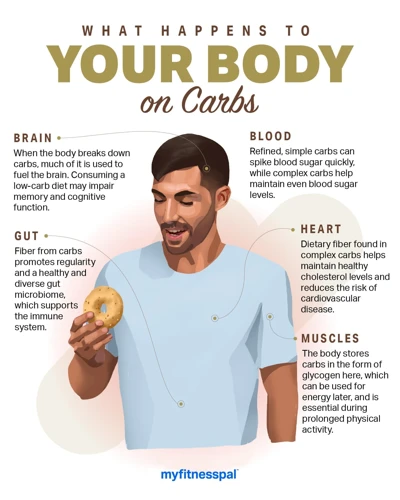
Carbohydrates are a macronutrient that play a vital role in our overall health and wellbeing. They are found in a variety of foods and are often the subject of controversy among health experts and dieticians. Some tout their benefits for providing energy, aiding in digestion, and regulating blood sugar levels, while others warn of the negative effects of consuming too many carbs. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the complex world of carbohydrates, their functions in the body, their impact on health, and provide recommendations for optimal consumption levels. Whether you’re a fitness enthusiast or just looking to improve your diet, this guide will equip you with the knowledge you need to make informed decisions about your carbohydrate intake.
What are Carbohydrates?

Carbohydrates are one of the three macronutrients necessary for a balanced diet, along with protein and healthy fats. They are the most important source of energy for the human body because they provide glucose, which is the primary fuel for the brain and muscles. Carbohydrates can be classified as simple or complex, depending on their chemical structure. In this section, we will explore the different types of carbohydrates and their functions in the body. To learn more about macronutrients and their impact on overall health, check out our article on daily macronutrient intake.
Simple Carbohydrates
Simple Carbohydrates:
Simple carbohydrates, also known as simple sugars, are made up of one or two sugar molecules that are quick to digest and provide an immediate burst of energy. However, the energy provided by simple carbohydrates is short-lived and may leave you feeling tired and lethargic after a while.
The following table lists some examples of simple carbohydrates:
| Simple Carbohydrates | Food Sources |
|---|---|
| Fructose | Fruits, honey, and some vegetables |
| Glucose | Carbohydrate-rich foods such as bread, pasta, and rice |
| Lactose | Milk and dairy products |
| Maltose | Some grains such as barley and malt beverages |
| Sucrose | Table sugar, maple syrup, and honey |
Consuming too many simple carbohydrates can lead to a rapid spike in blood sugar levels, which can result in a host of adverse health effects. Eating too many foods high in simple carbohydrates like table sugar and candy can cause weight gain, tooth decay, and even type 2 diabetes.
It is recommended to limit your consumption of simple carbohydrates and focus on consuming complex carbohydrates like whole grains, fruits, and vegetables, which provide long-lasting energy and are packed full of essential vitamins and minerals.
Complex Carbohydrates
Complex carbohydrates, also known as oligosaccharides and polysaccharides, are made up of three or more sugar molecules bonded together. These carbohydrates are found in many nutrient-dense foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes. They are broken down more slowly in the body, providing a steady stream of energy and helping to regulate blood sugar levels.
Here are some examples of complex carbohydrates:
| Food | Serving Size | Amount of Complex Carbohydrates (in grams) |
|---|---|---|
| Oatmeal (cooked) | 1 cup | 27 |
| Sweet Potato (cooked) | 1 medium | 24 |
| Quinoa (cooked) | 1 cup | 39 |
| Brown Rice (cooked) | 1 cup | 45 |
| Lentils (cooked) | 1 cup | 40 |
| Black Beans (cooked) | 1 cup | 41 |
In addition to providing energy, complex carbohydrates are an excellent source of fiber, vitamins, minerals, and phytonutrients. A high-fiber diet has been linked to numerous health benefits, including improved digestion, lower cholesterol levels, and a reduced risk of cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and certain types of cancer.
It is important to note that not all carbohydrates are created equal. While complex carbohydrates are beneficial to our health, highly processed carbohydrates such as white bread and sugary snacks can have negative effects on our health. It is crucial to choose complex carbohydrates as part of an overall healthy diet.
Increasing fiber intake and choosing whole food sources of complex carbohydrates can also help with weight management and maintaining steady energy levels throughout the day, rather than the energy spikes and crashes that come with consuming highly processed carbohydrates.
Functions of Carbohydrates

Carbohydrates play a crucial role in our body’s normal functioning, becoming the primary source of energy that fuels our cells. The human body requires energy not only for basic movement and daily activities but also for more significant tasks such as exercise, which is why it is essential to understand the functions of carbohydrates thoroughly. In this section, we will explore the vital functions of carbohydrates, such as energy production, blood glucose level maintenance, and digestion assistance. These functions are critical to maintaining our overall health, well-being, and energy levels, making carbohydrates an essential macronutrient even when compared to protein-muscle-growth and health-benefits-healthy-fats-oils.
Energy Production
Carbohydrates play an important role in energy production within the body. When consumed, the body breaks down carbohydrates into glucose which can be used as energy. Glucose is transported to the cells through the bloodstream and is either used immediately or stored for later use. An adequate supply of carbohydrates is necessary for the body to function properly and to support physical activity.
Carbohydrates are particularly important for those who engage in intense physical activity, as the body requires energy to sustain the workout. A diet low in carbohydrates can cause fatigue and a decrease in energy levels, making it difficult to maintain a proper exercise routine.
In fact, daily macronutrient intake for athletes often consists of a higher percentage of carbohydrates to support their energy and performance needs. Endurance athletes, in particular, need a large supply of carbohydrates to fuel their bodies during long periods of activity.
The following table outlines the number of calories one can expect to receive from consuming certain carbohydrates:
| Food | Serving Size | Calories from Carbohydrates |
|---|---|---|
| White Bread | 1 slice | ~70 |
| Whole Wheat Bread | 1 slice | ~70 |
| Spaghetti | 1 cup | ~220 |
| Brown Rice | 1 cup | ~215 |
| Quinoa | 1 cup | ~222 |
| Banana | 1 medium | ~105 |
| Apple | 1 medium | ~95 |
| Orange | 1 medium | ~60 |
It is important to note that not all carbohydrates are created equal. Simple carbohydrates, such as those found in sugary drinks and candy, can cause a quick spike in energy followed by a crash. Complex carbohydrates, however, provide a sustained release of energy and are found in foods such as whole grains, fruits, and vegetables.
While carbohydrates are an essential part of a healthy diet, it is important to consume them in moderation and with a balance of other macronutrients such as protein for muscle growth and healthy fats to maintain optimal health.
Regulation of Blood Glucose Levels
Carbohydrates play an essential role in regulating blood glucose levels, also known as blood sugar levels. Glucose is the primary source of energy for our bodies, but excessive amounts of it can be detrimental to our health. The body relies on insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas, to help regulate blood glucose levels.
When we consume carbohydrates, the body breaks them down into glucose, which is then transported through the bloodstream. The pancreas then secretes insulin to move glucose from the bloodstream into the cells where it can be used for energy production or stored as glycogen. Insulin also helps prevent high blood glucose levels by signaling the liver to convert excess glucose into glycogen for storage.
However, when we eat processed or refined carbohydrates that are high in sugar, such as candy or soda, the body rapidly absorbs glucose, leading to a spike in blood sugar levels. This causes the pancreas to produce more insulin to bring blood glucose levels back down to a healthy range.
Over time, consuming excessive amounts of refined carbohydrates can lead to insulin resistance, where the body becomes less responsive to insulin. This can lead to high blood glucose levels, metabolic disorders, and type 2 diabetes. It is crucial to consume carbohydrates that are less refined, such as whole grains, fruits, and vegetables, to ensure a slower and more sustainable release of glucose into the bloodstream.
Eating a balanced diet that includes adequate amounts of protein and healthy fats can also help regulate blood glucose levels by slowing digestion and preventing the rapid absorption of glucose into the bloodstream.
Carbohydrates are necessary for our bodies, but we need to consume them in moderation and choose the right types to maintain healthy blood glucose levels. By selecting more complex carbohydrates and incorporating other macronutrients into our diet, we can help prevent insulin resistance, metabolic disorders, and even type 2 diabetes.
Assisting in Digestion
Carbohydrates play a crucial role in digestion as well. Carbohydrates provide dietary fiber that promotes healthy digestion. Dietary fiber is the part of plant foods that our bodies cannot digest. Still, it remains an essential nutrient for regulating digestion and improving digestive health. It acts as a sponge that soaks up water and helps soften stools, making them easier to pass through the intestines. Dietary fiber also speeds up transit time in the digestive tract, ensuring waste products move quickly and efficiently through the colon, reducing the risk of constipation and other gastrointestinal problems.
Dietary fiber can also help prevent other diseases such as colon cancer. When bacteria in the colon ferment the dietary fiber, they produce short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) which have anti-inflammatory properties that help protect the colon from cancer.
| Benefits of Dietary Fiber | Foods Rich in Fiber |
|---|---|
| Prevents Constipation | Berries (raspberries, strawberries, blueberries), apples, carrots, broccoli, nuts, whole grains |
| Regulates Blood Sugar Levels | Oats, beans, lentils, sweet potatoes, peas, veggies |
| Reduces LDL Cholesterol Levels | Oatmeal, almonds, flaxseeds, chia seeds, legumes, veggies |
| Helps in Weight Management | Barley, quinoa, brown rice, whole wheat pasta, beans, lentils |
| Prevents Colon Cancer | Beans (navy, kidney, black), broccoli, artichokes, apples with skin, peas, berries |
It is important to note that not all carbohydrates contain fiber, and the amount of it varies depending on the type of carbohydrate. Simple carbohydrates such as sugars and refined grains generally contain very little to no fiber. On the other hand, complex carbohydrates such as whole grains, fruits, and vegetables are high in fiber.
Eating a diet high in fiber-rich complex carbohydrates can improve digestive health and reduce the risk of digestive problems such as constipation, hemorrhoids, and colon cancer. To learn more about macronutrients and how they impact your body, read our article on macronutrients and energy levels. If you’re interested in plant-based sources of macronutrients, read our article on plant-based macronutrients. And to dispel common myths about macronutrients and weight loss, read our article on myths and facts about macronutrients and weight loss.
The Impact of Carbohydrates on Health

As we continue to explore the role of carbohydrates in our body, it’s important to understand their impact on our overall health. While carbohydrates are one of the primary sources of energy for our body, their effects extend far beyond just fueling our daily activities. The impact of carbohydrates can be both positive and negative, which is why it’s crucial to understand how our body processes them and how we can make informed choices about our diet. In this section, we’ll take a closer look at the impact of carbohydrates on our health and discuss both the benefits and potential drawbacks of consuming them.
The Good: Health Benefits of Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are an essential macronutrient and offer several health benefits for the body. Here are some of the benefits of consuming carbohydrates:
- Improved Energy Levels: One of the primary functions of carbohydrates is to provide energy to the body. Carbohydrates are broken down into glucose, which is the primary source of fuel for the body’s cells. Eating carbohydrates can help improve energy levels and keep you feeling energized throughout the day.
- Regulation of Mood and Mental Health: Carbohydrates can also help regulate mood and mental health. Studies have shown that consuming carbohydrates can increase the production of serotonin, a neurotransmitter that plays a vital role in regulating mood, appetite, and sleep.
- Maintaining Muscle Mass: Eating carbohydrates can help maintain and build muscle mass. Carbohydrates are necessary to fuel physical activity, and if you don’t consume enough carbohydrates, your body may break down muscle tissue for energy.
- Reduced Risk of Chronic Disease: Consuming a diet rich in vegetables, fruits, and whole grains (all of which contain carbohydrates) has been linked to a reduced risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and certain types of cancer. This is due to the fact that these foods contain fiber, which helps regulate blood sugar levels and promote feelings of fullness.
- Improved Digestive Health: Carbohydrates, particularly those found in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, are a great source of fiber. Fiber plays a vital role in digestive health by promoting regular bowel movements, preventing constipation, and reducing the risk of gastrointestinal disorders like diverticulitis.
There are many health benefits associated with consuming carbohydrates. However, it’s important to focus on consuming complex carbohydrates from whole food sources rather than simple carbohydrates from processed or refined foods.
The Bad: Negative Effects of Consuming Too Many Carbohydrates
Consuming too many carbohydrates can have negative effects on our health. Here are some of the possible downsides:
- Weight Gain: Eating too many simple carbohydrates, such as sugar and refined flour, can contribute to weight gain. Simple carbohydrates are quickly digested and absorbed by the body, leading to a rapid rise in blood sugar levels. This can trigger the release of insulin, which is a hormone that signals the body to store excess glucose as fat.
- Inflammation: High intake of refined carbohydrates can also cause inflammation in the body. When we eat too many refined carbs, our bodies release more inflammatory cytokines and free radicals, which can cause damage to our cells and tissues. Chronic inflammation has been linked to many serious health conditions, such as heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and cancer.
- Increased Risk of Chronic Diseases: Eating too many carbohydrates, particularly those that are high in sugar or refined flour, can increase the risk of chronic diseases such as type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and certain types of cancer. This is because high-carbohydrate diets can lead to insulin resistance, which is a condition in which the body becomes less responsive to insulin and has trouble regulating blood sugar levels.
- Dental Problems: Eating too many sugary or starchy foods can also increase the risk of dental problems, such as cavities and gum disease. This is because the bacteria that cause these problems feed on sugar, and starchy foods can stick to teeth and provide a breeding ground for bacteria.
- Low Energy: While carbohydrates are an important source of energy for our bodies, consuming too many can actually leave us feeling tired and sluggish. This is because consuming too many carbs can cause a rapid rise and fall in blood sugar levels, which can lead to a crash in energy.
It’s important to limit our intake of simple carbohydrates and focus on consuming mostly complex carbohydrates, which are slower to digest and provide a more sustained release of energy. It’s also important to balance our carbohydrate intake with protein and healthy fats to help keep our blood sugar levels stable and promote overall health.
The Ugly: The Effects of a Low-Carb Diet
While low-carb diets have gained popularity in recent years, they may not be as beneficial for our health as we once thought. In fact, consuming too few carbohydrates can have some negative effects on our bodies.
Effects of a Low-Carb Diet:
| Effects | Description |
|---|---|
| Increased Risk of Nutritional Deficiencies | In restricting carbohydrate intake, it can be difficult to consume enough of certain nutrients, such as fiber, vitamins, and minerals. |
| Dehydration | Lack of carbohydrates may cause increased urination and electrolyte imbalances, leading to dehydration. |
| Bad Breath | In a process known as ketosis, the body produces chemicals that can lead to foul-smelling breath. |
| Weakened Immune System | Carbohydrates play a role in immune system function, so a low-carb diet may lead to a weakened immune system. |
| Increased Risk of Heart Disease | A low-carb diet that is high in animal protein and fats may increase the risk of heart disease, especially in those with pre-existing risk factors. |
A low-carb diet may not be the best choice for everyone. It is important to consult with a healthcare provider before making any significant dietary changes.
How Much Carbohydrates Should You Consume?
When it comes to determining the appropriate amount of carbohydrates to consume, it can be a bit perplexing. On one hand, carbohydrates are an essential macronutrient that provides the body with energy and numerous other benefits. However, consuming too many carbohydrates can lead to negative health effects, such as weight gain and elevated blood sugar levels. In this section of the article, we will explore the recommended daily intake of carbohydrates and provide some guidance on which carbohydrate-rich foods to prioritize and which to limit in order to maintain optimal health.
Recommended Daily Intake of Carbohydrates
The amount of carbohydrates an individual should consume each day varies based on several factors, including age, gender, physical activity level, and overall health goals. The recommended daily intake of carbohydrates for the average adult ranges between 45% to 65% of total daily calories, according to the Dietary Guidelines for Americans.
To better understand how many carbohydrates you should consume, it is important to calculate your total daily calorie needs. This can be determined by using a calorie calculator, which takes into account your age, gender, weight, height, and physical activity level.
Once you determine your total daily calorie needs, you can use a percentage-based approach to calculate your recommended carbohydrate intake. For example, if your daily calorie needs are 2,000 calories, your recommended carbohydrate intake would be between 225-325 grams per day, based on the recommended 45% to 65% range.
It is important to note that the type of carbohydrates consumed also plays a role in overall health. Complex carbohydrates, found in foods like whole grains, vegetables, and beans, are preferred over simple carbohydrates, found in sugary foods and drinks. Complex carbohydrates provide sustained energy and contain important nutrients like fiber, while simple carbohydrates provide quick energy but lack important nutrients.
Below is a table that outlines the recommended daily intake of carbohydrates based on total daily calorie needs for adults:
| Total Daily Calories | Grams of Carbohydrates |
|---|---|
| 1,200 | 135-195 |
| 1,500 | 169-244 |
| 1,800 | 203-293 |
| 2,000 | 225-325 |
| 2,500 | 281-406 |
It is important to consult with a healthcare provider or registered dietitian to determine the appropriate amount and type of carbohydrates for your individual needs and health goals.
Foods High in Complex Carbohydrates
Complex carbohydrates are an essential part of a healthy and balanced diet. They provide sustained energy to the body while also maintaining stable blood sugar levels. If you want to include more complex carbohydrates in your diet, here are some foods you should consider:
- Whole grains: These include brown rice, quinoa, oats, and barley. They are great sources of fiber, vitamins, and minerals, and can be consumed as a side dish or added to salads and soups.
- Legumes: These include beans, lentils, and peas. They are high in protein, fiber, and complex carbohydrates, making them an excellent addition to vegetarian and vegan diets. Legumes can be consumed as a side dish or added to soups and stews.
- Fruit: While most fruit contains simple carbohydrates, some are excellent sources of complex carbohydrates. These include bananas, apples, and berries. They are also rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, making them a healthy addition to any diet.
- Vegetables: Starchy vegetables such as sweet potatoes, carrots, and beets are excellent sources of complex carbohydrates. They are also high in fiber, vitamins, and minerals, making them an important part of any healthy diet.
- Nuts and seeds: These are great sources of healthy fats, protein, and complex carbohydrates. They can be eaten as a snack or added to salads and oatmeal.
By incorporating these complex carbohydrate-rich foods into your diet, you can reap the benefits of sustained energy and good health. Remember to strive for a balanced and varied diet, including both complex and simple carbohydrates in moderation, along with other essential nutrients.
Foods to Limit
There are certain foods that should be limited in our diet due to their high carbohydrate content. These foods may provide a quick boost of energy, but can also lead to weight gain and other negative health effects if consumed in excess.
Sugary drinks: Sugary drinks such as soda, energy drinks, and fruit juice can be a major source of carbohydrates and can quickly add up to excess sugar intake. It is recommended to limit or avoid these drinks altogether and opt for water, herbal tea, or unsweetened beverages instead.
White bread and pasta: White bread and pasta are made from refined flour and are often stripped of fiber and nutrients. These refined carbohydrates can cause blood sugar spikes, leading to feelings of hunger and overeating. It is recommended to choose whole grain options instead, which provide more fiber and nutrients.
Sweets and desserts: Sweets and desserts such as candy, cookies, and cakes are often high in sugar and refined carbohydrates. These should be limited in our diet and saved for occasional treats.
Processed snacks: Processed snacks such as chips, crackers, and snack bars are often high in refined carbohydrates and added sugars. These should be limited or replaced with healthier snack options such as fresh fruits and vegetables, nuts, and seeds.
Alcohol: Alcoholic beverages can be high in carbohydrates, especially beer and sweet mixed drinks. It is recommended to limit or avoid alcohol consumption, or opt for lower carbohydrate options such as wine or spirits mixed with a low-carb mixer.
It is important to balance our intake of carbohydrates and choose healthier, whole food options whenever possible. Limiting or avoiding these high-carbohydrate foods can help us maintain a healthy weight and reduce the risk of negative health effects.
Conclusion
In conclusion, carbohydrates play a crucial role in our body’s overall functioning. They are a necessary source of energy for cellular activities, and help regulate blood glucose levels. Additionally, they play a pivotal role in digestion and promote healthy bowel movements.
While consuming carbohydrates in moderation is essential for optimal health, overindulging in simple carbohydrates such as sugar can lead to adverse health effects such as obesity and diabetes. On the other hand, following a low-carb diet can lead to nutritional deficiencies and reduced energy levels.
It is important to strike a balance when consuming carbohydrates and aim to consume more complex carbohydrates such as whole grains, legumes, fruits, and vegetables, while limiting consumption of refined and processed foods.
Overall, understanding the role of carbohydrates in our body and making informed choices about our diet can lead to a healthier and more balanced lifestyle.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the different types of simple carbohydrates?
The two types of simple carbohydrates are monosaccharides, such as glucose and fructose, and disaccharides, such as sucrose and lactose.
Can carbohydrates provide energy for the body?
Yes, carbohydrates are the main source of energy for the body as they are broken down into glucose, which can be used for fuel.
What are some examples of complex carbohydrates?
Foods that are high in complex carbohydrates include whole grains, beans, fruits, and vegetables.
How do carbohydrates help with digestion?
Dietary fiber, a type of carbohydrate, helps with digestion by adding bulk to the stool and promoting regular bowel movements.
What happens if you consume too many carbohydrates?
Consuming too many carbohydrates can lead to weight gain, elevated blood sugar levels, and an increased risk for type 2 diabetes.
Is a low-carb diet healthy?
While a low-carb diet may lead to weight loss in the short-term, it may have negative effects on long-term health, such as increased risk for heart disease.
How much carbohydrates should I consume per day?
The recommended daily intake of carbohydrates for adults is 130 grams per day, but this may vary depending on individual needs and activity levels.
Can carbohydrates have a positive impact on cardiovascular health?
Consuming foods that are high in fiber and complex carbohydrates has been linked to a lower risk of heart disease and improved heart health.
Are all carbohydrates created equal?
No, not all carbohydrates are created equal. Complex carbohydrates are generally considered healthier than simple carbohydrates, which can lead to spikes in blood sugar levels.
Can a low-carb diet lead to nutrient deficiencies?
Yes, a low-carb diet may limit the consumption of certain nutrient-rich foods, such as fruits and whole grains, which can lead to deficiencies in vitamins and minerals.