For many people, building muscle may seem like a daunting and challenging task. However, with the right mindset, planning, and most importantly, diet, gaining muscle can be within reach. When it comes to protein sources, most people typically rely on animal-based products such as meat, eggs, and dairy. But what if you prefer a plant-based diet or want to minimize your consumption of animal products? Fortunately, there are plenty of plant-based protein sources that can help you build muscle and achieve your fitness goals. In this article, we’ll explore various plant-based protein sources, how to measure your protein intake, the differences between plant-based and animal-based protein, supplement options, and tips for building muscle with a plant-based diet.
Why Choose Plant-Based Protein?

When it comes to building muscle, getting enough protein is essential. While animal-based protein sources are often the go-to for many athletes and fitness enthusiasts, plant-based protein has been gaining popularity in recent years for good reason. Choosing plant-based protein can offer a range of benefits, from being more nutritious and better for digestion to being eco-friendly. So, before you hit the gym or start a new workout routine, consider the benefits of plant-based protein and how it can help you reach your muscle-building goals. Want to learn more? Check out our article on the benefits and drawbacks of plant-based protein powder.
More Nutritious
Plant-based protein sources are generally considered to be more nutritious than animal-based sources. This is because they are rich in essential nutrients, including fiber, vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. Additionally, a recent study published in the Journal of the American Medical Association found that consuming more plant-based protein was associated with a lower risk of death from cardiovascular disease.
Here are some examples of the nutritional benefits of popular plant-based protein sources:
| Source of Protein | Nutritional Benefits |
|---|---|
| Legumes | High in fiber, iron, folate, potassium, and magnesium |
| Nuts and Seeds | Rich in healthy fats, vitamin E, magnesium, and protein |
| Grains | Good source of fiber, B vitamins, iron, and protein |
| Soy Products | Complete protein source, high in calcium, iron, and vitamin B12 (for fortified products) |
| Vegetables | Varying levels of protein, vitamins, and minerals depending on the vegetable |
Consuming a variety of plant-based protein sources can help ensure that you are getting a wide range of nutrients. To learn more about how to incorporate high protein plant-based meals into your diet, check out our article on high protein plant-based meals. For tips on how to cook plant-based proteins on a budget, read our article on affordable plant-based protein sources.
Better for Digestion
Plant-based protein sources are known to be easier on the digestive system compared to animal-based protein sources. Animal proteins take longer to break down in the body and can leave us feeling heavy and sluggish. On the other hand, plant-based proteins are generally more easily digestible and can be absorbed more quickly by the body. This is especially beneficial for those with digestive issues or sensitivities.
One reason for this is that plant-based protein sources are often accompanied by fiber, which slows down digestion and helps regulate blood sugar levels. Additionally, plant-based proteins are typically lower in saturated fat and cholesterol, which can contribute to digestive problems in some individuals.
Legumes are an excellent source of plant-based protein and are generally easier to digest than meat products. Lentils, chickpeas, and black beans, for example, are rich in both protein and fiber, making them great options for those looking to improve their digestion.
Nuts and Seeds are also fantastic options for plant-based protein that is easy to digest. Nuts like almonds, cashews, and walnuts are high in protein, healthy fats, and fiber, making them a great snack option that won’t weigh you down. Seeds like pumpkin, chia, and hemp seeds are also packed with protein and can be added to smoothies, salads, or oatmeal for an extra protein boost.
Grains are another group of plant-based proteins that are easy to digest. Quinoa, for example, is a complete protein that is also high in fiber and minerals. Brown rice, oats, and barley are also great options that are rich in protein and other essential nutrients.
Soy products like tofu, tempeh, and edamame are excellent plant-based protein sources that are easily digestible. Unlike some of the other legumes, soy products are complete proteins, meaning they contain all essential amino acids.
Lastly, many vegetables like broccoli, spinach, and Brussels sprouts are surprisingly high in protein and also bring plenty of other nutrients to the table. These veggies are also high in fiber, helping to regulate digestion and make it easier on the body.
If you’re looking for more information on affordable plant-based protein sources, check out our article on affordable plant-based protein sources. For some non-soy plant protein exploration, head over to our non-soy plant protein exploration article.
Incorporating more plant-based proteins into your diet can be a simple and effective way to improve your digestion and your overall health. For more vegan protein tips, check out our vegan protein tips article or our plant protein for athletes article for plant protein ideas geared towards those looking to build muscle. And for some plant protein snack ideas, head over to our article on 15 plant protein snacks.
Eco-Friendly
Eco-Friendly
Choosing plant-based protein sources can have a positive impact on the environment. Animal agriculture is a major contributor to greenhouse gas emissions, deforestation, and water pollution. By choosing plant-based sources, we can reduce our carbon footprint and protect natural resources.
Here are some ways that plant-based protein sources are eco-friendly:
- Reduced Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Animal agriculture is responsible for a significant portion of greenhouse gas emissions, including methane and nitrous oxide. These gases contribute to climate change and can have devastating effects on the environment. Plant-based protein sources generally have lower greenhouse gas emissions, making them a more eco-friendly choice.
- Conservation of Natural Resources: Producing animal-based foods requires more resources than plant-based foods. Animal agriculture uses more land, water, and energy to produce the same amount of protein as plant-based sources. Choosing plant-based sources can help conserve these natural resources.
- Reduced Water Pollution: Animal agriculture is a major contributor to water pollution. Livestock operations produce waste that can contaminate nearby water sources, leading to health risks for humans and animals. Plant-based sources generally have lower water pollution impact, making them a more eco-friendly choice.
By choosing plant-based protein sources, we can take steps towards reducing our impact on the environment. To learn more about the environmental impact of plant-based versus animal-based proteins, check out our article on the impact of plant-based and animal-based proteins.
Top Plant-Based Protein Sources

When it comes to building muscle with plant-based protein, it’s important to know which foods are high in protein. Fortunately, there are plenty of options to choose from! Whether you’re a vegan athlete or simply looking to add more plant-based protein to your diet, incorporating a variety of legumes, nuts and seeds, grains, soy products, and vegetables can help you reach your protein goals. In this section, we’ll take a closer look at some of the best plant-based protein sources available.
Legumes
One of the best sources of plant-based protein is legumes, which include beans, lentils, and chickpeas. These versatile foods not only provide a great source of protein, but they are also high in fiber, vitamins, and minerals. Below are some of the top legumes to incorporate into your diet:
- Black beans: Black beans are an excellent source of protein, with around 7 grams of protein per half-cup serving. They are also high in fiber, folate, and magnesium, making them a nutritional powerhouse. Add black beans to salads, soups, or tacos to increase your protein intake.
- Lentils: Lentils are another great source of protein, with around 8 grams of protein per half-cup serving. They are also high in iron, folate, and fiber. Lentils can be used in a variety of dishes, including soups, stews, and salads.
- Chickpeas: Chickpeas, also known as garbanzo beans, are a delicious and versatile legume. They contain around 7 grams of protein per half-cup serving, as well as fiber, folate, and manganese. Use chickpeas in hummus, salads, or roasted as a snack.
- Edamame: Edamame is a type of soybean that is high in protein, with around 8 grams of protein per half-cup serving. It is also a good source of fiber, iron, and calcium. Enjoy edamame as a snack or add it to stir-fries or salads.
- Peas: Peas are a great source of plant-based protein, with around 8 grams of protein per one-cup serving. They are also high in fiber, vitamin C, and vitamin K. Incorporate peas into soups or stews, or enjoy them as a side dish.
Incorporating a variety of legumes into your diet can help you meet your daily protein needs while also providing a range of other beneficial nutrients for your body. Try experimenting with different types of legumes in your meals to keep things interesting and flavorful.
Nuts and Seeds
Nuts and seeds are excellent plant-based sources of protein that also contain healthy fats and essential vitamins and minerals. Almonds and pumpkin seeds are particularly high in protein, with 6 grams of protein per ounce and 9 grams of protein per quarter cup, respectively. Chia seeds and hemp seeds are also great options, with both packing in around 6 grams of protein per two tablespoons.
In addition to protein, nuts and seeds contain healthy fats that are important for muscle growth and overall health. They also provide key vitamins and minerals like magnesium, which helps with muscle and nerve function, and vitamin E, which acts as an antioxidant in the body.
One easy way to incorporate nuts and seeds into your diet is by adding them to smoothies or oatmeal in the morning. You can also snack on them throughout the day or top salads and roasted vegetables with them for a protein and nutrient boost.
It’s worth mentioning that while nuts and seeds are nutritious options, they can be high in calories, so be mindful of portion sizes if you’re trying to build muscle while maintaining a healthy weight. A small handful or a tablespoon or two of seeds is generally a good serving size.
Grains
Grains are another great plant-based protein source that can be easily incorporated into your diet. Not only are they a good source of protein, but they also contain essential nutrients such as fiber, B vitamins, and minerals.
Here are some of the top grains you can include in your muscle-building diet:
- Quinoa: A complete protein containing all nine essential amino acids. It is also high in iron, magnesium, and fiber.
- Brown Rice: A good source of protein, fiber, and complex carbohydrates. It is also rich in vitamins and minerals such as manganese and selenium.
- Buckwheat: Another complete protein that is also gluten-free. It is a good source of fiber, magnesium, and antioxidants.
- Amaranth: A gluten-free grain that is high in protein and fiber. It is also rich in minerals such as iron, magnesium, and phosphorus.
- Millet: A gluten-free grain that is high in protein, fiber, and B vitamins. It is also high in minerals such as iron and magnesium.
In addition to the grains listed above, you can also incorporate whole grain bread, pasta, and cereal into your diet for a boost of protein and nutrients. Just be sure to read labels and choose options that are high in protein and fiber and low in added sugars.
Soy Products
Soy products are another great source of plant-based protein that can help you build muscle. One of the most popular soy products is tofu, which is made from soybeans and has a similar texture to cheese. It’s a versatile ingredient that can be used in savory dishes like stir-fries or scrambled like eggs for a protein-packed breakfast.
Another soy product you may have heard of is tempeh, which is made from fermented soybeans. It has a nutty flavor and a firm texture, making it a great substitute for meat in recipes like tacos or sandwiches.
Edamame is another soy product that’s packed with protein. It’s basically just immature soybeans that are cooked and eaten as a snack or added to salads for a protein boost. If you’re looking for a quick and easy snack that’s high in protein and low in calories, edamame is the way to go.
Soy milk is a popular alternative to dairy milk and is a great source of plant-based protein. It can be used in smoothies or poured over cereal for a protein-rich breakfast.
When it comes to incorporating soy products into your diet, it’s important to note that not all soy products are created equal. Some studies suggest that consuming large amounts of soy-based products may have negative health effects, so it’s best to consume soy in moderation and opt for organic, non-GMO varieties whenever possible.
Vegetables
When it comes to plant-based protein sources, vegetables may not be the first thing that comes to mind, but many green vegetables are actually great sources, particularly for those following a vegetarian or vegan diet. Here are some of the top vegetable sources of protein:
| Vegetable | Protein Content (per 100g) |
|---|---|
| Broccoli | 2.8g |
| Sweetcorn | 3.2g |
| Spinach | 2.9g |
| Brussels Sprouts | 3.4g |
| Kale | 4.3g |
While the protein content of vegetables may not be as high as that of other sources such as legumes or soy products, they can still contribute to overall protein intake and provide a range of other important nutrients. Additionally, their fiber content can aid digestion and promote satiety, making them useful for weight management.
It is important to note that vegetables alone may not provide sufficient amounts of protein for those looking to build muscle, but they can make a valuable addition to meals in conjunction with other protein sources.
Measuring Your Protein Intake
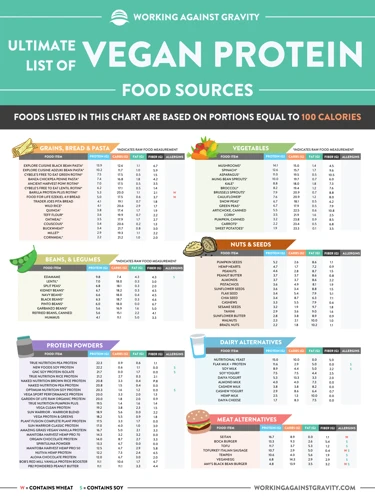
One important aspect of building muscle is measuring your protein intake. It can be difficult to know how much protein you need, and how to measure it accurately. However, by taking the time to learn about recommended daily intake, measuring protein content, and combining sources for complete proteins, you can ensure that your body is getting the nutrients it needs to build muscle efficiently. Let’s explore these topics in more detail.
Recommended Daily Intake
The amount of protein you need in a day depends on various factors, such as your physical activity, age, and gender. Generally, it is recommended that adults consume at least 0.8 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight per day. However, this amount may increase depending on your fitness goals.
If you are looking to build muscle, you need to increase your protein intake. A study published in the Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition found that consuming 1.6 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight can lead to a significant increase in muscle mass and strength.
To calculate your protein needs, multiply your weight in kilograms by the recommended protein intake per day. For example, if you weigh 70 kilograms, you would need at least 56 grams of protein per day. However, if you are looking to build muscle, you would need to consume around 112 grams of protein per day.
It is important to note that protein needs may vary depending on your personal circumstances. Pregnant or lactating women, athletes, and individuals with certain medical conditions may require more protein than the average person.
Incorporating a variety of plant-based protein sources can help you reach your daily protein goals. Legumes, nuts and seeds, grains, soy products, and vegetables all contain protein and can be easily incorporated into meals and snacks throughout your day.
Measuring Protein Content
When it comes to building muscle with plant-based protein, it’s important to know how to measure protein content in different sources. While some plant-based proteins may not contain all essential amino acids, they can still provide adequate protein content when combined with others.
In order to measure protein content, it’s helpful to know the protein content of some popular plant-based protein sources:
| Plant-Based Protein Source | Protein Content per Serving |
|---|---|
| Lentils | 9g |
| Chickpeas | 6g |
| Quinoa | 8g |
| Oats | 6g |
| Almonds | 6g |
| Hemp Seeds | 10g |
| Tempeh | 15g |
It’s important to note that some plant-based sources may not have as high protein content as animal-based sources. However, this doesn’t mean that you can’t build muscle on a plant-based diet – it just means you may need to consume slightly larger quantities of protein-rich plant-based foods.
In addition to measuring protein content, it’s also important to pay attention to the other nutrients that different plant-based proteins provide. For example, lentils also provide a good source of iron and fiber, while hemp seeds are high in healthy fats and minerals. By choosing a variety of plant-based protein sources, you can ensure that you’re not only meeting your protein needs, but also getting a diverse range of nutrients.
Combining Sources for Complete Proteins
To get the full spectrum of essential amino acids, it’s important to combine different plant-based protein sources in the same meal. This is because most plant-based protein sources are deficient or low in at least one essential amino acid.
Here are some combinations:
- Beans and Rice: Combining legumes with grains, such as rice or quinoa, creates a complete protein. For example, black beans and rice or lentil soup with whole-grain bread.
- Hummus and Pita: Combining legumes with whole-grain pita provides a complete protein. Hummus is made from chickpeas, which are a good source of protein, and whole-grain pita provides the missing amino acids.
- Trail Mix: Combining nuts and seeds with dried fruit is a great snack option that provides all essential amino acids. For example, almonds with raisins or pumpkin seeds with dried cranberries.
- Stir Fry: Tofu or tempeh with a variety of vegetables over brown rice creates a complete protein meal. Soy products are a complete protein, and combining them with whole grains and vegetables ensures a balanced meal.
- Salad: Dark leafy greens combined with chickpeas or quinoa provides a complete protein. For example, a kale salad with quinoa or spinach salad with chickpeas.
By combining different plant-based protein sources, you can ensure that you are consuming a complete protein with all the necessary amino acids. It’s important to vary your protein sources to ensure that you are getting all the nutrients your body needs.
Plant-Based Vs. Animal-Based Protein

When it comes to protein sources, the debate between plant-based and animal-based is a heated one. Many argue that animal-based protein is the superior choice for building muscle and gaining strength, while others maintain that a plant-based diet can provide just as much (if not more) nutrition. While both options have their benefits and drawbacks, it’s important to consider factors like quality, environmental impact, and cost when making a decision on which protein to consume. Let’s explore the differences between plant-based and animal-based protein and how they can impact your muscle-building goals.
Quality and Digestibility
When it comes to comparing plant-based and animal-based protein, quality and digestibility are important factors to consider. While animal protein sources are typically considered complete proteins, meaning they contain all essential amino acids, many plant-based sources are incomplete. However, this does not mean that plant-based protein is of lower quality or less digestible.
Plant-based protein sources can be combined to create complete proteins, and many plant-based sources also offer additional nutrients that are beneficial for overall health. It’s also important to note that the digestibility of plant-based protein can vary between sources.
To illustrate the differences in quality and digestibility, let’s compare a few common plant-based and animal-based protein sources:
| Protein Source | Protein Quality | Protein Digestibility |
|---|---|---|
| Chicken Breast | High (Complete protein) | High |
| Black Beans | Medium (Incomplete protein) | Medium |
| Quinoa | High (Complete protein) | High |
| Eggs | High (Complete protein) | High |
| Chickpeas | Medium (Incomplete protein) | Low |
| Soybeans | High (Complete protein) | High |
As we can see from the table, plant-based protein sources can vary in both quality and digestibility. However, with careful planning and a variety of protein sources, it is possible to meet all of your protein needs with plant-based sources. Additionally, plant-based protein sources often provide other important nutrients such as fiber, vitamins, and minerals that are essential for overall health.
Environmental Impact
Environmental Impact
When it comes to choosing between plant-based or animal-based protein sources, the environmental impact is an important factor to consider. Animal agriculture has a significant impact on the environment, including deforestation, water pollution, and greenhouse gas emissions. On the other hand, plant-based protein sources have a much lower environmental footprint.
Here is a comparison of the environmental impact of plant-based and animal-based protein sources:
| Plant-based Protein | Animal-based Protein | |
|---|---|---|
| Land Use | Requires significantly less land to produce the same amount of protein | Requires large amounts of land to raise livestock for meat and dairy products, leading to deforestation |
| Water Use | Uses much less water compared to animal agriculture | Animal agriculture uses large amounts of water for livestock feed and to clean animal waste, which can pollute water sources |
| Greenhouse Gas Emissions | Produces significantly fewer greenhouse gas emissions than animal agriculture | Animal agriculture is a major contributor to greenhouse gas emissions, primarily due to methane produced by livestock |
| Waste Production | Produces significantly less waste compared to animal agriculture | Animal waste can lead to water and air pollution, as well as greenhouse gas emissions |
Switching to plant-based protein sources for muscle building not only benefits your health, but also has a positive impact on the environment. By choosing plant-based protein, you can reduce your environmental footprint and support sustainable agriculture.
Cost and Convenience
When it comes to cost and convenience, plant-based protein sources have both advantages and disadvantages compared to animal-based protein sources. While some plant-based proteins can be more expensive than animal-based options, others are considerably cheaper. It all depends on the specific food and where you live. However, one thing that is generally true is that plant-based protein sources can be more convenient to store and prepare.
Cost Comparison: Plant-Based Vs. Animal-Based Protein
To give you an idea of how the cost compares, let’s take a look at some common protein sources and their prices:
| Protein Source | Cost (per serving) |
|---|---|
| Chicken breast (4 oz) | $1.49 |
| Eggs (2 large) | $0.32 |
| Salmon (4 oz) | $3.99 |
| Plain Greek yogurt (6 oz) | $1.12 |
| Black beans (1/2 cup) | $0.25 |
| Almonds (1 oz) | $0.58 |
| Tofu (3 oz) | $0.50 |
| Lentils (1/2 cup) | $0.21 |
As you can see, some plant-based protein sources like black beans, lentils, and tofu are considerably cheaper than animal-based options like chicken and salmon. On the other hand, almonds are more expensive than eggs and plain Greek yogurt.
Convenience of Plant-Based Protein Sources
One of the biggest advantages of plant-based protein sources is their convenience. Many plant-based proteins like lentils, beans, and seeds can be stored for long periods of time without going bad. They can also be bought in bulk and used in a variety of different dishes, making meal planning and preparation much easier.
Additionally, many plant-based proteins can be cooked relatively quickly, especially compared to meat that needs to be cooked through. For example, lentils can be cooked in as little as 20 minutes, while beans can be cooked in an hour or less if presoaked. Tofu and tempeh can also be prepared quickly and used in a variety of different dishes.
However, it’s worth noting that some plant-based proteins like nuts and seeds can be more difficult to store and may have a shorter shelf life compared to some animal-based proteins. So, it’s important to keep this in mind when planning your meals and grocery shopping.
Supplementing Plant-Based Protein

Now, you may be wondering – is it necessary to supplement with plant-based protein? The answer to that is, it depends on your individual needs and goals. While it is definitely possible to meet your protein requirements solely through whole food sources, sometimes supplementation can be helpful in reaching your desired levels. In this section, we will explore the different types of plant-based protein supplements available, and how they can fit into your diet and fitness routine.
Protein Powders
Protein powders are a popular supplement for those who want to build muscle and increase their protein intake. There are many types of protein powders available, including pea protein, soy protein, rice protein, and hemp protein. These powders are often used in smoothies, shakes, or mixed in with foods like oatmeal or yogurt.
Pea protein is a great option for people looking for a hypoallergenic and easily digestible protein source. It is also high in branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs), which are important for muscle growth and recovery. Soy protein is a complete protein source, meaning it contains all essential amino acids. It is also known to have potential health benefits such as reducing cholesterol levels. Rice protein is easily digested and low in fat, making it a great option for those looking to supplement with protein without adding too many extra calories. Hemp protein is a good source of omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, which can help reduce inflammation in the body.
When shopping for protein powders, it’s important to read the labels carefully and look for products with minimal added ingredients, such as sugar or artificial flavors. Opt for products that are certified organic or Non-GMO Project verified to ensure the protein is coming from high-quality sources.
It’s worth noting that while protein powders can be a convenient way to increase protein intake, they should not be relied on as the sole source of nutrition. Whole food sources of protein, such as those mentioned in the previous section, should make up the majority of one’s protein intake. Additionally, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian before starting any new supplement regimen.
Other Supplements
There are a variety of other supplements available that can help in building muscle with plant-based protein. Some of these include:
- Creatine: This supplement has been shown to increase muscle mass and strength in both plant-based and animal-based athletes.
- Branched-Chain Amino Acids (BCAAs): These amino acids, which include leucine, isoleucine, and valine, can help with muscle recovery and growth.
- Glutamine: This amino acid is important for muscle recovery and can also help boost the immune system.
- Beta-Alanine: This supplement can improve muscle endurance and delay fatigue during workouts.
- Vitamin D: This vitamin is important for maintaining healthy bones and muscles.
- Zinc: This mineral is essential for protein synthesis and muscle growth, making it an important supplement for athletes.
It’s important to note that while these supplements can be helpful, they should not replace a well-rounded diet and exercise routine. Additionally, it’s always a good idea to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen.
Building Muscle with Plant-Based Protein
When it comes to building muscle, many people assume that animal-based protein is the only way to go. However, plant-based proteins can be just as effective when it comes to building and maintaining muscle mass. The key is to ensure that you are consuming enough protein, along with the other nutrients your body needs to support muscle growth. In this section, we will explore how to build muscle with plant-based protein sources, as well as tips for tracking your progress and adjusting your diet as needed.
Plan Your Meals
One of the most important steps for building muscle with plant-based protein sources is to plan your meals. This will ensure that you are consuming enough protein as well as other essential nutrients to support muscle growth.
Here are some tips for planning your meals:
- Include a variety of protein sources: To ensure that you are getting all the essential amino acids, it’s important to incorporate a variety of plant-based protein sources in your meals. This can include legumes, nuts and seeds, grains, soy products, and vegetables.
- Balance your macros: While protein is essential for muscle growth, it’s also important to balance your intake of carbohydrates and fats. Make sure to include complex carbohydrates and healthy fats in your meals as well.
- Prep ahead: To save time during the week, consider prepping some of your meals and snacks ahead of time. This can include cooking a big batch of quinoa or roasting vegetables that you can incorporate into meals throughout the week.
- Snack smart: Incorporating protein-rich snacks throughout the day can help you meet your daily protein needs. Some examples include hummus with veggies or apple slices with almond butter.
- Stay hydrated: Drinking enough water is essential for proper muscle function and recovery. Make sure to sip on water throughout the day and during workouts.
By planning your meals ahead of time, you can take the guesswork out of meeting your protein and nutrient needs for muscle growth. Plus, you’ll save time and be less likely to rely on processed or convenience foods that may not support your goals.
Eat Enough Calories
To build muscle with plant-based protein, it’s important to eat enough calories each day. This means consuming more calories than your body burns in a day, also known as a calorie surplus. When you’re in a calorie surplus, it provides the extra energy your body needs to build muscle.
Calculating Your Calorie Needs
To determine how many calories you need to be eating each day, you can use an online calorie calculator or consult with a registered dietitian. Factors that affect your calorie needs include your age, gender, weight, height, and activity level.
Increasing Your Calorie Intake
If you’re not currently eating enough calories to support muscle growth, you may need to increase your calorie intake. This can be done by adding more plant-based protein sources, as well as healthy fats and complex carbohydrates, to your diet.
Here is a list of high-calorie plant-based foods to help you reach your daily calorie goals:
| Food | Calories per 100g |
|---|---|
| Avocado | 160 |
| Nuts and seeds (such as almonds, walnuts, and sunflower seeds) | 500-600 |
| Whole grain bread and pasta | 250-300 |
| Potatoes | 75 |
| Hummus | 300 |
Remember to balance your calorie intake with exercise and strength training. Consistency is key when it comes to building muscle, so make sure you’re staying on track with your meal plan and training regimen.
Track Your Progress
Tracking your progress is crucial when building muscle with plant-based protein. It helps you stay motivated and see how far you’ve come. You can use a variety of methods to track your progress, including:
| Method | What to Track | How Often |
|---|---|---|
| Body measurements | Weight, body fat percentage, measurements of specific body parts (e.g. arms, waist) | Every 4-6 weeks |
| Photos | Full-body photos or photos of specific body parts | Every 4-6 weeks |
| Strength gains | Record the amount of weight lifted for exercises like bench press, squat, and deadlift | Every workout |
| Energy levels | Subjective rating of energy levels throughout the day | Every day |
| Sleep quality | Subjective rating of sleep quality and duration | Every day |
By tracking your progress using one or more of these methods, you can objectively see the changes in your body and energy levels. If you’re not making progress, you can adjust your diet or exercise routine accordingly. It’s also important to celebrate your successes, no matter how small they may seem. Building muscle takes time and consistency, so tracking your progress can help you stay on track and see the results of your hard work.
Conclusion
In conclusion, it is clear that building muscle with plant-based protein sources is not only possible but also comes with several benefits. Plant-based protein sources are more nutritious and better for digestion. They are also eco-friendly, which makes them a great choice for those who want to make a positive impact on the environment.
If you are looking to build muscle with plant-based protein, you must ensure that you consume enough protein every day. Measuring your protein intake and combining different sources to create complete proteins will help ensure that you meet your daily recommended intake.
When comparing plant-based protein sources with animal-based protein sources, it is clear that plant-based sources offer several benefits. They are more environmentally friendly and often more cost-effective. Additionally, they have been proven to be just as effective in promoting muscle growth and strength when consumed in the right amounts.
To supplement your plant-based protein intake, you may choose to use protein powders or other supplements. However, it is important to remember that supplements should not replace whole foods, and they should be used as a complement to a balanced diet.
In order to build muscle with plant-based protein, it is important to plan your meals carefully, consume enough calories, and track your progress. This will help you to reach your goals and maintain a healthy, plant-based diet.
Overall, building muscle with plant-based protein is a great way to achieve your fitness goals while promoting a healthy lifestyle and making a positive impact on the environment. By making small changes to your diet and lifestyle, you can make significant strides towards a healthier, more sustainable future.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the best plant-based protein sources for building muscle?
The best plant-based protein sources for building muscle include legumes, nuts and seeds, grains, soy products, and vegetables. Each of these sources offers a unique set of amino acids that can be combined to create complete proteins.
How much protein do I need to build muscle on a plant-based diet?
The recommended daily protein intake for building muscle on a plant-based diet is 1.6-2.2 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight. This means that a 150-pound person would need 109-150 grams of protein per day.
Can I build muscle on a plant-based diet without supplements?
Yes, it is possible to build muscle on a plant-based diet without supplements. However, supplements may be helpful if you have trouble meeting your daily protein needs or if you are looking to maximize your muscle growth.
Are plant-based proteins inferior to animal-based proteins?
No, plant-based proteins are not inferior to animal-based proteins. While animal-based proteins may have a slightly higher biological value, plant-based proteins can still provide all the necessary amino acids for building muscle.
Do I need to eat a lot of carbs to build muscle on a plant-based diet?
No, you do not need to eat a lot of carbs to build muscle on a plant-based diet. While carbs are important for providing energy during workouts, they are not essential for muscle growth. However, it is important to eat enough calories overall to support muscle growth.
Can I get enough protein from plant-based sources if I am gluten-free?
Yes, you can still get enough protein from plant-based sources if you are gluten-free. Gluten-free protein sources include legumes, nuts and seeds, soy products, and vegetables.
Is it possible to build muscle on a vegan diet?
Yes, it is possible to build muscle on a vegan diet. As long as you are getting enough protein and calories, you can build muscle on a plant-based diet.
Are plant-based protein powders effective for building muscle?
Yes, plant-based protein powders can be effective for building muscle. Look for powders that contain at least 20 grams of protein per serving and a complete amino acid profile.
What are some good plant-based protein sources for post-workout recovery?
Good plant-based protein sources for post-workout recovery include a protein shake made with plant-based protein powder, a quinoa and vegetable stir-fry, or a salad with beans or tofu.
Can I still build muscle on a plant-based diet if I am on a budget?
Yes, you can still build muscle on a plant-based diet if you are on a budget. Focus on affordable protein sources like beans, lentils, and tofu, and buy in bulk when possible. Meal planning and cooking at home can also help save money.







