As we strive to maintain a healthy lifestyle, consuming a variety of fruits and vegetables is a crucial aspect. However, the nutrient value of these natural foods can be significantly impacted by the cooking methods we employ. With so many different cooking techniques available, it can be challenging to discern which methods are optimal for retaining the highest nutritional value. In this article, we will explore the impact of cooking methods on the nutrient value of fruits and vegetables and provide cooking techniques that can help retain the maximum amount of nutrients in these foods.
How Cooking Affects Nutrients
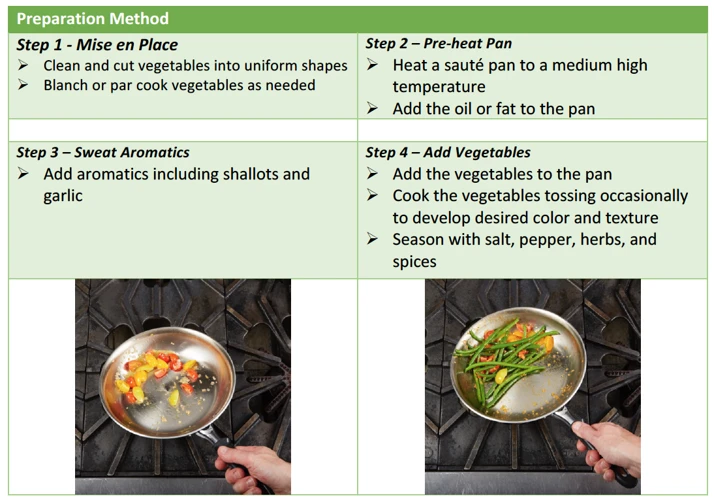
The preparation of fruits and vegetables through cooking can have varying effects on their nutrient content. While cooking methods can enhance the flavor and texture of produce, it can also lead to the loss of vital vitamins and minerals. Understanding how cooking impacts nutrient value is crucial for individuals seeking to maximize the nutritional benefits of their food. Choosing the right cooking technique for specific fruits and vegetables can help preserve nutrients and ensure a healthy diet. To learn more about the importance of food choices when it comes to a healthy lifestyle, check out 10 Ways to Eat More Fruits and Vegetables Every Day.
Heat Degradation
Heat Degradation: Heat degradation is one of the major ways in which cooking can impact the nutritional value of fruits and vegetables. Certain nutrients, such as vitamin C, are heat-sensitive and can degrade when exposed to high temperatures during cooking. The longer the cooking time and higher the heat, the greater the nutrient loss. The table below shows the degree of nutrient loss for various cooking methods:
| Cooking Method | Percent Nutrient Loss |
|---|---|
| Boiling | 25-55% |
| Baking | 35-55% |
| Frying | 25-50% |
| Microwaving | 10-30% |
To minimize nutrient loss due to heat degradation, cooking methods that require lower temperatures and shorter cooking times, such as steaming or stir-frying, are preferred. It is also important to avoid overcooking and to monitor the temperature during cooking. Additionally, cutting fruits and vegetables into smaller pieces before cooking can reduce nutrient loss by minimizing cooking time.
Leaching
Leaching is a phenomenon in which nutrients are lost from fruits and vegetables during cooking and are transferred to the cooking water or oil. This can lead to a significant loss of essential vitamins and minerals, especially in water-soluble nutrients such as vitamin C and B vitamins. To minimize nutrient loss due to leaching, it is important to use cooking methods that involve minimal water or oil.
One way to reduce leaching is to use the cooking water or oil to prepare a sauce or gravy that can be served with the cooked fruits and vegetables. This can help to retain some of the leached nutrients and also enhance the flavor of the dish. Another method is to steam or sauté the fruits and vegetables using a minimal amount of water or oil, or to microwave them in a covered dish with a small amount of water.
To illustrate the different levels of nutrient loss due to leaching, the following table shows the nutrient content of boiled broccoli before and after cooking.
| Nutrient | Raw Broccoli (1 cup) | Boiled Broccoli (1 cup) | % Nutrient Loss |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vitamin C | 81.2 mg | 50.6 mg | 38.4% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.2 mg | 0.1 mg | 50% |
| Potassium | 230 mg | 162 mg | 29.6% |
| Magnesium | 21.8 mg | 16.8 mg | 22.9% |
As shown in the table, boiled broccoli can lose up to 38.4% of its vitamin C content, as well as significant amounts of other key nutrients. To minimize nutrient loss due to leaching, it is recommended to use cooking methods such as steaming, stir-frying, or roasting instead of boiling or simmering.
Anchor text: Click here to learn more about the health benefits of eating a rainbow of fruits and vegetables
Enzymatic Browning
Enzymatic browning is a chemical reaction that occurs when certain enzymes, such as polyphenol oxidase, are exposed to oxygen. This reaction can cause discoloration and a loss of nutrients, such as vitamin C and antioxidants, in fruits and vegetables.
Table:
| Factors | How they affect enzymatic browning |
|---|---|
| pH | Acidic conditions can slow down enzymatic browning, while alkaline conditions can speed it up. |
| Temperature | Higher temperatures can speed up enzymatic browning, while lower temperatures can slow it down. |
| Water activity | Fruits and vegetables with high water content are more susceptible to enzymatic browning. |
| Oxygen exposure | Enzymatic browning requires oxygen, so reducing exposure to air can slow down the reaction. |
To prevent or slow down enzymatic browning, it is important to store fruits and vegetables properly and consume them as soon as possible. Some cooking methods, such as blanching or adding an acidic ingredient like lemon juice, can also help slow down the reaction. To learn more about proper fruit and vegetable storage, check out our article on fruit and vegetable storage.
Internal link:
Fruit and vegetable storage
While some nutrient loss is inevitable during cooking, using the right cooking methods and techniques can help minimize it. In the next section, we will explore the cooking techniques that retain the maximum nutrients in fruits and vegetables.
Freezing/Thawing
Freezing fruits and vegetables is a convenient way to keep them available for consumption throughout the year. However, it is important to note that freezing can affect the nutrient content of fruits and vegetables. Freezing fruits and vegetables can cause damage to cell walls, leading to a loss in texture, and a decrease in nutrient content.
Freezing can lead to the leaching of certain water-soluble nutrients into the surrounding fluid. Some vitamins and minerals, such as vitamin C and potassium, are particularly susceptible to leaching during the freezing process. In order to minimize nutrient loss during freezing, it is recommended to blanch the fruits or vegetables quickly before freezing. This process involves placing the produce in boiling water for a short period of time, and then cooling them immediately in ice water. Blanching can help to preserve the color and texture of the produce, as well as help to retain some of the nutrient content.
Another way to minimize nutrient loss during freezing is to freeze the fruits and vegetables as quickly as possible. This can be done by placing the produce in a single layer on a baking sheet and freezing for a couple of hours before transferring to a freezer-safe bag or container. Additionally, it is recommended to minimize the length of time that the produce is stored in the freezer, and to consume it as soon as possible after thawing.
While freezing can lead to a loss in some nutrients, it is important to note that frozen fruits and vegetables can still be a healthy and convenient option. A comparison of fresh versus frozen produce found that frozen produce may actually have higher nutrient content than fresh produce that has been shipped and stored for a long period of time. Studies have also found that frozen fruits and vegetables can retain a significant amount of their vitamin and mineral content for up to a year when stored properly.
While freezing can lead to some nutrient loss, the benefits of having access to a variety of fruits and vegetables year-round may outweigh any potential drawbacks. By blanching produce before freezing, freezing quickly, and consuming as soon as possible after thawing, it is possible to minimize nutrient loss during the freezing process.
Cooking Techniques to Retain Maximum Nutrients

When it comes to cooking fruits and vegetables, the way you prepare them can have a significant impact on their nutritional value. Different cooking methods can either help retain or deplete the nutrients present in the produce. In order to ensure that you are getting the maximum nutrients out of your produce, it is important to choose cooking techniques that preserve as many nutrients as possible. Here are some recommended cooking techniques to retain the maximum nutrient content in your meals. And if you’re looking to improve your overall fruit and veggie intake, check out our top 5 nutrient-packed fruits and veggies or learn about the nutritional difference between organic and conventional produce.
Steaming
One of the best cooking methods for retaining maximum nutrients in fruits and vegetables is steaming. Steaming is a quick and easy way to cook produce without excessive heat, which can lead to nutrient degradation. Steaming also helps to retain the natural colors and flavors of fruits and vegetables. Below are some tips for steaming different produce:
- Leafy greens: Steamed leafy greens like spinach, kale, and collard greens only need a few minutes to cook. Overcooking can make them mushy and result in nutrient loss. For more healthy ways to enjoy leafy greens, check out our article on 5 healthy ways to eat leafy greens.
- Root vegetables: Steaming root vegetables like carrots and beets can help to preserve their nutrients while softening them for eating.
- Broccoli and cauliflower: Steaming these cruciferous vegetables can help to soften them while preserving their strong flavors and beneficial compounds. For more tips on cooking cruciferous vegetables, check out our article on the benefits of cruciferous vegetables.
- Asparagus: Steaming asparagus can help to soften it and retain its vibrant green color.
- Green beans: Steaming green beans can help to retain their crunch and nutritional value.
- Tomatoes: Steaming tomatoes can help to soften them and make them easier to peel. For more benefits of cooking and eating tomatoes, check out our article on the benefits of juicing and blending with tomatoes.
By steaming your fruits and vegetables, you are helping to retain their maximum nutrient value while also enjoying their natural flavors and textures. So next time you’re in the kitchen, consider steaming your produce for a quick and healthy meal option.
Stir-frying
Stir-frying is a popular cooking technique that originated in China. The method involves quickly cooking small pieces of food in a hot pan while stirring constantly. Stir-frying is a great method for retaining the nutrients in fruits and vegetables due to its quick cooking time and minimal use of oil. Here are some tips for maximizing the nutrient value of stir-fried fruits and vegetables:
- Use a high-quality oil: Choose an oil with a high smoke point, such as avocado, coconut, or peanut oil. This will prevent the oil from breaking down and releasing harmful compounds.
- Prepare ingredients beforehand: Cut fruits and vegetables into small, uniform pieces to ensure even cooking. Pre-cook any meats to reduce overall cooking time.
- Start with a hot pan: Heat the pan until it’s hot before adding oil and ingredients. This will prevent food from sticking to the pan and ensure even cooking.
- Stir constantly: Keep ingredients moving in the pan to prevent overcooking and sticking.
- Season with herbs and spices: Add flavor to stir-fried fruits and vegetables with fresh or dried herbs, spices, and seasonings. Avoid using too much salt, as it can lead to dehydration and nutrient loss.
- Don’t overcook: Stir-frying should only take a few minutes, so be careful not to overcook. Overcooking can cause nutrient loss and result in a mushy texture.
Stir-frying is a great way to cook a variety of fruits and vegetables. Some examples include stir-fried broccoli, bell peppers, onions, carrots, and snap peas. By following these tips, you can retain the maximum nutrient value in your stir-fried fruits and vegetables while also creating a delicious and healthy meal.
Roasting
Roasting is a dry-heat cooking method that involves cooking food in an oven or over an open flame, such as on a grill. It is an ideal cooking method for vegetables that have a low water content, such as root vegetables and hardy greens. Roasting can enhance the flavor and texture of these vegetables, but it can also cause nutrient losses if not done correctly. Here are some tips for roasting vegetables while retaining their maximum nutrient value:
- Use high heat: Roasting at a high temperature, around 425°F, can help vegetables to retain more of their nutrients. This is because the high heat can cause the vegetables to caramelize on the outside while keeping the inside tender and flavorful.
- Don’t overcook: Overcooking vegetables can lead to nutrient losses, so it’s important to take them out of the oven as soon as they are cooked to your liking. Test the tenderness of vegetables by inserting a fork or knife into them; they should be tender but not mushy.
- Use healthy fats: Drizzle vegetables with healthy fats such as olive oil or coconut oil before roasting. The fats can help the vegetables to retain their moisture and nutrients during the cooking process.
- Add herbs and spices: Adding herbs and spices to your roasted vegetables can add flavor and nutrients. For example, rosemary can enhance the flavor of roasted potatoes while also providing health benefits such as antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties.
By following these tips, you can roast vegetables in a way that retains their maximum nutrient value. Remember to use high heat, don’t overcook, use healthy fats, and add herbs and spices for added flavor and nutrients.
Raw
One of the most simple and effective cooking methods to retain nutrients in fruits and vegetables is to consume them raw. Eating fruits and vegetables raw means that they are not exposed to heat, and this preserves the nutrients that could otherwise be lost during cooking. Raw fruits and vegetables contain high levels of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, which are all essential for maintaining good health.
Here are some examples of raw fruits and vegetables that are packed with nutrients:
- Carrots – These are a great source of vitamin A and antioxidants, which can help protect against cancer and other diseases.
- Apples – These are high in fiber and vitamin C, and have been shown to help lower cholesterol levels.
- Spinach – This leafy green vegetable is loaded with iron and vitamin K, both of which are important for maintaining healthy bones.
- Blueberries – These berries are rich in antioxidants, which can help reduce inflammation and protect the body from disease.
- Bell peppers – These vegetables are high in vitamin C and carotenoids, which can help protect the eyes and skin.
While consuming raw fruits and vegetables is beneficial for nutrient retention, it’s important to keep in mind that certain cooking methods can actually enhance the availability of some nutrients. For example, cooking tomatoes and carrots can increase the levels of lycopene and beta-carotene, respectively. It’s worth experimenting with different cooking methods to find the best way to enhance the nutrient value of the fruits and vegetables you consume.
Boiling/Simmering
Boiling/Simmering: This cooking method involves cooking food in a pot of boiling water or a broth. While this method is commonly used, it can also lead to nutrient loss. However, there are some tips that can help to retain nutrients.
- Use minimal water: Using minimal water can help to prevent nutrient loss. Too much water can cause water-soluble vitamins and minerals to leach out of the food.
- Reduce cooking time: Overcooking vegetables can lead to nutrient loss. Reducing the cooking time can help to retain more nutrients.
- Save the water: After boiling vegetables, save the water to use as a broth in soups or stews. The broth contains nutrients that were lost during cooking and can prevent them from going to waste.
- Eat the cooked vegetables: While boiling and simmering may cause some nutrient loss, it is important to remember that cooked vegetables are still packed with nutrients and are much better than not eating vegetables at all.
Boiling and simmering vegetables can be a quick and easy way to prepare them. However, following these simple tips can help to retain more nutrients and ensure that you are getting the most out of your vegetables.
Grilling
One common and delicious way to cook fruits and vegetables during the summer months is grilling. This cooking technique uses direct, high heat to cook food quickly and impart a smoky flavor. However, it’s important to keep in mind that grilling can also cause nutrient loss, especially if the food is overcooked or charred.
Impact of Grilling on Nutrient Value:
Grilling typically causes nutrient loss through heat degradation and formation of harmful compounds called heterocyclic amines (HCAs) and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). These compounds are formed when meat, poultry, or fish are grilled at high temperatures, and can increase the risk of certain cancers.
In fruits and vegetables, grilling can cause a loss of water-soluble vitamins such as vitamin C and B vitamins. Additionally, grilling can cause the breakdown of carotenoids, which are important antioxidants found in many colorful fruits and vegetables.
Cooking Tips for Maximum Nutrient Retention:
While grilling can cause nutrient loss, there are ways to minimize this loss and still enjoy the delicious flavor of grilled fruits and vegetables.
One tip is to marinate the fruits and vegetables before grilling. This can help reduce the formation of HCAs and PAHs, as well as enhance the flavor of the food. Another tip is to grill the fruits and vegetables until they are just tender, rather than overcooking or charring them.
| Do: | Don’t: |
|---|---|
| – Marinate fruits and vegetables before grilling | – Overcook or char food |
| – Use a lower temperature setting on the grill | – Grill food for too long |
| – Precook the fruits and vegetables partially to reduce grilling time | – Use lighter fluid, which can cause chemical contamination of the food |
Using a lower temperature setting on the grill can also help reduce nutrient loss, as well as using a grilling basket or skewers to prevent smaller pieces of food from slipping through the grates. Another option is to precook the fruits and vegetables partially before grilling, which can reduce the amount of grilling time needed.
Conclusion:
Grilling can be a tasty and enjoyable way to cook fruits and vegetables, but it’s important to be mindful of nutrient loss and harmful compound formation. By following these tips for maximum nutrient retention, you can still enjoy the fantastic smoky flavor of grilled fruits and vegetables while also getting the most nutritional benefit from your food.
Cooking Tips for Nutrient Retention in Specific Fruits and Vegetables
As we have learned, cooking certain fruits and vegetables can result in nutrient loss, but there are ways to maximize nutrient retention while still enjoying flavorful meals. Each type of fruit and vegetable varies in its nutrient composition and response to cooking methods. Here are some cooking tips for specific fruits and vegetables that can help preserve their nutrient content and provide the most health benefits. Let’s explore how to properly cook different types of produce to retain as many vitamins and minerals as possible.
Cruciferous Vegetables
Cruciferous vegetables are a great source of vitamins, fiber, and minerals. However, they can also be challenging to cook without losing many nutrients. The cooking method and duration play a vital role.
| Cooking Method | Effect on Nutrients |
|---|---|
| Steaming: | Increases antioxidant activity, preserves vitamin C and glucosinolates |
| Stir-frying: | Reduces vitamin C and chlorophyll, but maintains glucosinolates |
| Boiling/Simmering: | Significant loss of nutrients: vitamin C, glucosinolates, and other phytochemicals |
| Raw: | Provides maximum nutrient value |
It is recommended to steam cruciferous vegetables such as broccoli, kale, and cauliflower. Steaming increases the antioxidant activity, preserves the vitamin C and glucosinolates contents. Stir-frying is also an excellent option, as it maintains a significant amount of glucosinolates despite reducing vitamin C and chlorophyll levels.
On the other hand, boiling or simmering cruciferous vegetables leads to significant nutrient loss, including vitamins C and glucosinolates. If you prefer to consume them raw, it provides the maximum nutrient value, though some people find the taste of raw cruciferous vegetables rather unappealing.
By choosing the right cooking method, we can significantly retain the nutrient value of cruciferous vegetables. Steaming and stir-frying are the best choices for preserving the nutrients in these vegetables.
Tomatoes
Tomatoes are a great source of vitamin C, fibre, and potassium. They also contain lycopene, an antioxidant that has been linked to a reduced risk of certain diseases. However, cooking tomatoes can reduce the levels of vitamin C and lycopene. To retain the maximum nutrient value of tomatoes, it is important to choose the right cooking method.
| Cooking Method | Nutrient Retention |
|---|---|
| Raw | The best way to retain the maximum nutrients of tomatoes is to eat them raw. This is because vitamin C and lycopene are heat-sensitive and can be degraded during cooking. |
| Stir-frying or Sautéing | Cooking tomatoes quickly over high heat can help to retain their nutrient value. Stir-frying or sautéing are good options because they involve brief cooking times. |
| Roasting | While roasting tomatoes can lead to some nutrient loss, it can also enhance the bioavailability of lycopene. This is because roasting breaks down the cell walls of tomatoes, making it easier for the body to absorb lycopene. |
| Boiling/Simmering | Boiling or simmering tomatoes for extended periods can lead to significant nutrient loss, particularly for vitamin C and lycopene. However, the water used for boiling or simmering can still be used in other cooking applications, such as a base for soups or stews. |
It is best to consume tomatoes in their raw form, but if cooked, stir-frying or roasting are the best options to help retain their nutrient value. Boiling or simmering should be avoided where possible, but the water used in these methods can still be utilized in other cooking applications.
Garlic
Garlic is a flavorful and aromatic vegetable that adds depth to many dishes, but it is also well-known for its nutritional benefits. However, cooking garlic can significantly affect its nutrient content. Fortunately, there are certain cooking techniques that can help retain the maximum amount of nutrients.
One important nutrient in garlic is allicin, which has potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Heat and pH levels can affect allicin’s stability, resulting in reduced nutrient content. To retain allicin, it is best to avoid boiling or microwaving garlic for long periods of time.
Instead, using raw or lightly cooked garlic is the best option. Crushing or chopping garlic and letting it sit for a few minutes before cooking can also help activate enzymes that increase allicin formation. Additionally, roasting garlic at a moderate temperature (around 375°F/190°C) for about 20-30 minutes can help retain its nutrient value.
A study showed that boiling garlic for just six minutes can reduce the total antioxidant capacity by up to 29%. It is important to cook garlic for shorter periods of time if boiling is your preferred cooking method.
When cooking garlic, it is best to use techniques that are gentle and do not overcook the vegetable. The following table provides a summary of some recommended cooking methods for retaining the maximum nutritional value of garlic.
| Cooking Technique | Effect on Nutrient Retention |
|---|---|
| Raw | Maximizes allicin content |
| Lightly Cooked | Retains allicin content, avoid boiling or microwaving for long periods of time |
| Roasted | Retains nutrient value at moderate temperature for around 20-30 minutes |
| Boiled | Cook for shorter periods of time to minimize nutrient loss |
By using these cooking techniques, you can maximize the nutritional benefits of garlic and enjoy its delicious flavor in a healthy way.
Sweet Potatoes
Sweet potatoes are a nutrient-dense vegetable that can be enjoyed in a variety of ways. However, the cooking method used can have a significant impact on the retention of certain nutrients. Here are some tips for retaining maximum nutrients when cooking sweet potatoes:
| Cooking Method | Nutrients Retained |
|---|---|
| Boiling | Potassium, Vitamin C |
| Baking/Roasting | Fiber, Vitamin C, Beta-Carotene |
| Microwaving | Fiber, Vitamin C, Beta-Carotene |
Boiling sweet potatoes can cause water-soluble nutrients like Vitamin C and potassium to leach out into the water. To retain these nutrients, it’s best to keep the cooking time short and use a minimal amount of water. Steaming or microwaving are also good alternatives that can help with nutrient retention.
Baking or roasting sweet potatoes can help to retain their fiber, Vitamin C, and beta-carotene content. This is because the heat causes the natural sugars in the sweet potatoes to caramelize, bringing out their natural flavors and nutrients. Plus, the skin becomes crispy and delicious, so there’s no waste.
Microwaving sweet potatoes is a quick and easy way to cook them, and it can help to retain their nutrients. Research has shown that microwaving sweet potatoes for eight minutes resulted in higher levels of beta-carotene and Vitamin C compared to boiling or baking.
There are several ways to cook sweet potatoes while retaining their vital nutrients. Whether you choose to boil, bake, or microwave them, keeping the cooking time and water to a minimum will help to preserve their maximum nutritional value.
Berries
Berries are one of the healthiest fruits out there, packed with antioxidants, vitamins, and fiber. However, cooking berries can result in a loss of some nutrients. Here are some cooking tips to retain maximum nutrients in berries:
- Don’t overcook: Cooking berries for too long can result in a loss of nutrients. It’s best to cook them briefly, just enough to soften them.
- Use minimal water: Berries are delicate and can easily be overcooked. To avoid leaching of nutrients, it’s better to cook them with a minimal amount of water.
- Raw: The best way to consume berries is raw, as cooking can lead to loss of nutrients. Add them to smoothies or eat them as a snack.
- Bake: Baking berries is a good way to retain their nutrient value. Mix them with whole-grain flour, oats, and nuts, and bake them to make a delicious and healthy dessert.
Berries are also rich in vitamin C, which can be destroyed by exposure to heat and air. To preserve vitamin C content:
- Eat them fresh: To get the maximum benefit of vitamin C, eat berries fresh as soon as you buy them.
- Store properly: Berries should be stored in the refrigerator immediately after purchase to maintain their vitamin C content.
- Avoid cutting: Cutting berries can expose them to air and reduce their vitamin C levels. It’s better to eat them whole.
- Add citrus: Adding vitamin-C-rich citrus fruits, such as oranges or lemons, to berries can help preserve their vitamin C content.
By following these cooking tips and storage guidelines, you can ensure that you get maximum nutrient value from delicious and healthy berries.
Conclusion
In conclusion, it is important to consider how cooking methods can impact the nutrient value of fruits and vegetables. Heat degradation and leaching are two common ways that nutrients can be lost. However, there are also cooking techniques that can help retain the maximum nutrients, such as steaming, stir-frying, roasting, raw, boiling/simmering, and grilling.
It is important to note that different fruits and vegetables require different cooking methods for optimal nutrient retention. For example, cruciferous vegetables are better cooked using steaming or boiling/simmering, whereas tomatoes are better cooked using roasting or grilling.
Other fruits and vegetables, such as garlic, sweet potatoes, and berries, also have specific cooking tips to help retain as many nutrients as possible.
Overall, the key takeaway is that cooking can have a significant impact on the nutrient value of fruits and vegetables. By using the right cooking techniques and tips for specific produce, it is possible to retain the maximum nutrients and enjoy delicious and nutritious meals.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is the nutrient value of fruits and vegetables important?
The nutrient value of fruits and vegetables is important for maintaining a healthy body and preventing chronic diseases.
What nutrients are affected by cooking?
Nutrients such as vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants can be affected by cooking methods.
What is heat degradation?
Heat degradation refers to the loss of nutrients due to exposure to high temperatures during cooking.
What is leaching?
Leaching is the process where water-soluble nutrients leach out of fruits and vegetables during cooking.
What is enzymatic browning?
Enzymatic browning is the natural process that occurs when fruits and vegetables are cut or bruised, leading to the loss of nutrients.
What is freezing/thawing?
Freezing and thawing can lead to the loss of nutrients in fruits and vegetables due to the formation of ice crystals.
What are the best cooking techniques to retain maximum nutrients?
Steaming, stir-frying, roasting, raw eating, boiling/simmering, and grilling are the best cooking techniques to retain maximum nutrients.
Is raw always the best option for nutrient retention?
Not always, as some nutrients in fruits and vegetables are more bioavailable after being cooked.
How can I retain nutrients in cruciferous vegetables during cooking?
One way to retain nutrients in cruciferous vegetables is by steaming them lightly, for no longer than five minutes.
How can I retain nutrients in berries during cooking?
One way to retain nutrients in berries is by avoiding overcooking or overheating, as this can lead to the loss of nutrients.







