As we all strive to make healthier food choices, there is an ongoing debate regarding the nutritional value of organic versus conventional produce. Some people believe that organically grown food is more nutritious, while others argue that there is little to no difference. With so much conflicting information, it can be perplexing to determine if choosing organic is worth the extra cost. In this article, we’ll explore the definitions, benefits, and nutritional value of both organic and conventional produce to help you make an informed decision about what kind of food to eat.
What is Organic Produce?
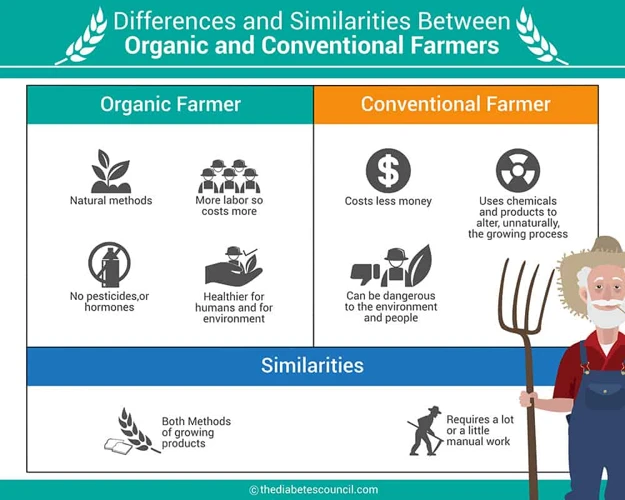
Organic produce is becoming increasingly popular among consumers, but what exactly does it mean? Organic food is grown and processed using certain methods that prioritize the use of natural ingredients and minimize the use of synthetic materials. This means that organic produce is free of synthetic pesticides, fertilizers, and other additives that are commonly used in conventional agriculture. In this article, we will explore the definition and benefits of organic produce and compare it to its conventional counterpart. Additionally, we’ll look at the nutritional value of organic and conventional produce, as well as other factors to consider when choosing what to buy. For more information on healthy eating habits, check out our article on 10 Ways to Incorporate More Fruits and Vegetables into Your Meals.
Definition of Organic Produce
Organic produce refers to crops that are grown without the use of synthetic pesticides, fertilizers, or genetically modified organisms (GMOs). To meet organic standards, organic farmers use natural methods to control pests and weeds, enhance soil quality, and conserve water and energy. Additionally, they rely on crop rotation and composting to ensure long-term soil health rather than using synthetic nutrients.
Organic produce is not only better for the environment, but can also be better for your health. Studies have shown that organic produce has higher levels of beneficial nutrients such as vitamin C, iron, and magnesium, as well as antioxidants.
It’s important to note that just because a product is labeled as organic, it doesn’t necessarily mean it is healthier than conventional produce in terms of its nutrient content. The nutritional value of produce can vary widely depending on factors such as the variety of the plant, how it was grown, and how long it has been in storage. Regardless, choosing organic produce can reduce your exposure to synthetic chemicals and support sustainable farming practices.
For more tips on getting the most nutrients out of your produce, check out our article on the top 5 nutrient-rich fruits and veggies, as well as our guides on proper washing and storing, how cooking methods affect nutrient value, and the benefits of fresh vs. frozen produce.
Benefits of Organic Produce
Organic produce is often touted as being superior to conventional produce due to its many benefits. These benefits can be broken down into several categories, including health benefits, environmental benefits, and safety benefits.
One of the main benefits of organic produce is that it is grown without the use of synthetic pesticides, herbicides, or fertilizers. This means that there is a reduced risk of consuming harmful chemicals when eating organic produce. Additionally, some studies have suggested that organic produce may contain higher levels of certain nutrients than conventionally-grown produce. For example, a study published in the Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry found that organic tomatoes contained significantly higher levels of vitamin C than conventionally-grown tomatoes.
Another benefit of organic produce is that it is often produced using sustainable farming practices that are better for the environment. Organic farming methods typically focus on conserving water, minimizing soil erosion, and reducing pollution. Additionally, organic farms may use natural methods to control pests and diseases, such as crop rotation and companion planting.
Organic produce may also be beneficial for those with allergies or sensitivities. Because organic farming methods do not involve the use of synthetic chemicals, some people may find that they experience fewer allergic reactions when eating organic produce.
Organic produce offers a variety of benefits over conventional produce, including potential health benefits, environmental benefits, and a reduced risk of consuming harmful chemicals. If you’re interested in improving your health and well-being through healthy eating, consider incorporating more organic fruits and vegetables into your diet. For additional tips on healthy eating, check out these articles on the health benefits of eating a rainbow of fruits and veggies, healthy ways to eat more leafy greens, and the benefits of juicing and blending. And if you need help getting started with meal planning, be sure to read our article on creating a fruit and veg meal plan.
What is Conventional Produce?

When we talk about produce that is not labeled as organic, it falls under the category of conventional produce. This term refers to fruits and vegetables that are grown using traditional farming methods, which often includes the use of synthetic pesticides, fertilizers, and other chemicals to promote growth, prevent disease, and control pests. While conventional produce is widely available and typically less expensive than organic produce, there are some potential downsides to consider when deciding whether to choose conventionally grown or organic produce. Let’s take a closer look at what conventional produce is and what benefits it may offer, as well as some of the drawbacks that may be associated with its use.
Definition of Conventional Produce
Conventional produce refers to the food products that are grown using conventional farming practices. These practices involve the use of synthetic fertilizers, pesticides, and herbicides to enhance crop growth and protect them from pests and diseases. Conventional farming also utilizes genetically modified organisms (GMOs) to create crops that are more resistant to pests and diseases, and can withstand harsh weather conditions.
Pros of Conventional Produce:
| Pros | Explanation |
| Lower Cost | Conventional produce is generally less expensive than organic produce as the use of synthetic products reduces the cost of production. |
| Availability | Conventional farming practices are used on a larger scale and can yield more produce. This makes conventional produce more readily available in grocery stores. |
| Longer Shelf Life | Conventional produce is often treated with preservatives that help extend its shelf life, making it easier for consumers to purchase and use the produce over a longer period of time. |
Cons of Conventional Produce:
Despite the pros, conventional produce has its fair share of cons. The use of synthetic fertilizers, pesticides, and herbicides can have negative environmental impacts, such as water pollution and soil degradation. Additionally, the use of GMOs can lead to unintended health consequences for both humans and animals. Finally, conventional produce may contain harmful residues of the synthetic products used during farming practices, which can negatively impact human health.
While conventional produce may be more widely available and less expensive than organic produce, the use of synthetic products in its production can have negative impacts on both human and environmental health.
Benefits of Conventional Produce
When it comes to conventional produce, there are also some benefits to consider. Although the use of pesticides and synthetic fertilizers may be a concern for some, it is important to note that these practices also have their advantages.
One of the main benefits of conventional farming is that it allows for greater crop yields. The use of pesticides and fertilizers can help protect crops from pests and diseases, which can lead to a larger harvest. This can help keep costs down for consumers and ensure a more stable food supply.
Additionally, conventional farming can be more efficient in terms of land use. Since crops are better protected, there is less risk of crop loss or failure. This means that less land is needed to produce the same amount of food as organic farming.
Conventional farming is often more affordable for farmers to implement in terms of production costs. This means that they can sell their produce at a lower price point, making it more accessible to a wider range of consumers.
It is important to note, however, that there are also concerns about the use of pesticides and synthetic fertilizers in conventional farming. These chemicals can potentially harm the environment and human health, and their long-term effects are still being studied.
Here is a table summarizing the benefits of conventional produce:
| Benefits of Conventional Produce |
|---|
| Greater crop yields |
| Efficient use of land |
| Lower production costs |
Nutritional Value Comparison

As consumers become more health-conscious and mindful of their food choices, the debate between choosing organic or conventional produce has become increasingly relevant. A major consideration when it comes to choosing between these options is the nutritional value of the fruits and vegetables. Many studies have compared the macro and micronutrient content of organic and conventional produce, with varying results. In this section, we will delve into the nutritional differences between the two options, explore the studies conducted on this topic, and consider the implications for consumers.
Overview of Studies
Research comparing the nutritional value of organic and conventional produce has yielded mixed results. Some studies have found no significant difference in the nutritional content of organic and conventional produce, while others have shown that organic produce may have higher levels of certain nutrients.
One study published in the Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry analyzed the nutritional content of organic and conventional strawberries. The study found that the organic strawberries had significantly higher levels of vitamin C, total phenolics, and anthocyanins than the conventional strawberries.
Another study published in the Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine compared the nutritional content of organic and conventional fruits and vegetables and found that the organic produce had significantly higher levels of vitamin C, iron, magnesium, and phosphorus.
However, a meta-analysis published in the British Journal of Nutrition reviewed 343 studies comparing the nutrient content of organic and conventional crops and found no significant difference in total protein or fat content between the two types of produce. The only significant difference found was in the levels of nitrogen, with conventional crops having higher nitrogen content.
It is important to note that the quality of the studies reviewed in the meta-analysis varied widely, with some studies showing significant differences in nutrient content between organic and conventional produce while others found no differences. Additionally, the studies reviewed in the meta-analysis only measured the nutrient content of the crops and did not take into account other factors that may affect the healthfulness of the produce, such as pesticide residue or environmental impact.
While some studies have suggested that organic produce may have higher levels of certain nutrients, the evidence is not conclusive and more research is needed in order to draw firm conclusions about the nutritional value of organic versus conventional produce.
Macro-nutrients Comparison
To compare the macro-nutrient content of organic and conventional produce, several studies have been conducted. These studies have focused on the levels of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats in both types of produce. The results of these studies have been inconsistent, with some showing higher levels of macro-nutrients in organic produce and others showing no significant difference.
One such study published in the British Journal of Nutrition analyzed the levels of macro-nutrients in fruits and vegetables. The study found that organic produce had higher levels of carbohydrates and proteins compared to conventional produce. However, there was no significant difference in the fat content between the two types of produce.
Another study published in the Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry compared the macro-nutrient content of organic and conventional tomatoes. The study found that organic tomatoes had higher levels of carbohydrates and proteins compared to conventional tomatoes, but there was no significant difference in the fat content.
To provide a summarized comparison of macro-nutrients in organic and conventional produce, the following table is presented:
| Carbohydrates | Proteins | Fats | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Organic Produce | Varies by produce type | Varies by produce type | Varies by produce type |
| Conventional Produce | Varies by produce type | Varies by produce type | Varies by produce type |
While some studies have found higher levels of certain macro-nutrients in organic produce, the differences are not significant enough to make a substantial impact on overall nutrition. It is important to note that the nutrient content of produce can be affected by various factors such as soil quality, farming practices, and storage conditions, regardless of whether it is organic or conventional.
Micro-nutrients Comparison
When it comes to micro-nutrients, there are some key differences between organic and conventional produce. Micro-nutrients are the essential vitamins and minerals that our bodies need in smaller quantities, but are crucial for overall health and well-being.
Organic produce:
- Studies have shown that organic produce contains higher levels of certain micro-nutrients, such as vitamin C, iron, and magnesium.
- One reason for this could be that organic farming practices prioritize soil health, which in turn leads to higher nutrient levels in the produce.
- Organic produce has also been found to contain more flavonoids, which are beneficial phytochemicals that have antioxidant properties.
- Studies have shown that organic produce has lower levels of harmful heavy metals, such as cadmium and lead, which can accumulate in the body over time and cause health problems.
Conventional produce:
- While conventional produce may have lower levels of some micro-nutrients, it is important to note that the differences are usually not significant enough to cause a major impact on overall health.
- Conventional farming practices often involve the use of synthetic fertilizers, which can lead to depleted soil quality and therefore lower nutrient levels in the produce.
- However, conventional produce is still a good source of essential micro-nutrients and can be a convenient and affordable option for those on a budget.
While there may be some differences in micro-nutrient levels between organic and conventional produce, the most important thing is to prioritize a varied and balanced diet that includes plenty of fruits and vegetables, whether organic or not.
Antioxidant Levels Comparison
When it comes to comparing antioxidant levels between organic and conventional produce, several studies have been conducted to examine if there is a difference.
One study, published in the Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, found that organic blueberries had significantly higher levels of antioxidants, specifically anthocyanin and total phenolic compounds, compared to conventionally grown blueberries.
Another study, published in the Journal of Food Composition and Analysis, found that organic tomatoes had higher levels of antioxidants, such as lycopene, compared to conventional tomatoes.
However, not all studies have shown a significant difference in antioxidant levels between organic and conventional produce. One study, published in the British Journal of Nutrition, compared organic and conventional apples and found no significant difference in antioxidant levels.
It’s worth noting that antioxidants are just one component of overall nutrition and do not necessarily indicate that one type of produce is inherently more nutritious than the other. Additionally, the amount of antioxidants in produce can be influenced by factors such as soil, climate, and growing conditions.
Other Considerations
As with any food-related topic, there are a variety of factors to consider beyond just nutritional value. It’s important to take a holistic approach when evaluating the merits of organic versus conventional produce. Here are some other key considerations to take into account:
Environmental Impact
One important consideration when deciding between organic and conventional produce is the environmental impact of each type of farming. Organic farming practices tend to be more sustainable and have a lower impact on the environment overall. This is because organic farming prioritizes soil health, crop rotation, and natural pest control methods over the use of synthetic fertilizers, pesticides, and herbicides.
| Environmental Impact | Organic Farming | Conventional Farming |
|---|---|---|
| Sustainability | Organic farming practices typically prioritize sustainability by focusing on soil health, crop rotation, and natural pest control methods. | Conventional farming methods often prioritize high yields and profits over long-term sustainability. |
| Water Usage | Organic farming methods tend to use less water overall than conventional farming methods. | Conventional farming methods often rely on large-scale irrigation systems that can use significant amounts of water. |
| Biodiversity | Organic farms tend to have higher levels of biodiversity, with more native plants and animals present. | Conventional farms may use monoculture systems that reduce biodiversity and harm the surrounding ecosystem. |
| Soil Health | Organic farming practices tend to prioritize soil health, which can lead to healthier, more nutrient-rich soil over time. | Conventional farming methods may rely heavily on synthetic fertilizers, which can harm soil health in the long term. |
In addition to these concerns, conventional farming practices have been linked to a range of negative environmental impacts, including water pollution, soil erosion, and damage to local ecosystems. By choosing organic produce over conventional options, consumers can help support more sustainable and environmentally-friendly farming practices.
Safety
When it comes to the safety of produce, both organic and conventional options have their own potential risks. However, it’s important to note that the risk of consuming contaminated produce is low overall. Here are some potential safety concerns to keep in mind:
- Pesticide Residues: Conventional produce is often treated with synthetic pesticides, which can leave behind residues on the produce. While these residues are strictly regulated by the government and deemed safe for consumption, some people prefer to avoid them.
- Bacterial Contamination: Both organic and conventional produce can be contaminated with harmful bacteria like E. coli or salmonella. This is especially true for produce that is eaten raw, like lettuce or spinach, which can be difficult to wash thoroughly. To reduce the risk of bacterial contamination, it’s important to wash all produce before consuming.
- GMOs: Conventional produce may be genetically modified to improve resistance to pests and disease, which can have potential long-term health effects that are not yet fully understood.
It’s up to the individual to decide which safety concerns are most important to them when choosing between organic and conventional produce. While it’s impossible to completely eliminate all potential risks, washing produce thoroughly and being aware of potential risks can help minimize those risks.
Conclusion
After examining the available literature, it is safe to say that there is no significant difference in the nutritional value between organic and conventional produce. Both types of produce offer similar macro and micro-nutrient profiles, and antioxidant levels. However, organic produce may offer some benefits in terms of environmental impact and potential safety concerns.
Environmental Impact: Organic farming practices often involve using fewer pesticides and fertilizers, which can reduce the amount of harmful chemicals released into the environment. Additionally, organic farming methods may be more sustainable in the long-term, as they focus on soil health and biodiversity.
Safety Concerns: While both organic and conventional produce are generally safe to eat, some studies have suggested that conventional produce may contain higher levels of pesticide residue. However, it is important to note that the levels of pesticides found in conventional produce are still within legal limits and are not likely to cause harm to most people.
In conclusion, the decision to choose organic or conventional produce may come down to personal preference, budget, and environmental concerns. Whichever option you choose, it is important to incorporate plenty of fruits and vegetables into your diet for optimal health.
Frequently Asked Questions
What does it mean for produce to be organic?
Organic produce is grown without the use of synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, genetic modification, or irradiation.
Is organic produce always more expensive than conventional produce?
Yes, organic produce is generally more expensive due to the higher cost of production and certification requirements.
What are the benefits of consuming organic produce?
Organic produce may contain higher levels of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, and is often grown using more sustainable and environmentally-friendly practices.
How is conventional produce grown and treated?
Conventional produce is often grown using synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, and may be genetically modified or irradiated to increase yields and shelf life.
Are there any benefits to consuming conventional produce?
Conventional produce is often more affordable and readily available, and may have longer shelf life due to the use of preservatives.
Are there any health risks associated with consuming conventional produce?
Consuming conventionally grown produce may increase one’s exposure to synthetic pesticides and fertilizers, which have been linked to various health issues.
Is there a significant difference in the nutritional value of organic vs. conventional produce?
There is some evidence to suggest that organic produce may contain higher levels of certain nutrients, but more research is needed to draw definitive conclusions.
What are some environmental benefits of consuming organic produce?
Organic farming practices often prioritize conservation and sustainability, leading to improved soil health and reduced pollution and greenhouse gas emissions.
Are there any safety concerns associated with consuming organic produce?
While organic produce is generally considered safe, there is always a risk of food-borne illness or contamination if proper food handling and storage practices are not followed.
What are some factors to consider when deciding between organic and conventional produce?
Consumers may consider factors such as cost, availability, nutrition, environmental impact, and personal values when making the decision between organic and conventional produce.







