on choosing the right types and portion sizes for your body and goals.
Putting It All Together: Tips for Incorporating Carbohydrates into Your Diet
One of the most important steps in harnessing the power of carbohydrates for energy is learning how to incorporate them into your diet in a balanced and sustainable way. Here are some tips for doing just that.
1. Choose whole, minimally processed carbohydrate sources. This means opting for foods like whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and legumes over refined grains and sugar-laden snacks. Whole foods contain more fiber and other important nutrients that help to slow the absorption of carbohydrates and keep you feeling full and satisfied.
2. Be aware of portion sizes. While carbohydrates are an important part of a healthy diet, it’s easy to overdo it on the carbs when you’re not paying attention. Use measuring cups or a food scale to help you get a better sense of the appropriate portion sizes for different carbohydrate sources, and don’t forget to factor in the carbohydrate content of added sugars and other sweeteners.
3. Limit your intake of high-sugar beverages and snacks. Sugary drinks like soda and fruit juice can contain a surprising amount of carbohydrates and can quickly spike your blood sugar levels. Instead, reach for water, unsweetened tea or coffee, or other low-sugar beverage options. Similarly, indulge in high-sugar snacks like candy and cookies only in moderation.
4. Prioritize carbohydrates around your workouts. Carbohydrates can be especially beneficial when consumed before or after exercise, as they help to provide your muscles with the energy they need to perform at their best. Consider having a small carb-rich snack like a banana or a granola bar before a workout, and include some carbohydrates in your post-workout meal or snack as well.
5. Don’t forget about variety. One of the keys to a healthy diet is getting a wide range of nutrients from different foods. Try to incorporate a variety of carbohydrate sources into your meals and snacks to ensure that you’re getting enough fiber, vitamins, and minerals. This might mean experimenting with lesser-known grains like quinoa or farro, or trying out new vegetable or fruit recipes.
By following these tips, you can help to ensure that carbohydrates are a positive and energizing part of your diet rather than a source of confusion or frustration. Remember, when it comes to fueling your body and staying active, the right balance of carbohydrates is key.
Conclusion: The Bottom Line on Carbohydrates and Energy
After exploring the benefits and types of carbohydrates, it’s clear that they play an essential role in increasing energy levels. Carbohydrates are not only the primary source of energy for the body, but they also provide sustained energy for endurance and mental alertness.
It’s important to note that not all carbohydrates are created equal. While simple carbohydrates can provide a quick burst of energy, they are often accompanied by a crash and should be consumed in moderation. On the other hand, complex carbohydrates, such as whole grains and vegetables, provide sustained energy and should make up the majority of one’s carbohydrate intake.
Fiber, often overlooked as a carbohydrate, also plays an important role in increasing energy levels. It aids in digestion and can help regulate blood sugar levels, leading to more sustained energy throughout the day.
Determining one’s daily carbohydrate needs depends on factors such as activity level and weight loss goals. However, a general guideline is that carbohydrates should make up 45-65% of one’s daily calorie intake.
Incorporating carbohydrates into one’s diet can be done in simple ways such as choosing whole grain bread over white bread or adding vegetables to a meal. It’s important to focus on incorporating healthy sources of carbohydrates rather than overindulging in processed and sugary foods.
Carbohydrates are crucial for increasing energy levels and should be a staple in one’s diet. It’s important to choose healthy sources of carbohydrates and incorporate them into one’s diet in a balanced way. By doing so, one can experience sustained energy levels throughout the day.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the benefits of carbohydrates for athletic performance?
Carbohydrates are the primary fuel source for high-intensity exercise and can help improve endurance and delay fatigue.
Are simple carbohydrates always bad for you?
No, simple carbohydrates can be found in healthy foods like fruits, vegetables, and dairy products. It’s the added sugars in processed foods that can be harmful to your health.
Can carbohydrates help with weight loss?
Yes, consuming complex carbohydrates can help with weight loss by providing sustained energy and keeping you feeling fuller for longer periods of time.
How much carbohydrate do I need per day?
It depends on your age, gender, weight, and activity level. Generally, adults should aim for 45% to 65% of their daily caloric intake to come from carbohydrates.
What are some good sources of complex carbohydrates?
Whole grains, fruits, vegetables, beans, and legumes are all good sources of complex carbohydrates.
Can a low-carb diet be harmful to your health?
Yes, a low-carb diet can deprive your body of important nutrients and lead to fatigue, constipation, and nutrient deficiencies.
Does fiber count as a carbohydrate?
Yes, fiber is a type of carbohydrate that is important for digestive health and can help regulate blood sugar levels.
Can carbohydrates affect your mood?
Yes, carbohydrates can affect your mood by increasing the production of serotonin in your brain, which can help improve your mood and reduce stress.
Are there any risks to consuming too many carbohydrates?
Consuming too many carbohydrates, especially from simple sugars, can lead to weight gain, increased risk of type 2 diabetes, and other health issues.
Can I still consume carbohydrates if I have a gluten intolerance?
Yes, there are many gluten-free sources of carbohydrates, such as quinoa, brown rice, sweet potatoes, and fruits and vegetables.







