As the world continues to grapple with various health challenges, the importance of a strong immune system cannot be overemphasized. It is no news that certain micronutrients play significant roles in maintaining a healthy immune system. But what are these micronutrients, and how do they work to boost immunity? In this article, we will explore the world of micronutrients and their relationship with immunity. We will also delve into the various vitamins and minerals that contribute to a healthy immune system and where to find them. Join us as we uncover tips and tricks to help you achieve optimum health and immunity.
What Are Micronutrients and Why Are They Important?
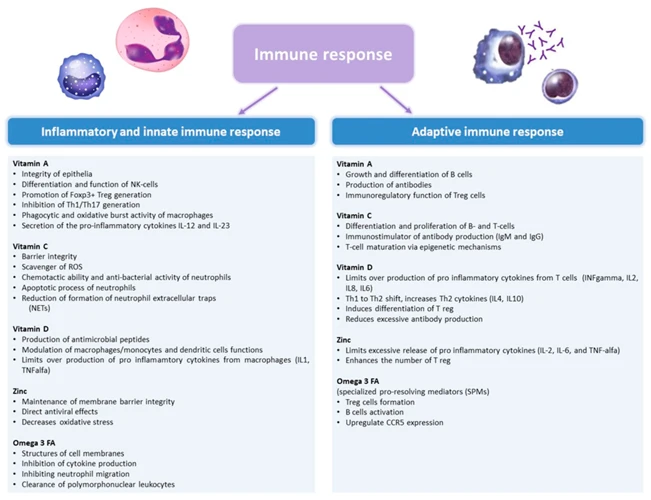
Micronutrients play a vital role in keeping your body healthy, but what exactly are they and why are they important? These nutrients are required in small quantities but their absence can lead to significant health problems. From supporting immune system function to promoting healthy skin, hair, and nails, micronutrients are necessary for optimal health. In this section, we will explore the definition of micronutrients and their importance in detail. Understanding the role of micronutrients in the body is the first step towards maintaining good health. To learn more about the importance of micronutrients in a balanced diet, check out our related article.
What Are Micronutrients?
Micronutrients are nutrients that the body needs in small amounts but are essential for growth, development, and overall health. They include vitamins and minerals and are required in varying amounts depending on the nutrient. Vitamins are organic compounds that the body cannot produce on its own, they are necessary for various bodily functions and are available in different types such as A, B, C, D, E, and K. Minerals, on the other hand, are inorganic compounds required in smaller amounts that help the body to function properly.
Micronutrients are essential for numerous bodily functions such as normal growth and development, immune system function, brain function, and bone health. They are also involved in energy metabolism, red blood cell formation, and hormone synthesis.
To ensure a healthy body, it is important to consume a balanced diet containing adequate amounts of all essential nutrients. In the next section, we will discuss the importance of micronutrients in more detail. To learn about the top 10 micronutrients in the diet, check out this article.
Why Are Micronutrients Important?
Micronutrients are important for several reasons, and their deficiency can lead to various health problems. Here are some of the reasons why micronutrients are important:
- Energy production: Micronutrients, such as B vitamins, are crucial in converting food into energy that our body needs.
- Growth and development: Micronutrients play an essential role in the growth and development of our body. For example, calcium and vitamin D are necessary for strong bones, while iron is necessary for the formation of red blood cells.
- Immune function: Micronutrients are essential for maintaining a healthy immune system. For example, vitamin C and vitamin E are powerful antioxidants that help prevent cell damage from free radicals, which can weaken the immune system.
- Brain function: Micronutrients such as omega-3 fatty acids, B vitamins, and iron are critical for proper brain development and function.
- Prevention of chronic diseases: Micronutrient deficiencies have been linked to an increased risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, cancer, and osteoporosis. For example, getting enough calcium and vitamin D can help prevent osteoporosis, while getting enough vitamin C can reduce the risk of heart disease.
- Skin, hair, and nails: Micronutrients such as vitamins A, C, and E, as well as biotin and zinc, are essential for healthy skin, hair, and nails.
It is crucial to consume enough micronutrients to ensure optimal health and prevent deficiencies that can lead to various health problems. To learn more about the benefits of micronutrients, you can visit the relevant link on our website. If you want to know more about the effects of micronutrient deficiencies, you can check out our article on micronutrient deficiencies and their effects.
Vitamins and Their Role in Immunity
As we learned in the previous section, micronutrients play a vital role in keeping our immune system healthy. Vitamins, which are a type of micronutrient, are particularly important for maintaining our body’s defense system. They are responsible for supporting the production and function of immune cells, as well as neutralizing harmful compounds in the body. In this section, we’ll explore the role of some key vitamins in immunity, including Vitamin C, Vitamin D, Vitamin E, Vitamin A, and B Vitamins. Understanding how these vitamins support our immune system can help us make informed choices about our diet and supplement intake. For more information on micronutrients, check out our previous article on Understanding Vitamins, Minerals, and Micronutrients Explained.
Vitamin C
Vitamin C is an essential micronutrient that is well-known for its immune-boosting properties. It acts as an antioxidant, protecting cells from damage caused by free radicals. This is particularly important for immune cells as they require a lot of energy to function properly. Vitamin C also helps to stimulate the production and function of white blood cells, which are the key players in the immune system’s response to infections.
The Benefits of Vitamin C:
| Benefit | Description | Sources |
|---|---|---|
| Protects against infections | Vitamin C enhances the production of white blood cells and antibodies, which fight infections and diseases. | Citrus fruits, kiwi, strawberries, tomatoes, bell peppers |
| Reduces the severity of colds | Vitamin C can reduce the duration and severity of cold symptoms and improve overall immune function. | Citrus fruits, kiwi, strawberries, tomatoes, bell peppers |
| Helps wounds heal faster | Vitamin C plays a crucial role in collagen synthesis, which is important for wound healing. | Oranges, lemons, limes, grapefruit, kiwi, guava, papaya |
| Protects against chronic diseases | Vitamin C is a powerful antioxidant that can help protect against chronic diseases such as cancer, heart disease, and stroke. | Broccoli, kale, strawberries, grapefruit, oranges, bell peppers |
It’s important to note that vitamin C is water-soluble, meaning it’s not stored in our body and should be consumed on a daily basis. The recommended daily intake of vitamin C is 75 milligrams for women and 90 milligrams for men.
Good food sources of vitamin C include citrus fruits, kiwi, strawberries, tomatoes, and bell peppers. Vitamin C supplements are also available, but it’s recommended to get your intake from whole foods whenever possible to ensure you’re getting a variety of other essential micronutrients as well.
Including vitamin C-rich foods in your diet is an easy way to support your immune system and overall health. To learn more about other essential micronutrients, check out our article on 12 Essential Micronutrients.
Vitamin D
Vitamin D is a unique micronutrient, as our body can produce it in response to sunlight. However, many people still do not get enough of it. This vitamin plays a crucial role in bone health and immune function.
Why is Vitamin D important for immunity?
Vitamin D helps to regulate the immune system by enhancing the function of immune cells such as T-cells and macrophages. It has been shown to reduce the risk of respiratory infections and may be particularly important in reducing the risk of autoimmune diseases.
Sources of Vitamin D
The most natural source of vitamin D is sunlight, but it can also be found in certain foods such as fatty fish, egg yolks, and fortified foods like milk or cereal. However, it can be difficult to get enough vitamin D from food alone. In some cases, supplements may be necessary to achieve optimal levels.
How much Vitamin D do we need?
The recommended daily dose of vitamin D for adults is 600-800 IU (International Units). However, some research suggests that higher levels of vitamin D may be needed for optimal immune function.
To learn more about other micronutrients and their effects on various aspects of health, check out our articles on /micronutrients-brain-function-mental-health/ and /micronutrient-intake-chronic-diseases/.
Vitamin E
Vitamin E is a powerful antioxidant that helps protect cells from oxidative stress. It is a fat-soluble vitamin that is found in many foods, including nuts, seeds, and vegetable oils.
Role in Immunity: Vitamin E has been shown to enhance the immune response in both animal and human studies. It helps to maintain the integrity of cell membranes, which is important for the proper functioning of immune cells. It may increase antibody production, which is crucial for fighting off infections.
Recommended Daily Intake: The recommended daily intake of vitamin E for adults is 15 mg.
Food Sources: Good food sources of vitamin E include:
| Food | Amount of Vitamin E (mg) |
|---|---|
| Almonds | 7.3 per 1 ounce |
| Sunflower seeds | 7.4 per 1 ounce |
| Avocado | 2.7 per 1 medium fruit |
| Spinach, cooked | 0.6 per 1/2 cup |
| Sweet potato, baked | 0.3 per 1/2 cup |
Supplements: Vitamin E supplements are available in the form of capsules, tablets, or oils. However, it is important to be cautious when taking supplements, as high doses of vitamin E may increase the risk of bleeding.
Vitamin E plays an important role in immune function and can be obtained through a well-balanced diet or supplements if necessary. In addition to its immune-boosting properties, vitamin E is also known for its benefits for skin, hair, and nails.
Vitamin A
Vitamin A: Vitamin A is another powerful antioxidant that supports the immune system. It is important for maintaining healthy vision, and also plays a role in promoting skin health. In fact, it is often used in topical treatments for various skin conditions.
| Food Sources: | Benefits: |
|---|---|
| Liver | High in vitamin A and easily absorbed by the body |
| Sweet Potato | Good source of beta carotene, which the body converts to vitamin A |
| Carrots | Good source of beta carotene |
| Spinach | Good source of vitamin A and other important nutrients |
| Broccoli | Good source of vitamin A and other important nutrients |
It is important to note, however, that consuming too much vitamin A can also be harmful to the body. It is recommended to consume vitamin A through food sources rather than supplements, as it allows for better control of intake. If you are concerned about your vitamin A levels, speak with a healthcare provider.
In addition to supporting the immune system and promoting skin health, vitamin A also plays a role in maintaining healthy vision. In fact, vitamin A deficiency is one of the leading causes of preventable blindness in the world (source: micronutrients-skin-hair-nails).
B Vitamins
B vitamins play an important role in immunity by helping the body produce energy and maintain healthy skin, eyes, muscles, and nerves. There are eight different B vitamins, all of which have unique functions in the body.
Vitamin B1 (Thiamine) helps turn food into energy and plays a role in nerve function.
Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin) is important for healthy skin and vision, and it helps the body produce energy.
Vitamin B3 (Niacin) plays a role in DNA repair and can reduce inflammation. It also helps the body produce energy.
Vitamin B5 (Pantothenic acid) is involved in the production of hormones and helps the body produce energy.
Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine) helps the body produce antibodies that fight infection and supports nerve function.
Vitamin B7 (Biotin) is necessary for healthy hair, skin, and nails, and it also helps the body convert food into energy.
Vitamin B9 (Folate) is essential for proper cell growth and development, making it especially important during pregnancy.
Vitamin B12 (Cobalamin) helps the body produce red blood cells and supports nerve function.
To ensure adequate intake of B vitamins, a balanced diet rich in sources such as whole grains, legumes, nuts, seeds, and leafy greens is recommended. For those who may not be getting enough through diet alone, supplements such as B-complex vitamins can be taken under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
Minerals and Their Role in Immunity
As we dive deeper into the relationship between micronutrients and immunity, we cannot overlook the importance of minerals in maintaining a healthy immune system. These essential nutrients play a crucial role in various immune functions, from producing immune cells to combating harmful pathogens. In this section, we will explore the different minerals that are vital for immunity and how they contribute to our overall well-being. So, let’s delve into the fascinating world of minerals and their impact on our health!
Zinc
Zinc is a vital mineral that plays multiple roles in the human body, including supporting the immune system. It is involved in the development and function of immune cells and helps to produce enzymes that act as antioxidants, neutralizing harmful free radicals.
Studies have shown that zinc may help to decrease the duration and severity of colds and other respiratory infections. It may boost the production of T-cells, which are essential for the immune system to fight off infections.
It is important to note that consuming too little or too much zinc can have negative effects on the body. While a deficiency can lead to impaired immune function and increased susceptibility to infections, excessive zinc intake can lead to toxicity and cause symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain.
| Zinc-rich Foods | Serving Size | Zinc Content (mg) |
|---|---|---|
| Beef | 3 ounces | 4.8 |
| Pork | 3 ounces | 2.9 |
| Chicken | 3 ounces | 1.3 |
| Legumes (chickpeas, lentils) | 1 cup | 2.5-4.7 |
| Nuts and seeds (cashews, pumpkin seeds) | 1 ounce | 0.6-2.2 |
| Whole grains (wheat germ, quinoa) | 1 cup | 1.1-2.9 |
In addition to food sources, zinc supplements are also widely available. It is important to talk to a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement regimen and to follow the recommended dosage guidelines closely.
Consuming adequate amounts of zinc as part of a balanced diet can help to support the immune system and promote overall health.
Selenium
Selenium is a trace mineral that is essential for our health as it plays a crucial role in the immune system. Our bodies require only small amounts of selenium, but it works together with other micronutrients to boost our immune defenses.
This micronutrient is a powerful antioxidant that helps to protect our bodies against free radical damage. It also helps to reduce inflammation and strengthen our immune response to infections. One of the vital functions of selenium is to support the production of white blood cells, which are vital in fighting infections and diseases.
Research has shown that selenium deficiency is linked to a weaker immune system, which can lead to more frequent infections and chronic diseases. Studies have even shown that supplementation with selenium can improve immune function and reduce the risk of infection.
So where can we find selenium? Here are some of the best dietary sources of selenium:
| Food Source | Selenium Content (mcg per serving) |
|---|---|
| Brazil nuts (1 ounce) | 544 |
| Tuna (3 ounces) | 68 |
| Beef (3 ounces) | 33 |
| Chicken (3 ounces) | 22 |
| Eggs (1 large) | 15 |
It is important to note that consuming too much selenium can also be harmful. The daily recommended intake for selenium is between 55-70 micrograms per day, with a maximum safe level of 400 micrograms. It is important to try to obtain selenium from natural food sources, rather than relying on supplements.
Incorporating selenium-rich foods into our daily diet can help to support our immune system function and protect our bodies from infections and disease.
Iron
Iron is a crucial micronutrient that plays a significant role in maintaining a healthy immune system. This mineral is necessary for the production of red blood cells, which transport oxygen throughout the body. Additionally, iron is involved in the formation of certain white blood cells, which are essential for fighting off infections.
It is essential to consume adequate amounts of iron in order to maintain optimal immune function. Interestingly, iron deficiency is one of the most common nutrient deficiencies worldwide, and it can lead to an increased risk of infections.
Here are some excellent sources of iron that you can include in your diet:
| Food | Iron Content (per serving) |
|---|---|
| Red meat (beef, lamb) | 3-5 mg |
| Poultry (chicken, turkey) | 0.9-1.2 mg |
| Seafood (clams, oysters) | 2.8-8 mg |
| Beans (lentils, chickpeas) | 2.5-3.6 mg |
| Tofu | 2.1-3.6 mg |
| Spinach | 0.8-1.2 mg |
It’s worth noting that the body absorbs iron from animal sources (i.e. heme iron) more efficiently than plant sources (i.e. non-heme iron). However, consuming plant-based sources of iron alongside foods that are high in vitamin C can enhance absorption.
While it’s important to get enough iron in your diet, it’s also important not to consume too much. Iron toxicity is a serious condition that can cause symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, and even organ damage.
Iron is a vital micronutrient that plays a crucial role in maintaining overall health and a robust immune system. By incorporating iron-rich foods into your diet, you can help ensure that your body has the nutrients it needs to fight off infections and stay healthy.
Copper
Copper is another micronutrient that plays a vital role in maintaining our immune function. It helps in the production of red blood cells and collagen, which is important for wound healing. Apart from that, copper also works as an antioxidant, protecting our cells from damage caused by free radicals.
Here are some of the key benefits and sources of copper:
Blood health: Copper helps in the absorption and utilization of iron in the body, which is important for healthy blood cells.
Nervous system: Copper is essential for the proper functioning of our nervous system. It helps in the synthesis of neurotransmitters, which are chemicals that carry signals between nerve cells.
Bone health: Copper is necessary for the maintenance of healthy bones. It is involved in the production of collagen, a protein that makes up the structure of bones.
Immunity: Copper has been found to have antimicrobial properties, which means it can help fight against harmful bacteria and viruses. It also works as an antioxidant, helping to protect our cells from damage.
Some dietary sources of copper include:
– Shellfish, such as oysters and mussels
– Nuts, particularly cashews and almonds
– Seeds, such as sesame and sunflower seeds
– Whole grains, including barley and oats
– Dark chocolate
While it’s important to make sure you’re getting enough copper in your diet, it’s also important to not exceed the recommended daily intake, as excessive copper intake can lead to toxicity. The recommended intake for adults is around 900 micrograms per day.
Copper is an important micronutrient that plays a crucial role in maintaining our overall health and immunity. Make sure to include copper-rich foods in your diet, but also be mindful of not consuming too much.
Magnesium
Magnesium is an essential mineral that contributes to many bodily functions, including nerve and muscle function, blood glucose control, and protein synthesis. It also plays a vital role in maintaining a healthy immune system.
Benefits of Magnesium for Immunity
Magnesium intake has been linked to the activation and function of immune cells. It has been found to enhance the function of white blood cells and increase the production of cytokines (proteins that regulate the immune system). This mineral also helps reduce inflammation, which is important for a healthy immune response.
Sources of Magnesium
Some foods that are high in magnesium include spinach, nuts and seeds, avocado, whole grains, and dark chocolate. It is also found in seafood, beans, and dairy products.
Below is a table showcasing some common food sources of magnesium:
| Food Source | Magnesium Content (mg per serving) |
|---|---|
| Spinach (cooked, 1 cup) | 157 |
| Almonds (1 ounce) | 80 |
| Avocado (1 medium) | 58 |
| Quinoa (cooked, 1 cup) | 118 |
| Dark chocolate (70-85% cacao, 1 ounce) | 64 |
Magnesium Supplements
If you have trouble getting enough magnesium through your diet, supplements may be a good option for you. However, it’s important to consult with your healthcare provider before taking any new supplement to ensure that it is safe for you.
Conclusion
Magnesium is an essential mineral that contributes to many bodily functions, including a healthy immune system. Incorporating magnesium-rich foods and supplements, as needed, can be an effective way to support immune health.
Where to Find Micronutrients?
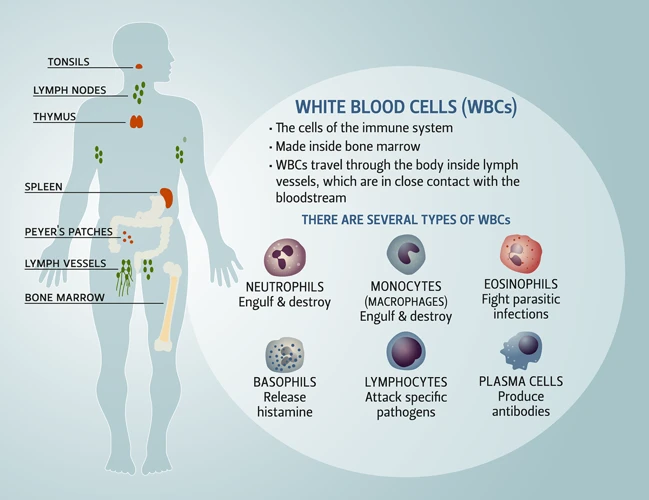
Now that we know how important micronutrients are for our immune system, it’s time to learn where we can find them. In order to maintain a healthy diet, it’s essential to incorporate various food sources that are rich in essential vitamins and minerals. Although supplements can be a good option in certain cases, getting nutrients from natural sources is always the best choice. Let’s explore some of the top food sources that will provide your body with the necessary micronutrients for optimal immune function.
Food Sources
Micronutrients are essential for our overall well-being and immunity. We can obtain them through a balanced diet that includes a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein sources. Here are some examples of foods that are rich in micronutrients:
- Vitamin C: Citrus fruits (such as oranges and grapefruits), strawberries, kiwi, mango, papaya, pineapple, broccoli, Brussels sprouts, bell peppers, tomatoes, and spinach.
- Vitamin D: Fatty fish (such as salmon and tuna), egg yolks, fortified milk and cereal, and mushrooms.
- Vitamin E: Nuts (such as almonds, hazelnuts, and peanuts), seeds (such as sunflower seeds), avocados, and leafy green vegetables (such as spinach and kale).
- Vitamin A: Sweet potatoes, carrots, pumpkin, spinach, kale, collard greens, and liver.
- B Vitamins: Whole grains (such as brown rice, quinoa, and oats), dairy products, eggs, lean meats (such as chicken and turkey), and leafy green vegetables (such as spinach).
- Zinc: Oysters, crab, beef, pork, chicken, beans, nuts (such as cashews and almonds), and whole grains (such as brown rice).
- Selenium: Brazil nuts, tuna, shrimp, chicken, turkey, whole grains (such as brown rice), and eggs.
- Iron: Lean red meat (such as beef and lamb), poultry (such as chicken and turkey), fish (such as salmon and halibut), beans, lentils, tofu, and fortified cereal.
- Copper: Shellfish (such as oysters and crabs), nuts (such as cashews), seeds (such as sesame seeds), chocolate, and liver.
- Magnesium: Spinach, almonds, cashews, peanuts, black beans, edamame, avocado, and whole grains (such as brown rice and quinoa).
Remember that a varied diet is key to ensuring that you get all the necessary micronutrients your body needs to maintain a healthy immune system. While supplements can be helpful in some cases, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen.
Supplements
Supplements are a great way to ensure adequate intake of micronutrients, especially for those with a restricted diet or difficulty in meeting the recommended daily intake through food alone. However, it is important to note that supplements should not replace a healthy and balanced diet. Instead, they should be used as a complement to it.
There are various types of micronutrient supplements available in the market. Here are some of the commonly used ones:
| Supplement Name | Micronutrient(s) it Provides | Form |
|---|---|---|
| Multivitamin | Multiple micronutrients, including vitamins and minerals | Pill or capsule form |
| Vitamin C | Vitamin C | Pill or chewable tablet form |
| Vitamin D | Vitamin D | Pill or liquid form |
| Zinc | Zinc | Pill or lozenge form |
| Selenium | Selenium | Pill form |
| Iron | Iron | Pill or liquid form |
| Magnesium | Magnesium | Pill or powder form |
It is important to note that supplements should be taken as recommended by a healthcare professional. Overconsumption of certain micronutrients, such as vitamin A and iron, can have adverse health effects. It is crucial to follow the dosage instructions on the supplement label or as advised by a healthcare professional.
Supplements can be a helpful way to ensure adequate intake of micronutrients, especially for those with special dietary restrictions. However, they should not be used as a replacement for a healthy and balanced diet and should be taken with caution under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
Immune-Boosting Meal Plan
Now that you understand the importance of micronutrients in supporting your immune system, it’s time to put that knowledge into action. One way to increase your intake of these essential vitamins and minerals is by following an immune-boosting meal plan. By incorporating nutrient-dense foods and strategic supplements, you can help strengthen your defenses against illness and disease. Let’s explore some delicious and healthy meal ideas that are packed with immune-boosting micronutrients.
Breakfast
For a breakfast that is rich in micronutrients, consider starting your day with a bowl of oatmeal topped with fresh berries and sliced almonds. Oatmeal is a great source of fiber and provides important minerals such as iron, magnesium, and zinc.
Adding a handful of fresh berries, such as strawberries or blueberries, not only adds flavor, but also provides a boost of vitamin C and antioxidants which can assist in immune function. Additionally, a sprinkling of sliced almonds adds healthy fats and vitamin E.
For those who prefer a savory breakfast, consider an omelette made with eggs and spinach. Eggs are a great source of high-quality protein and vitamin D, while spinach provides iron and vitamin A.
To complete the meal, add a slice of whole grain toast and avocado for a dose of healthy fats and B vitamins. Don’t forget to top it off with a cup of green tea, which contains antioxidants and has the potential to enhance immune function.
Breakfast ideas:
- Oatmeal with fresh berries and sliced almonds
- Egg and spinach omelette with whole grain toast and avocado
- Green tea
Lunch
For lunch, aim for a balanced meal that includes plenty of vegetables, healthy fats, protein, and complex carbohydrates. Here are some ideas for an immune-boosting lunch:
- Clear broth soup with chicken, lots of vegetables, and herbs like ginger and garlic. Chicken is a good source of protein, while the vegetables provide vitamins and minerals. Herbs like ginger and garlic have anti-inflammatory and anti-bacterial properties that can help fight off infections.
- Salmon salad with mixed greens, avocado, and a vinaigrette dressing. Salmon is high in Omega-3 fatty acids which have anti-inflammatory properties. The mixed greens and avocado provide vitamins, minerals, and healthy fats. The dressing can be made with olive oil, vinegar, and herbs like basil or oregano.
- Quinoa bowl with roasted vegetables and hummus. Quinoa is a good source of protein and complex carbohydrates. Roasted vegetables provide vitamins and minerals, while hummus is a good source of healthy fats and protein. This meal can be easily customized with your favorite vegetables and seasonings.
- Tuna sandwich on whole-grain bread with spinach, tomato, and avocado. Tuna is a good source of protein and Omega-3 fatty acids. Whole-grain bread provides complex carbohydrates, while the spinach, tomato, and avocado provide vitamins, minerals, and healthy fats.
- Bean and vegetable stir-fry over brown rice. Beans are a good source of protein and fiber, while the vegetables provide vitamins and minerals. Brown rice is a good source of complex carbohydrates. The stir-fry can be seasoned with garlic, ginger, and soy sauce for added flavor.
Remember to drink plenty of water throughout the day to stay hydrated and keep your immune system functioning properly.
Dinner
When it comes to dinner, it’s important to choose foods that are rich in micronutrients that can help boost your immunity. Here are some dinner options that are both delicious and nutritious:
- Salmon: This fish is a great source of vitamin D, which has been shown to enhance immune function. Try grilling or baking salmon and serving it with a side of roasted vegetables for a balanced meal.
- Spinach and Mushroom Risotto: This comforting dish is not only delicious but also packed with nutrients. Spinach is rich in vitamins A and C, while mushrooms are a good source of selenium. Add in some brown rice for a boost of immune-boosting B vitamins.
- Quinoa Chili: This plant-based meal is a great source of protein and fiber, both of which are important for a strong immune system. Quinoa is also rich in magnesium, while kidney beans are a good source of zinc. Serve with a side of avocado for some healthy fats.
- Grilled Chicken with Sweet Potato and Broccoli: Chicken is a good source of vitamin B6, which plays a role in immune function. Sweet potato is packed with beta-carotene, while broccoli is rich in both vitamins A and C. Grill the chicken for a healthy protein option, and roast the sweet potato and broccoli for a delicious side dish.
- Vegetable Stir-Fry: This simple meal is a great way to get a variety of nutrients in one dish. Load up on colorful vegetables like bell peppers, carrots, and broccoli for a boost of immune-boosting vitamins and minerals. Serve with a side of brown rice for some extra fiber.
Making sure that your dinner plate is packed with nutrient-rich foods is an important part of supporting a healthy immune system. By incorporating a variety of micronutrient-rich foods into your dinner routine, you can help keep your body in top shape.
Snacks
When it comes to snacks, it’s important to choose options that are both nutritious and tasty. Here are some snack ideas that are rich in micronutrients to help support a healthy immune system:
| Snacks | Nutrients |
|---|---|
| Apple slices with almond butter | Vitamin E, magnesium, zinc |
| Carrot sticks with hummus | Vitamin A, magnesium |
| Greek yogurt with berries | Vitamin C, zinc, selenium |
| Trail mix with nuts and dried fruit | Vitamin E, magnesium, selenium |
| Sliced bell peppers with guacamole | Vitamin C, vitamin E, magnesium |
These snacks offer a range of essential vitamins and minerals that are crucial for maintaining a strong immune system. Vitamin E, for example, is a powerful antioxidant that helps protect the body against harmful free radicals, while magnesium plays a key role in immune function and supports healthy nerve and muscle function.
By incorporating these snacks into your daily diet, you can help ensure that your body is getting the micronutrients it needs to stay healthy and fend off illness. Remember to always choose whole, minimally processed foods and opt for fresh, seasonal produce whenever possible.
Conclusion
After exploring the role of micronutrients in immunity, it’s clear that a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals is essential for maintaining optimal health. Our body needs a variety of micronutrients to support our immune system and help fight off infections and illnesses, from vitamin C and vitamin D to zinc and iron.
While supplements can be a helpful addition to our diet, the best way to obtain micronutrients is through a balanced diet of whole, nutrient-dense foods. It’s important to incorporate a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats into our meals to ensure we are getting all the necessary micronutrients to support our immune system.
Creating an immune-boosting meal plan can be a helpful tool to ensure we are getting all the necessary micronutrients. By including a variety of foods rich in vitamins and minerals, we can create a well-rounded daily menu that supports our immune system. Don’t forget to also stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water and limiting sugary drinks.
Overall, by prioritizing a nutrient-dense diet and incorporating immune-boosting foods into our meals, we can support our immune system and promote overall health and well-being. Remember to consult with a healthcare professional before making any major dietary changes or starting a new supplement regimen.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are micronutrients?
Micronutrients are nutrients required in small amounts by the body in order to maintain good health and function properly.
What is the difference between micronutrients and macronutrients?
Macronutrients are nutrients that are required in large amounts by the body, while micronutrients are needed in smaller amounts.
Is it better to get micronutrients from food or supplements?
It is generally better to get micronutrients from whole foods, as they often contain other beneficial nutrients and substances that may be missing from supplements.
What are some common signs of micronutrient deficiencies?
Common signs of micronutrient deficiencies include fatigue, weakness, a weakened immune system, and an increased risk of chronic diseases.
Can micronutrient deficiencies be corrected with diet alone?
In some cases, yes. However, in cases of severe deficiency or when nutrient needs cannot be met solely through diet, supplements may be necessary.
What is the role of vitamins in immune function?
Vitamins play a crucial role in supporting immune function, as many of them have antioxidant properties that can protect the body against oxidative stress and inflammation.
Which vitamin is most important for immune function?
While all vitamins play a role in immune function, vitamin C is perhaps the most well-known for its ability to support the immune system.
What minerals are important for immune function?
Minerals such as zinc, selenium, iron, copper, and magnesium all play important roles in immune function.
What are some foods that are high in micronutrients?
Foods such as leafy greens, berries, nuts, seeds, whole grains, and fatty fish are all good sources of micronutrients.
Are there any risks associated with taking micronutrient supplements?
Yes, some micronutrients can be harmful in high doses, so it is important to follow recommended dosages and speak with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen.







