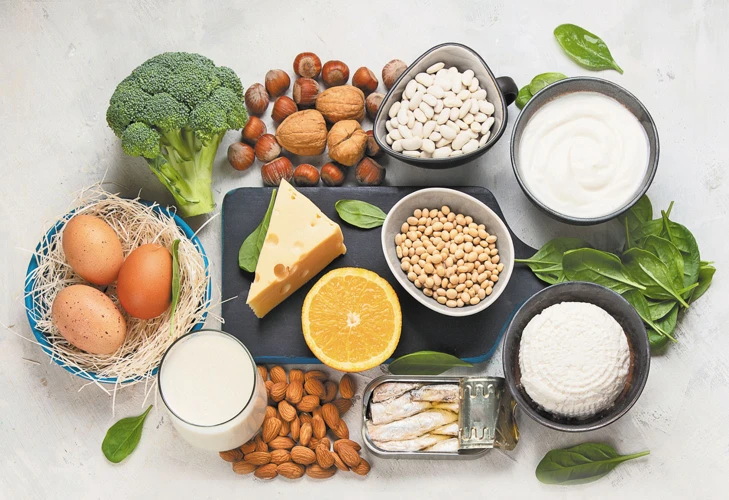
As we age, there are numerous health concerns that can arise, one of which is osteoporosis. This condition has become a major concern, especially among senior citizens, as it can lead to fractures and other related injuries that can severely affect their quality of life. The good news is that a balanced diet can help prevent osteoporosis, but with so much conflicting information out there, getting started can be overwhelming. In this article, we will explore the importance of a balanced diet in preventing osteoporosis and provide a step-by-step guide on what a balanced diet for osteoporosis looks like, along with an exercise plan and other lifestyle changes to consider.
What is Osteoporosis?

Osteoporosis is a common condition that affects the bones, causing them to become weak and brittle over time. This disease can lead to an increased risk of fractures, especially in the hips, wrists, and spine. According to the International Osteoporosis Foundation (IOF), over 200 million women worldwide suffer from this condition. While osteoporosis can affect anyone, it is most commonly seen in older women. In this article, we will discuss the risk factors associated with this condition, why it is a concern, and how a balanced diet can help prevent osteoporosis.
Risk Factors for Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a disease that weakens bones, making them fragile and more likely to break. There are several risk factors that may contribute to the development of osteoporosis. These include:
- Gender – Women are at a higher risk of developing osteoporosis than men.
- Age – The risk of osteoporosis increases as a person ages.
- Family history – If a person’s parents or siblings have had osteoporosis, they may be more likely to develop it themselves.
- Body size – People who have smaller body frames may be at a higher risk of osteoporosis.
- Low hormone levels – Low levels of estrogen and testosterone can contribute to the weakening of bones.
- Medical conditions – Certain medical conditions, such as celiac disease, inflammatory bowel disease, and lupus, can increase the risk of osteoporosis.
- Medications – Some medications, such as steroids and anti-seizure medications, can contribute to the loss of bone density.
- Lifestyle choices – Smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and a sedentary lifestyle can also increase the risk of osteoporosis.
It is important to be aware of these risk factors and take steps to reduce the risk of developing osteoporosis. This includes maintaining a healthy diet, engaging in regular exercise, and avoiding unhealthy habits such as smoking and excessive alcohol consumption. A balanced diet, rich in nutrients such as calcium and vitamin D, can play a crucial role in preventing osteoporosis.
Why Osteoporosis is a Concern
Osteoporosis is a serious concern, particularly for older people. It can lead to fractures and breaks, which can be debilitating and even life-threatening. Research has shown that hip fractures, in particular, can significantly reduce a person’s quality of life and increase their risk of mortality[1]. Additionally, the cost of treating osteoporosis and related injuries is substantial, placing a burden on individuals, families, and healthcare systems[2].
What’s more, osteoporosis is becoming increasingly prevalent as populations age. It is estimated that by 2050, the worldwide incidence of hip fractures alone will increase by 310% in men and 240% in women compared to 1990 levels[3]. This means that more and more people will be impacted by osteoporosis, making it even more critical to take preventative measures.
The good news is that there are ways to help prevent osteoporosis and reduce the risks associated with it. One of the most effective strategies is to maintain a healthy diet and lifestyle, which can help to keep bones strong and healthy. By consuming adequate amounts of calcium, vitamin D, protein, and other nutrients, individuals can give their bodies the tools they need to protect against osteoporosis and related conditions.
To learn more about the benefits of a healthy diet on preventing other conditions, check out our articles on healthy eating for heart disease, how diet can reduce cancer risk, foods that boost the immune system to fight infections, and foods that prevent diabetes. Additionally, a balanced diet is important for maintaining brain health and preventing disease.
The Role of Diet in Osteoporosis Prevention
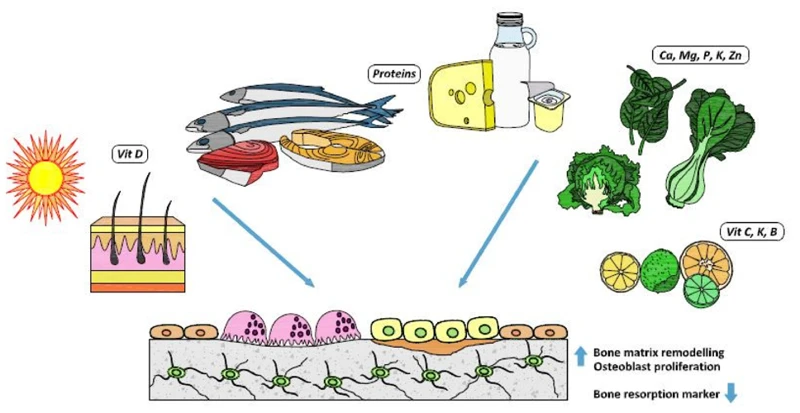
Ensuring a proper diet is an essential component of overall health and can play a key role in preventing numerous conditions, including osteoporosis. Studies have shown that nutrition can be a critical factor in determining bone health, and consuming a healthy and balanced diet can help reduce the risk of developing osteoporosis later in life. By focusing on specific nutrients and adopting healthy eating habits, individuals can fortify their bones and stave off the debilitating effects of this condition. In this section, we will explore the crucial role of diet in osteoporosis prevention and detail the specific nutrients that help support bone health.
Calcium and Vitamin D
Calcium and Vitamin D are two nutrients that are essential for maintaining good bone health and preventing osteoporosis. Calcium is the building block of bones, and Vitamin D helps the body absorb calcium. Without adequate amounts of these nutrients, bones can become weak and brittle, increasing the risk of fractures.
Recommended daily intake:
| Nutrient | Recommended Daily Intake |
|---|---|
| Calcium | 1000-1200mg/day for adults |
| Vitamin D | 600-800 IU/day for adults |
Sources of Calcium:
Calcium is found in many foods, including dairy products, leafy greens, and fortified foods. Here are a few examples:
- Milk: 1 cup of milk contains around 300mg of calcium
- Yogurt: 1 cup of yogurt contains around 400mg of calcium
- Kale: 1 cup of cooked kale contains around 100mg of calcium
- Fortified cereals: Some cereals are fortified with calcium and may contain up to 1000mg per serving
Sources of Vitamin D:
Vitamin D is found in oily fish, egg yolks, and fortified foods such as milk and cereal. However, it can be difficult to get enough Vitamin D through food alone, especially during winter months when sunlight is limited. Many people require supplements to meet their daily requirements.
Here are a few examples of Vitamin D-rich foods:
- Sockeye salmon: 3 ounces of sockeye salmon contains around 400-500 IU of Vitamin D
- Canned tuna: 3 ounces of canned tuna contains around 150-200 IU of Vitamin D
- Mushrooms: Some types of mushrooms, such as shiitake mushrooms, contain small amounts of Vitamin D
- Fortified milk: 1 cup of milk may be fortified with up to 100 IU of Vitamin D
Incorporating calcium and Vitamin D-rich foods into your diet is an important step towards preventing osteoporosis. Additionally, it may be helpful to talk to your healthcare provider about supplements if you are having difficulty meeting your daily requirements through food alone.
Protein and Other Nutrients
Protein is an essential nutrient for maintaining bone health. It provides the body with the necessary building blocks to create and repair bone tissue. It is important to consume both animal and plant-based sources of protein in order to maintain a healthy balance of nutrients. Additionally, getting enough vitamin C and vitamin K, as well as minerals like magnesium, phosphorus, and zinc, can also support bone health.
Animal-based sources of protein:
- Eggs – a great source of protein and vitamin D
- Salmon – rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which can reduce inflammation and improve bone health
- Lean meats – beef, pork, and chicken can provide both protein and minerals like zinc and phosphorus
- Dairy – milk, cheese, and yogurt are good sources of calcium and vitamin D
Plant-based sources of protein:
- Legumes – beans, lentils, and chickpeas provide both protein and minerals like magnesium and phosphorus
- Nuts and Seeds – almonds, chia seeds, and sesame seeds are good sources of protein and minerals like magnesium and phosphorus
- Tofu and Tempeh – made from soybeans, these plant-based protein sources also contain calcium
- Whole Grains – quinoa and brown rice are examples of whole grains that provide both protein and minerals like magnesium and phosphorus
Remember, a balanced diet for osteoporosis prevention also includes getting enough calcium and vitamin D. Incorporating a variety of nutrient-dense foods into your diet can help ensure that you are getting all the necessary nutrients for maintaining bone health.
The Importance of a Balanced Diet
Consuming a balanced diet is essential in preventing osteoporosis. A balanced diet comprises the right amount of all necessary nutrients that provide the body with the fuel it needs to function optimally. It is important to avoid a diet that is deficient in any macro or micronutrients. Let’s take a closer look at the role of different nutrients in osteoporosis prevention.
| Protein | is essential for bone health. It forms the building blocks for bones and muscles, and a deficiency in protein can lead to decreased bone density. |
| Calcium | is a crucial nutrient for bone health, as it is the main component of bone tissue. Adequate calcium intake can help prevent bone loss and reduce the risk of fractures. |
| Vitamin D | is required for the absorption and utilization of calcium in the body. Without sufficient vitamin D, the body cannot use calcium effectively, even if it is consumed in large amounts. |
| Magnesium | is necessary for the metabolism of calcium and vitamin D in the body. It helps regulate calcium levels in the blood and improves bone density. |
| Phosphorus | plays a key role in bone health, as it is a major component of bone tissue. It is also required for the absorption and utilization of calcium in the body. |
| Vitamin K | is needed to activate certain proteins that are involved in bone metabolism. It helps regulate calcium levels in the blood and improves bone density. |
| B vitamins | such as vitamin B6, B12, and folate are important for bone health. They help regulate homocysteine levels in the blood, which when high, can lead to bone loss and fractures. |
Eating a balanced diet that is rich in all these nutrients is crucial in preventing osteoporosis. Consuming a variety of foods from different food groups can ensure that the body receives all the necessary nutrients. A diet that is rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, dairy products, and whole grains can provide all the essential nutrients required for optimal bone health.
What a Balanced Diet for Osteoporosis Looks Like

When it comes to preventing osteoporosis, a balanced diet is crucial. But what does a balanced diet for osteoporosis actually look like? It may seem overwhelming at first, but with the right combination of foods, it can be simple and delicious. In this section, we’ll highlight the key nutrients to focus on and provide some examples of foods to incorporate into your diet. So let’s dive in and explore how you can eat your way to stronger bones!
Foods High in Calcium and Vitamin D
Calcium and Vitamin D are two crucial nutrients that help build and maintain strong bones. Incorporating foods that are high in calcium and vitamin D into your diet can help prevent the onset of osteoporosis. Here are some examples of such foods:
- Dairy Products: Milk, cheese, and yogurt are all excellent sources of calcium. Some dairy products, such as fortified milk and yogurt, also contain added vitamin D.
- Green Leafy Vegetables: Broccoli, kale, and turnip greens are all rich sources of calcium. These vegetables are also low in calories, making them a healthy choice for those watching their weight.
- Fatty Fish: Salmon, sardines, and canned tuna are all rich in vitamin D. These fish are also high in omega-3 fatty acids, which have been shown to have numerous health benefits.
- Egg yolks: Egg yolks are a good source of vitamin D. However, they are also high in cholesterol, so it is important to consume them in moderation.
- Fortified Foods: Many foods, such as breakfast cereals, orange juice, and tofu, are fortified with calcium and vitamin D. Be sure to check the labels to ensure that you are getting enough of these nutrients.
Incorporating a variety of these foods into your diet can help ensure that you are getting enough calcium and vitamin D to keep your bones strong and healthy. It is important to remember that a balanced diet is key to preventing osteoporosis, which means incorporating a variety of other nutrients as well.
Foods Rich in Protein and Other Nutrients
Protein is an essential nutrient that plays a crucial role in bone health. It helps to build and maintain muscles, which in turn helps support and protect bones. Some good sources of protein that you should include in your diet to prevent osteoporosis are:
| Food | Protein Content |
|---|---|
| Eggs | 6g per large egg |
| Lean meats (beef, pork, lamb) | around 25g per 3oz serving |
| Poultry (chicken, turkey) | around 25g per 3oz serving |
| Seafood (salmon, tuna, shrimp) | around 20-25g per 3oz serving |
| Beans (black beans, kidney beans, lentils) | around 15g per 1 cup serving |
| Nuts (almonds, pistachios) | around 6g per 1oz serving |
In addition to protein, it is important to make sure you are getting enough of other key nutrients that support bone health. These include:
– Magnesium: helps to activate vitamin D in the body and plays a role in bone formation. Good sources include spinach, almonds, avocados, and whole grains.
– Vitamin K: helps to build bone and also assists in the absorption of calcium. Good sources include leafy greens such as kale and collard greens, as well as broccoli and brussels sprouts.
– Phosphorus: works together with calcium to build strong bones. Good sources include dairy products, lean meats, and poultry.
By incorporating a variety of these foods into your diet, you can ensure that you are getting the nutrients that your body needs to build and maintain strong, healthy bones.
A Sample Meal Plan
To get a better idea of what a balanced diet for osteoporosis looks like, here is an example of a meal plan that includes all the essential nutrients needed to prevent this condition.
| Meal | Food | Portion Size | Nutrient Content |
|---|---|---|---|
| Breakfast | Low-fat Greek yogurt | 1 cup | Contains calcium and protein |
| 10-grain toast | 2 slices | Contains fiber, protein, and other nutrients | |
| Blueberries | 1/2 cup | Contains antioxidants and vitamin C | |
| Snack | Almonds | 1 oz | Contains calcium, vitamin E, and other nutrients |
| Dried apricots | 1/2 cup | Contains potassium and vitamin A | |
| Lunch | Grilled chicken breast | 3 oz | Contains protein and vitamin B6 |
| Kale salad with avocado | 2 cups | Contains calcium, vitamin K, and healthy fats | |
| Quinoa | 1/2 cup | Contains protein, fiber, and other nutrients | |
| Snack | Cottage cheese | 1/2 cup | Contains calcium and protein |
| Carrots with hummus | 1 cup | Contains vitamin A, fiber, and healthy fats | |
| Dinner | Grilled salmon | 3 oz | Contains protein, vitamin D, and healthy fats |
| Brown rice | 1/2 cup | Contains fiber and other nutrients | |
| Steamed broccoli | 1 cup | Contains calcium, vitamin K, and other nutrients | |
| Snack | Low-fat cottage cheese | 1/2 cup | Contains calcium and protein |
| Apple slices with almond butter | 1 medium apple, 1 tbsp almond butter | Contains fiber, healthy fats, and other nutrients |
This meal plan includes a variety of nutrient-rich foods, including calcium-rich dairy, leafy green vegetables, and seafood. It also includes lean protein sources and healthy fats. By including foods from all food groups and focusing on whole, nutrient-dense foods, you can help to prevent osteoporosis and maintain strong bones throughout your life.
Incorporating Exercise and Other Lifestyle Changes
When it comes to preventing osteoporosis, diet is only part of the equation. Exercise and lifestyle changes can also play a crucial role in maintaining healthy bones as we age. In fact, a sedentary lifestyle can increase your risk of developing osteoporosis, while regular weight-bearing exercise can help strengthen bones and reduce the risk of fractures. So, let’s take a closer look at how exercise and other lifestyle changes can further contribute to osteoporosis prevention.
How Exercise Helps Prevent Osteoporosis
Regular exercise is essential for maintaining strong bones and preventing osteoporosis. Strong bones are built by increasing bone density through activities that put stress on the bones. Here are some ways exercise can help prevent osteoporosis:
- Weight-bearing Exercises: These exercises cause the bones to work against gravity, which stimulates bone building. Examples include walking, running, aerobics, dancing, and hiking.
- Resistance Training: Resistance training involves lifting weights or using resistance bands to build muscle and strengthen bones. This type of exercise puts stress on the bones, which promotes bone density. Examples include weightlifting, pushups, lunges, and squats.
- Flexibility and Balance Exercises: Flexibility and balance exercises, such as yoga and tai chi, can help prevent falls and fractures by improving balance and coordination.
By incorporating these types of exercises into your regular routine, you can help prevent osteoporosis and maintain strong bones throughout your life. It’s important to consult with your doctor before starting a new exercise program, especially if you have a history of osteoporosis or bone fractures.
Other Lifestyle Changes to Consider
In addition to following a balanced diet and incorporating regular exercise, there are other lifestyle changes that can help prevent osteoporosis. Consider making the following changes to your daily routine:
- Quit smoking: Smoking is a known risk factor for osteoporosis, as it can lower bone density. Quitting smoking can help prevent further bone loss and protect your overall health.
- Avoid excessive alcohol consumption: Drinking more than 2-3 drinks per day has been linked to an increased risk of osteoporosis. Limiting alcohol intake or avoiding it altogether can help keep bones healthy and strong.
- Take breaks from sitting: Long periods of sitting can be detrimental to bone health, as it can result in weaker bones. Make sure to take breaks from sitting throughout the day and engage in weight-bearing activities such as walking or standing.
- Manage stress: Chronic stress can increase levels of the hormone cortisol, which has been linked to lower bone density. Finding healthy ways to manage stress such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises can help protect bones.
- Get enough sleep: Adequate sleep is important for bone health, as it allows the body to repair and build new bone tissue. Aim for 7-8 hours of sleep each night.
Making these lifestyle changes, in addition to following a balanced diet and incorporating exercise, can help reduce the risk of osteoporosis and maintain healthy bones throughout life. Remember, it’s never too early or too late to start taking steps towards osteoporosis prevention.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a balanced diet that includes adequate amounts of calcium, vitamin D, protein, and other nutrients is essential for preventing osteoporosis. It is important to be aware of the risk factors for osteoporosis and to take steps to minimize them. These steps may include maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, and engaging in regular exercise.
In addition to a balanced diet, it is important to incorporate weight-bearing and muscle-strengthening exercises into your routine to help prevent osteoporosis. These exercises can help improve bone density and reduce the risk of fractures.
Other lifestyle changes, such as getting enough rest and reducing stress, may also be beneficial in preventing osteoporosis. Additionally, it is important to have regular check-ups with your healthcare provider to monitor bone health and detect any potential issues early on.
In conclusion, taking a comprehensive approach to osteoporosis prevention through a balanced diet, exercise, and lifestyle changes can help ensure optimal bone health and reduce the risk of fractures in later life. By making simple changes to your diet and lifestyle, you can take control of your bone health and reduce your risk of developing osteoporosis.
Frequently Asked Questions
What other health conditions can having a balanced diet help prevent?
A balanced diet can help prevent a variety of health conditions, including heart disease, diabetes, and certain types of cancer.
Is osteoporosis more common in men or women?
Osteoporosis is more common in women, although it can affect men as well.
Can children or teenagers get osteoporosis?
Yes, although it is rare, children and teenagers can get osteoporosis – especially those with certain medical conditions or those who do not have a healthy diet and exercise regularly.
Can osteoporosis be cured?
Unfortunately, there is no cure for osteoporosis. However, healthy lifestyle changes can prevent it from getting worse and reduce the risk of fractures.
What happens if osteoporosis is left untreated?
If left untreated, osteoporosis can lead to an increased risk of fractures and disability.
Are dairy products the only source of calcium?
No, there are many other sources of calcium including dark leafy greens, almonds, and fortified foods like orange juice and cereal.
Can taking calcium supplements prevent osteoporosis?
While calcium supplements can be beneficial for some people, it is best to get calcium from natural food sources whenever possible. Additionally, calcium supplements are not a replacement for a healthy diet and lifestyle.
What types of exercise are best for preventing osteoporosis?
Weight-bearing exercises that involve impact and resistance training are best for preventing osteoporosis. Examples include jogging, hiking, weightlifting, and tennis.
How much calcium and vitamin D do I need every day?
Generally, adults need 1000-1200 mg of calcium and 600-800 IU of vitamin D per day. However, it is best to consult with a healthcare professional to determine your specific needs.
Is it possible to have too much calcium?
Yes, too much calcium can lead to health problems such as kidney stones and constipation. It is important to consume calcium in moderation and not exceed recommended daily intakes.







