It’s no secret that a healthy diet is essential for overall wellness. However, in the world of nutrition, it’s not just about calories and macronutrients like protein and carbohydrates. Something that is often overlooked but just as important are micronutrients. Have you ever wondered what they are? Why they matter? And how to get more of them? In this article, we will discuss what micronutrients are, why they are essential, and ways to incorporate them into a balanced diet.
What are Micronutrients?
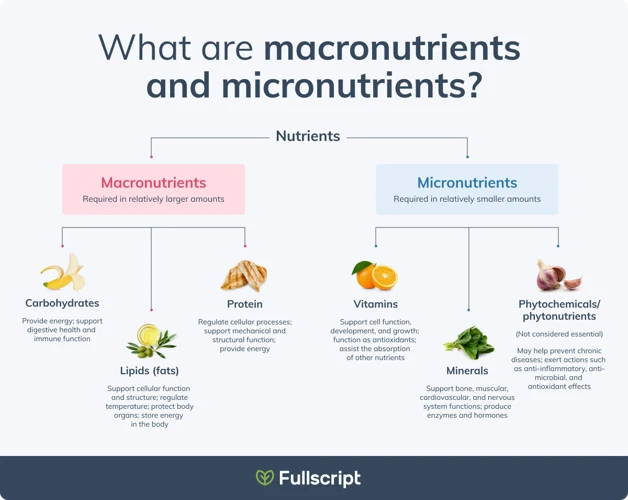
A balanced diet is crucial for overall health and well-being. It is important to not only consume a sufficient amount of macronutrients such as carbohydrates, proteins, and fats but also to make sure to include an adequate amount of micronutrients in our diets. Micronutrients are crucial vitamins and minerals that are essential for the proper functioning of our bodies. They play a vital role in maintaining our immune system, metabolism, and overall health. In this section, we’ll dive into the world of micronutrients and explore their importance in our diet. To learn more about the top 10 micronutrients you should include in your diet, please follow this link.
Calcium
Calcium is an essential micronutrient that is necessary for numerous bodily functions. It is crucial for the development and maintenance of strong bones and teeth, as well as proper muscle and nerve function. Calcium also plays a role in blood clotting and helps to regulate blood pressure.
Without enough calcium, the body may begin to pull calcium from bones, leading to weakened bones and an increased risk of fractures. Inadequate calcium intake has also been linked to osteoporosis, a disease that causes bones to become weak and more likely to break.
Some good food sources of calcium include:
- Dairy products: Milk, cheese, and yogurt
- Leafy greens: Kale, collard greens, and spinach
- Fish: Canned sardines and salmon
- Fortified foods: Some types of tofu and orange juice
It’s important to note that calcium needs can vary depending on age and gender, with adults between the ages of 19-50 requiring 1000mg per day. Pregnant and breastfeeding women, as well as individuals over the age of 50, may need more calcium.
If you’re unable to get enough calcium through your diet, a calcium supplement may be beneficial. However, it’s important to talk to your doctor before starting any new supplements. Overconsumption of calcium can lead to negative health effects, including kidney stones.
Calcium is an essential micronutrient that serves a variety of important functions in the body. Meeting recommended calcium intake is crucial for optimal bone health and muscle and nerve function, and may also help regulate blood pressure.
Magnesium
Magnesium is a crucial micronutrient needed for many bodily functions. This mineral is involved in over 300 enzymatic reactions and plays a role in muscle and nerve function, heart rhythm regulation, blood sugar control, and bone health. Magnesium helps boost the immune system and aids in DNA and protein synthesis.
Deficiency of magnesium can lead to a variety of health problems, including muscle weakness, fatigue, high blood pressure, and irregular heartbeat. Chronic magnesium deficiency has also been linked to osteoporosis and diabetes.
To ensure you are getting enough magnesium in your diet, aim to consume foods that are high in this nutrient. Some of the best dietary sources of magnesium include nuts, seeds, legumes, whole grains, and leafy green vegetables. Here is a table of foods that are high in magnesium:
| Food | Magnesium Content (mg per 100g) |
|---|---|
| Almonds | 268 |
| Pumpkin Seeds | 262 |
| Spinach | 79 |
| Black Beans | 75 |
| Brown Rice | 44 |
In some cases, you may need to supplement your diet with magnesium to meet your daily recommended intake. However, it is important to speak with a healthcare professional before taking any supplements.
Not only does magnesium play a crucial role in many bodily functions, but it also has numerous health benefits. Studies have shown that magnesium can help reduce inflammation, improve brain function, and promote better sleep. It is important to make sure you are getting enough of this essential micronutrient to reap these benefits.
For more information about the benefits and importance of micronutrients, check out our article on Micronutrient Benefits.
Vitamins
Vitamins are organic compounds that are essential for maintaining good health. They carry out various roles in the body, including growth, development, and metabolism. Vitamins can be divided into two categories: water-soluble vitamins and fat-soluble vitamins.
Water-soluble vitamins: These vitamins dissolve in water and cannot be stored in the body for extended periods. Hence, it is essential to consume them daily. Some of the vital water-soluble vitamins are Vitamin C, B1 (Thiamin), B2 (Riboflavin), B3 (Niacin), B5 (Pantothenic acid), B6, B7 (Biotin), B9 (Folic acid), and B12 (Cobalamin).
Fat-soluble vitamins: These vitamins dissolve in fat and are stored in the body for long periods, making it possible to consume them less frequently than water-soluble vitamins. However, their high storage rate can make them toxic if consumed in excess. Some of the essential fat-soluble vitamins include Vitamin A, D, E, and K.
Each vitamin plays a crucial role in maintaining overall health. For instance, Vitamin C is crucial for wound healing and immune system functioning. Vitamin D is essential for strong bones and teeth, while Vitamin E helps to protect against oxidative damage. Vitamin A is vital for vision, and Vitamin K plays a crucial role in blood clotting.
It is essential to consume a balanced diet that includes a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats to obtain an adequate amount of vitamins. A deficiency in any of the essential vitamins can lead to several health problems ranging from fatigue to severe chronic diseases.
Consuming sufficient vitamins is essential for maintaining a healthy immune system, mental health, skin, hair, and nails. People who lack essential vitamins are usually at risk of developing micronutrient deficiencies that can lead to various health complications.
To learn more about the importance of micronutrient deficiencies and its effects on the body, check out this article.
Consuming vitamins in sufficient quantity is essential for maintaining good health. A well-balanced diet that includes a variety of foods and a consistent approach to nutrient consumption are excellent ways to maximize vitamin intake in the body. To learn more about micronutrients and their functions, check out our micronutrients page.
Iron
Iron is an essential micronutrient that plays a critical role in carrying oxygen throughout the body as a part of hemoglobin. It also helps maintain healthy connective tissues, regulates cell growth and differentiation, and supports immune system function. Insufficient intake of iron can lead to anemia, which can cause fatigue, dizziness, weakness, and other symptoms, especially in women who experience heavy menstrual bleeding.
| Function | Sources |
| Carries oxygen throughout the body | Red meat, poultry, fish, beans, lentils, tofu, fortified cereals, spinach |
| Maintains healthy connective tissues | Liver, clams, oysters, lean beef, beans, tofu, spinach, fortified cereals |
| Regulates cell growth and differentiation | Poultry, fish, beans, lentils, fortified cereals, spinach, tofu |
| Supports immune system function | Lean beef, oysters, lentils, tofu, fortified cereals, spinach |
Iron can be found in two forms: heme and non-heme. Heme iron is more easily absorbed by the body and is found in animal products such as red meat, poultry, and fish. Non-heme iron is found in plant-based foods such as beans, lentils, tofu, and spinach. Consuming foods high in vitamin C, such as citrus fruits and bell peppers, can help increase the absorption of non-heme iron.
It is recommended that women aged 19-50 years consume 18 mg of iron daily, while men and women over 50 should aim for 8 mg per day. However, pregnant women have a higher iron requirement and should aim for 27 mg per day.
Incorporating iron-rich foods into the diet and paying attention to both heme and non-heme iron sources is crucial for maintaining overall health and preventing iron-deficiency anemia. Additionally, iron plays a vital role in immune system function and can help protect against chronic diseases, such as cancer and cardiovascular disease. It is important to make sure that you are getting enough iron to support your body’s needs.
Zinc
Zinc is a crucial micronutrient that plays a variety of important roles in the body. It is essential for immune function, wound healing, and cell growth and division. Additionally, zinc is involved in taste and smell sensation, DNA synthesis, and even fertility.
Table: Dietary Sources of Zinc
| Food | Serving Size | Zinc Content (mg) |
|—————————-|————–|——————-|
| Oysters | 6 medium | 32 |
| Beef chuck roast | 3 ounces | 7 |
| Crab | 3 ounces | 6 |
| Pork chop | 3 ounces | 2.9 |
| Baked beans, canned | 1/2 cup | 1.7 |
| Chicken | 3 ounces | 1.3 |
| Cashews | 1 ounce | 1.6 |
| Chickpeas, cooked | 1/2 cup | 0.8 |
| Yogurt | 1 cup | 2.2 |
| Cheese, cheddar | 1 ounce | 0.9 |
Unfortunately, zinc deficiency is fairly common especially among those who follow a strict vegetarian or vegan diet as plant-based sources of zinc are not as easily absorbed as animal-based sources. Symptoms of zinc deficiency can include hair loss, skin lesions, diarrhea, and a weakened immune system.
Studies have found that adequate zinc intake can have a positive impact on various health outcomes. For example, zinc can help reduce the duration and severity of the common cold, enhance cognitive function in children, and improve wound healing.
If you’re looking to increase your zinc intake, consider incorporating more foods like oysters, beef, crab, and cashews into your diet. You may also consider taking a zinc supplement, although it’s important to speak with a healthcare professional before doing so.
To learn more about other essential micronutrients, check out our article on 12 Essential Micronutrients. For information on how micronutrients can impact your immune system, take a look at our article on Micronutrients and Immunity.
Potassium
Potassium is a critical micronutrient that plays a vital role as an electrolyte in the body. It helps to regulate fluid balance, maintain healthy blood pressure, and support proper muscle and nerve function. Potassium also plays an essential role in the metabolism of carbohydrates and protein.
Some of the best sources of potassium include leafy greens, bananas, oranges, beans, peas, and sweet potatoes. Consuming enough potassium can help prevent electrolyte imbalances, which can cause muscle cramping and fatigue. Potassium deficiency may also lead to high blood pressure, kidney stones, and osteoporosis.
Studies have shown that a diet rich in potassium can help reduce the risk of stroke, lower blood pressure, and protect against heart disease. Potassium may even improve bone health, supporting the overall health of the body.
Adequate potassium intake may also help in the prevention of various chronic diseases, including cancer, cardiovascular disease, and diabetes. Micronutrient intake is often linked to the prevention of chronic diseases, and potassium is one of the most beneficial micronutrients in this regard.
To ensure appropriate potassium intake, the National Institutes of Health recommends that adults consume around 2,000 mg per day. However, it is essential to keep in mind that low potassium intake can have severe consequences for overall health.
Potassium is an indispensable micronutrient that helps maintain the proper functioning of the body. It is essential to include potassium-rich foods in the diet to ensure overall well-being and prevent chronic diseases. So, if you want to support your overall health, be sure to include plenty of foods that are high in potassium.
Why Micronutrients Matter
Micronutrients are an essential part of a balanced diet, and they play a crucial role in maintaining good health. These vital nutrients, which include calcium, magnesium, vitamins, iron, zinc, and potassium, are essential for numerous bodily functions. However, some individuals often neglect the importance of micronutrients, leading to various health problems. In this section, we will delve deeper into the reasons why micronutrients matter, and how they can significantly impact your overall well-being. We will explore how these nutrients can boost your health, prevent chronic diseases, improve digestion, increase energy levels, and aid in weight management. Additionally, we will provide tips on how to ensure that you get enough micronutrients in your diet. Let’s discover the significance of these nutrients for a better, healthier life. For more information on how micronutrients support brain function and mental health, click here. Or, click here to learn about micronutrients’ role in supporting healthy skin, hair, and nails.
Boost Overall Health
Micronutrients are essential nutrients that are required by our body in small quantities for proper functioning. They play a crucial role in maintaining overall health by supporting the immune system, aiding in tissue repair, and promoting proper organ function. Micronutrients include vitamins and minerals such as calcium, magnesium, iron, zinc, potassium, and more. Each of these micronutrients plays a unique role in maintaining overall health.
Calcium: is important for strong bones and teeth, proper blood clotting, and regulation of nerve and muscle functions.
Magnesium: is essential for many biochemical reactions in the body, including muscle and nerve function, regulating blood sugar levels, and supporting the immune system.
Vitamins: are essential for overall health, including maintaining healthy skin, eyes, and hair, supporting the immune system, and aiding in the production of important enzymes and hormones.
Iron: is critical for the production of red blood cells, which carry oxygen throughout the body.
Zinc: is essential for proper immune system function, wound healing, and cell growth and division.
Potassium: is important for proper heart and muscle function, regulation of fluid balance, and nerve transmission.
Consuming an adequate amount of micronutrients is essential for overall health. By including a variety of nutrient-dense foods in your diet, you can ensure that you are getting the micronutrients your body needs to function properly. Inadequate intake of micronutrients can lead to various health issues, such as weakened immune system, impaired vision, and poor bone health.
A balanced diet that includes a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats is the best way to ensure that you are getting an optimal amount of micronutrients. By consuming a balanced diet, you can give your body the micronutrients it needs to function properly and improve your overall health.
Prevent Chronic Diseases
Micronutrients are essential for preventing chronic diseases. Studies have shown that a diet rich in micronutrients can reduce the risk of chronic diseases like cancer, heart disease, and diabetes. Micronutrients such as calcium, magnesium, vitamins, iron, zinc, and potassium play a crucial role in maintaining the body’s optimum health.
Calcium: Calcium is an essential micronutrient that is vital for healthy bones and teeth. Low levels of calcium intake can lead to bone loss and osteoporosis, especially in postmenopausal women. Studies have shown that calcium can also reduce the risk of colon cancer.
Magnesium: Magnesium is essential for maintaining healthy muscles and nerves. It also plays a critical role in heart health, as low magnesium levels can increase the risk of heart disease, high blood pressure, and stroke.
Vitamins: Vitamins such as A, C, and E are antioxidants that protect the body from damage caused by free radicals. Free radicals are unstable molecules that can damage cells and contribute to the development of chronic diseases.
Iron: Iron is essential for the formation of hemoglobin in red blood cells, which carries oxygen from the lungs to the rest of the body. Low levels of iron can lead to anemia, fatigue, and reduced immune function.
Zinc: Zinc is essential for maintaining healthy immune function and wound healing. It also plays a critical role in maintaining healthy skin, hair, and nails.
Potassium: Potassium plays a crucial role in maintaining healthy blood pressure levels. Low potassium levels can lead to high blood pressure, which increases the risk of heart disease and stroke.
Incorporating a variety of micronutrients into your diet can help prevent chronic diseases. It is recommended to consume a wide variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats to ensure adequate micronutrient intake. Additionally, nutritional supplements can be helpful for individuals who have difficulty meeting their micronutrient needs through diet alone.
It is important to note that processed foods often contain low levels of micronutrients, so it is important to limit or eliminate these foods from your diet. Cooking food carefully and choosing whole foods can also help maintain micronutrient levels in your diet.
Ensuring adequate intake of micronutrients is crucial for maintaining optimal health and preventing chronic diseases. Incorporating a variety of micronutrient-rich foods and paying attention to your diet can help ensure you are getting the necessary nutrients your body needs.
Improve Digestion
Micronutrients are essential nutrients that are required in small amounts to maintain proper functioning of the body. While all micronutrients are important, some may play a specific role in improving digestion. Proper digestion is crucial for overall health since it allows the body to absorb essential nutrients from food. Some micronutrients that can aid in digestion are:
| Micronutrient | Role in Digestion | Food Sources |
|---|---|---|
| Calcium | Helps regulate muscle contractions, including those in the digestive tract, which can help prevent constipation | Milk, cheese, leafy greens, fortified cereals |
| Magnesium | Aids in muscle relaxation and can help prevent constipation | Nuts, seeds, whole grains, spinach |
| Vitamin A | Supports the production of digestive enzymes that aid in the breakdown of food | Carrots, sweet potatoes, dark leafy greens, liver |
| Vitamin B6 | Helps maintain healthy levels of digestive enzymes and may reduce inflammation in the digestive tract | Poultry, fish, potatoes, bananas |
| Vitamin C | Helps the body absorb iron from plant-based foods, which can aid in the prevention of anemia and support a healthy digestive tract | Citrus fruits, berries, tomatoes, peppers, leafy greens |
| Zinc | Helps in the production of digestive enzymes and supports the growth and repair of the digestive tract, which can aid in the prevention of leaky gut syndrome | Seafood, poultry, eggs, nuts, whole grains, beans |
Consuming a diet that is rich in these micronutrients can promote healthy digestion and prevent gastrointestinal problems such as constipation, diarrhea, and irritable bowel syndrome. In addition to consuming a balanced diet, it is also important to stay hydrated and engage in regular physical activity to support proper digestion.
Increase Energy Levels
Micronutrients play an important role in increasing energy levels. There are several micronutrients that are essential for optimal energy production and utilization in the body. One of these micronutrients is iron, which is necessary for the production of hemoglobin, a protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen to the body’s tissues. Without sufficient iron intake, the body may not be able to produce enough hemoglobin, leading to iron-deficiency anemia and extreme fatigue.
Another important micronutrient for energy production is magnesium, which is required for hundreds of biochemical reactions in the body, including the production of ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the body’s primary source of energy. Low magnesium levels have been linked to feelings of fatigue and weakness.
Vitamins are also important for energy production. Vitamin C plays a critical role in the formation of collagen, a protein found in connective tissues that supports and connects body structures. It also helps the body absorb iron, which is essential for energy production. Meanwhile, B vitamins such as vitamin B12 and vitamin B6 are important for the production of red blood cells and the metabolism of carbohydrates, respectively. Deficiencies in these B vitamins can lead to fatigue and weakness.
In addition to these micronutrients, potassium is also essential for energy production. It helps regulate fluid balance in the body and assists with nerve and muscle function. Low potassium levels can cause fatigue, weakness, and muscle cramps.
To increase energy levels through micronutrient intake, it is important to consume a variety of whole foods rich in these nutrients. Eating foods like leafy greens, nuts and seeds, tofu, salmon, and eggs can provide essential micronutrients for energy production. However, it is important to avoid processed foods and instead choose whole foods, as processed foods can deplete micronutrient levels. In some cases, nutritional supplements may also be necessary to address any deficiencies.
Aid in Weight Management
Micronutrients not only improve overall health, but can also aid in weight management. Vitamins, Calcium, Magnesium, Iron, Zinc and Potassium all play a role in maintaining a healthy weight.
Vitamins, particularly B vitamins, are essential in converting food into energy. Without sufficient B vitamins, the body may struggle to efficiently metabolize food and convert it into energy, potentially leading to weight gain.
Calcium has been linked to weight management, as studies have shown that adequate calcium intake may increase fat loss and decrease fat storage in the body. Incorporating calcium-rich foods, such as dairy products, leafy greens, and fortified cereals, into your diet can potentially aid in weight loss efforts.
Similarly, magnesium has been shown to play a role in weight management by regulating blood sugar levels and hormone balance, both of which are key factors in maintaining a healthy weight. Foods such as nuts, seeds, and whole grains are good sources of magnesium.
Iron also plays a role in weight management, as it is necessary for the proper function of red blood cells, which carry oxygen throughout the body. Without adequate iron intake, the body may not have enough oxygen, leading to fatigue and decreased physical activity. Including iron-rich foods, such as lean red meat, beans, and dark leafy greens, in your diet can help with weight management.
Zinc, another important micronutrient, has been linked to weight loss in some studies. It is thought that zinc may regulate appetite and reduce inflammation, both of which can contribute to weight gain if not properly managed. Foods such as oysters, beef, and pumpkin seeds are good sources of zinc.
Lastly, potassium can aid in weight management by helping to regulate fluid balance and reduce the bloating that can come with a high-sodium diet. Foods such as bananas, potatoes, and leafy greens are rich in potassium.
Incorporating a variety of micronutrient-rich foods into your diet can not only aid in overall health, but also in weight management efforts.
How to Get More Micronutrients
When it comes to maintaining a healthy diet, getting enough micronutrients is crucial. These essential vitamins and minerals play a role in everything from bone health to immune function. But with so many options out there, it can be overwhelming to know which foods to choose. Fortunately, there are simple strategies you can take to ensure you are getting enough micronutrients in your diet. From eating a variety of foods to choosing whole, unprocessed options, here are some tips on how to get more of these important nutrients into your daily routine.
Eat a Wide Variety of Foods
One of the most important steps in increasing your micronutrient intake is to eat a wide variety of foods. This is because different foods contain different types and amounts of micronutrients, and consuming a variety of foods ensures that you are getting all the micronutrients your body needs.
To make it easier to understand which foods are high in which micronutrients, we can use an html table:
| Micronutrient | Foods |
|---|---|
| Calcium | Milk, cheese, yogurt, leafy greens (kale, spinach), tofu, almonds |
| Magnesium | Whole grains (oatmeal, brown rice), leafy greens (spinach, chard), nuts and seeds (almonds, pumpkin seeds), beans and lentils |
| Vitamins | Fruits (citrus, berries), vegetables (red bell pepper, broccoli), fortified cereals and dairy products, fatty fish (salmon, tuna) |
| Iron | Red meat, poultry, fish (tuna, salmon), lentils and beans, tofu, spinach |
| Zinc | Red meat, poultry, beans and lentils, whole grains, nuts and seeds (cashews, pumpkin seeds) |
| Potassium | Bananas, orange juice, potatoes, sweet potatoes, avocado, spinach |
As you can see from the table, there are a variety of foods that contain each micronutrient. By incorporating a variety of these foods into your diet, you can ensure that you are getting all the necessary micronutrients for optimal health.
However, it is important to note that not all foods are created equal. Some foods may be higher in micronutrients than others, so it is important to pay attention to the types of foods you are eating. Additionally, some foods may be higher in calories or unhealthy fats, so it is important to choose a variety of healthy foods as well.
Incorporating a wide variety of healthy foods into your diet is not only important for increasing your micronutrient intake but also for overall health and wellness. So make sure to add a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats to your diet to ensure you are getting all the necessary micronutrients for optimal health.
Consider Nutritional Supplements
When it comes to getting enough micronutrients in your diet, sometimes it can be challenging to consume all the necessary vitamins and minerals from food alone. In such cases, considering nutritional supplements can help fill any gaps in your nutrient intake.
Supplements come in various forms, including pills, capsules, powders, and liquids. Before taking any supplement, it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare provider to ensure its safety and effectiveness.
Here are some examples of nutritional supplements that can help you meet your daily micronutrient needs:
| Supplement | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Multi-vitamins | Provide a broad range of micronutrients, including vitamins A, C, D, E, K, and B-complex vitamins. |
| Dependable iron supplement | Assist in the prevention of iron-deficiency anemia, especially for the blood donor, athletes or pregnant women. |
| Calcium and magnesium supplement | Important for bone health as they work together to keep bones strong and healthy. |
| Zinc supplement | Helps with immune system functions and wound healing. |
Supplements should never replace a varied and balanced diet, but they can help bridge the gap when there’s insufficient daily intake of certain nutrients. Keep in mind that megadoses of supplements, especially fat-soluble vitamins like A, D, E, and K, can have negative health effects. It’s essential to follow the recommended dosage and only take supplements under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
Choose Whole Foods
When it comes to getting enough micronutrients in your diet, choosing whole foods is one of the best ways to go. Whole foods refer to foods that are as close to their natural state as possible, meaning they haven’t been processed or refined. This often means that they still contain all the micronutrients that they naturally possess.
The Benefits of Whole Foods
Whole foods are often nutrient-dense, meaning they’re packed with micronutrients in every bite. Additionally, because they’re less processed, they’re often higher in fiber and lower in additives, such as sugar and salt.
Examples of Whole Foods
Some examples of whole foods include:
| Food | Micronutrients |
|---|---|
| Kale | Calcium, magnesium, vitamin K |
| Salmon | Omega-3 fatty acids, vitamin D |
| Sweet potato | Vitamin A, potassium, fiber |
| Almonds | Vitamin E, magnesium, fiber |
When choosing whole foods, it’s important to choose a variety of different types. Different fruits and vegetables will have different micronutrient profiles, so by eating a rainbow of colors, you can ensure you’re getting a wide variety of nutrients.
How to Incorporate Whole Foods into Your Diet
Incorporating more whole foods into your diet doesn’t have to be difficult. Start by making small changes, such as swapping out refined grains for whole grains or snacking on fresh fruit instead of processed snacks. Consider buying fresh produce when it’s in season, as it’ll be cheaper and likely more flavorful.
The Bottom Line
Choosing whole foods is a great way to ensure you’re getting all the micronutrients your body needs. By incorporating more whole foods into your diet, you can reap the benefits of a nutrient-dense diet while also enjoying a variety of delicious, unprocessed foods.
Cook Food Carefully
When it comes to cooking food, it’s important to be mindful of the impact it can have on the micronutrients in our meals. The way we prepare and cook food can affect the amount and availability of certain vitamins and minerals. Here are some tips for cooking food carefully to help preserve its micronutrient content:
- Avoid overcooking: Overcooking can cause the loss of important vitamins such as vitamin C and thiamin. Try to cook food for the minimum amount of time needed to achieve the desired doneness.
- Use cooking methods that preserve nutrients: Steaming, roasting and baking are cooking methods that help retain vitamins and minerals, whereas boiling can cause significant losses.
- Store and reheat food properly: Storing food in airtight containers and reheating it quickly can help prevent the loss of micronutrients. Avoid reheating food several times as this can cause further nutrient loss.
- Don’t peel vegetables unnecessarily: Many of the nutrients in vegetables are found just beneath the skin, so try not to peel them too much to retain these healthful micronutrients.
Taking care when cooking food is not only important for preserving its micronutrient content, but it also helps to ensure that the food is safe to eat by eliminating harmful bacteria that can develop during cooking. By following these tips, you can help preserve the micronutrient content of your meals and maintain a balanced diet for optimal health.
Limit or Eliminate Processed Foods
When it comes to getting enough micronutrients in your diet, one important step is to limit or even eliminate processed foods. These foods are often high in calories, unhealthy fats, added sugars, and salt, while lacking in essential nutrients. Instead of relying on packaged or processed foods, aim to incorporate more whole foods into your diet.
Why Should You Limit or Eliminate Processed Foods?
Processed foods are often high in calories, unhealthy fats, added sugars, and salt, while lacking in essential micronutrients. Consuming too many processed foods can contribute to chronic diseases such as obesity, diabetes, and heart disease.
Additionally, processed foods often contain additives and preservatives that have been linked to negative health effects. For example, some types of food preservatives have been linked to increased inflammation in the body and an increased risk of some cancers.
What are Some Examples of Processed Foods?
Processed foods can take many forms, from pre-packaged meals to frozen foods to fast food. Here are some common examples of processed foods:
| Processed Foods | Whole Food Alternatives |
|---|---|
| White bread | Whole grain bread |
| Instant noodles | Fresh vegetables and herbs with pasta |
| Candy bars | Dried fruits or dark chocolate |
| Soda | Water or fresh fruit juice |
How Can You Reduce Your Intake of Processed Foods?
Reducing your intake of processed foods can seem overwhelming at first, but there are a few simple steps you can take to make this transition easier:
- Choose whole foods instead of packaged or processed foods
- Cook meals at home with fresh, whole ingredients
- Avoid fast food restaurants and choose healthier options when eating out
- Read food labels carefully and look for added sugars, sodium, and unhealthy fats
- Try new recipes and experiment with different whole foods to keep your meals interesting and flavorful
By taking these steps, you can become more mindful of the processed foods you consume and take concrete steps towards a healthier, micronutrient-rich diet.
Pay Attention to Your Diet
The most important step in getting more micronutrients in your diet is paying close attention to what you eat. This means being mindful of the foods you choose and the nutrients they contain. One way to do this is by keeping a food diary or using a nutrition tracking app to monitor your daily intake.
Include a variety of nutrient-rich foods: To ensure that you are getting a balanced mix of micronutrients, include a variety of nutrient-rich foods in your diet. This includes whole grains, lean proteins, fresh fruits and vegetables, and healthy fats like nuts and seeds.
Take note of serving sizes: Many people consume more calories than they realize simply because they are not aware of serving sizes. Reading nutrition labels and measuring portions can help you stay within recommended serving sizes and avoid taking in too many calories.
Be aware of hidden sources of sugar and sodium: Many processed foods are loaded with hidden sources of sugar and sodium, which can be detrimental to your health. When reading nutrition labels, look for terms like “sugar-free” or “low-sodium,” and be wary of any packaged foods that contain a long list of ingredients.
Drink plenty of water: Staying hydrated is crucial for overall health and can help improve digestion, energy levels, and brain function. Aim to drink at least 8 glasses of water a day, and avoid sugary drinks like soda and fruit juices.
Avoid crash dieting: Crash dieting may lead to rapid weight loss, but it can also deprive your body of essential nutrients. Instead of restricting calories, focus on making sustainable lifestyle changes that include a balanced diet and regular exercise.
By paying careful attention to your diet and making small lifestyle changes, you can ensure that your body is getting the vitamins and minerals that it needs to function at its best.
Conclusion
In conclusion, it is clear that micronutrients play a vital role in maintaining optimal health and well-being. These essential nutrients may be required in small quantities by the body, but they serve a big purpose, supporting everything from healthy immune function to strong bones and teeth.
Calcium is necessary for building and maintaining healthy bones, while magnesium supports muscle and nerve function. Vitamins such as vitamin C and vitamin E, act as antioxidants that protect the body from damage caused by free radicals. Iron is critical to healthy blood and energy levels, and zinc helps to support a healthy immune system. Finally, potassium is essential for heart health and proper nervous system function.
Without adequate micronutrient intake, individuals may experience a variety of health problems such as fatigue, muscle weakness, anemia, and even chronic disease over time. Therefore, getting enough micronutrients is crucial, and eating a balanced diet rich in whole foods, fruits, and vegetables is the best way to achieve this.
While it may be challenging to get all of the necessary micronutrients in your daily diet, taking nutritional supplements and choosing whole, minimally processed foods can help. It’s also crucial to pay close attention to the foods you consume, choose high-nutrient options, and cook them carefully, to ensure that they retain as many nutrients as possible.
By incorporating these strategies, you can ensure that your body is receiving adequate micronutrients, improving your overall health and well-being, and reducing your risk of developing chronic diseases. Remember, every small change you make will have a significant impact on your health, so start taking small steps towards improving your dietary intake today.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between micronutrients and macronutrients?
Micronutrients are needed in small amounts, while macronutrients are required in larger quantities. Micronutrients are essential for many bodily functions, including maintaining a healthy immune system, while macronutrients provide the body with energy and support muscle growth.
How do micronutrients help prevent chronic diseases?
Micronutrients, such as antioxidants and anti-inflammatory nutrients, help to protect the body from damaging free radicals and reduce the risk of chronic diseases such as cancer, heart disease, and diabetes.
What are some food sources of micronutrients?
Calcium-rich foods include dairy products, leafy greens, and fortified cereals. Magnesium can be found in nuts, seeds, legumes, and whole grains. Vitamins can be found in fruits and vegetables, while iron is in red meat, poultry, and leafy greens. Zinc can be found in seafood, beef, and fortified cereals, while potassium is found in bananas, sweet potatoes, and leafy greens.
Can I get enough micronutrients through diet alone?
While it is possible to get enough micronutrients through diet alone, it can be challenging, especially if you have certain dietary restrictions or preferences. Adding nutritional supplements to your diet can help ensure you’re meeting your micronutrient needs.
What micronutrients are important for maintaining bone health?
Calcium, magnesium, and vitamin D are all essential for maintaining bone health. Calcium and magnesium help to build and maintain bone structure, while vitamin D is needed to absorb calcium.
How do I know if I’m deficient in micronutrients?
Deficiencies in micronutrients can lead to a variety of symptoms, including fatigue, weakness, hair loss, and even mental health issues. Blood tests can identify specific nutrient deficiencies.
Can taking too many micronutrient supplements be harmful?
Yes, taking excessive amounts of micronutrients in supplement form can be harmful and even dangerous. Consult with a healthcare professional before taking any supplements.
Are processed foods a good source of micronutrients?
No, processed foods are typically stripped of many important micronutrients during the refining process.
Can cooking affect the micronutrient content of food?
Yes, cooking can affect the micronutrient content of food, with some vitamins and minerals becoming more or less available depending on the cooking method. Steaming and roasting are generally considered the best methods for preserving nutrient content.
Can micronutrient deficiencies be corrected through diet alone?
In some cases, it may be possible to correct micronutrient deficiencies through diet alone. However, in severe cases or for those with certain medical conditions, supplements or fortified foods may be necessary.







