Athletic performance depends on many factors, but one that often goes overlooked is the role of carbohydrates. While most people understand that carbohydrates provide energy for the body, the specific ways in which they affect athletic performance may be less clear. What types of carbohydrates are best for athletes? How should they be incorporated into an athlete’s diet? In this article, we’ll explore the importance of carbohydrates in athletic performance, the different types of carbohydrates, and how to properly fuel your body for optimal athletic performance. So, whether you’re a professional athlete or a fitness enthusiast, read on to discover how carbohydrates can help take your performance to the next level.
The Importance of Carbohydrates in Athletic Performance
Carbohydrates are often considered the most important macronutrient for athletes, and for good reason. They provide the body with the energy it needs to power through the most intense workouts and competitions. But, what exactly are carbohydrates, and why are they so important for athletic performance? Understanding the role of carbohydrates in our diet is essential for every athlete. In this article, we will explore the importance of carbohydrates and their different types, as well as how to incorporate them into a balanced meal plan. So, whether you are a professional athlete or just enjoy staying active, read on to discover everything you need to know about carbohydrates and their role in athletic performance. To learn more about healthy carb options, check out our article on 10 Healthy Carbs to Include in Your Diet.
What are Carbohydrates?
Carbohydrates are one of the three macronutrients that provide energy to the body along with proteins and fats. They are one of the body’s primary sources of fuel and are essential for optimal athletic performance. Carbohydrates are made up of three elements: carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. They can be classified into two main types: simple and complex.
Simple carbohydrates, also known as “simple sugars,” are made up of one or two sugar molecules. They are quickly digested and absorbed by the body, resulting in a rapid increase in blood sugar levels. Examples of simple carbohydrates include table sugar, honey, and fruit juices.
Complex carbohydrates, on the other hand, are made up of many sugar molecules and are therefore slower to digest. They are found in foods such as whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and legumes. Complex carbohydrates provide more sustained energy and are less likely to cause a rapid increase in blood sugar levels.
Fiber is another type of carbohydrate. It is a complex carbohydrate that cannot be digested by the body. However, it plays an important role in maintaining digestive health and slowing down the absorption of other carbohydrates, which helps to regulate blood sugar levels.
While carbohydrates are important for athletic performance, it is also important to choose the right type of carbohydrates. Simple carbohydrates should be limited as they can cause a spike in blood sugar levels, leading to a subsequent crash in energy levels. Complex carbohydrates and fiber, on the other hand, provide sustained energy and help maintain steady blood sugar levels.
To learn more about simple vs complex carbs, click here. For information on incorporating carbohydrates into balanced meals, click here. For the benefits of whole grain carbs, click here. To learn about the top 5 gluten-free carb sources, click here. To find out what happens to blood sugar levels when consuming carbs, click here. And for information on the potential negative effects of consuming too many carbohydrates, click here.
How the Body Uses Carbohydrates for Energy
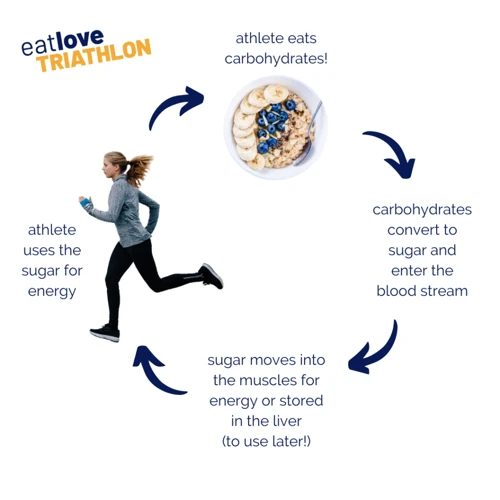
Carbohydrates are the primary fuel source for the body during exercise. When carbohydrates are consumed, they are broken down into glucose, which is then transported to the muscles and used for energy. Glucose can also be stored in the muscles and liver as glycogen, which can be used later for energy during exercise.
During exercise, the body first turns to stored glycogen for fuel. Once glycogen stores start to run low, the body will then turn to carbohydrates consumed during exercise to provide energy. If there aren’t enough carbohydrates available, the body will start to break down protein and fat for fuel, which can lead to muscle breakdown and fatigue.
It is important for athletes to consume carbohydrates before, during, and after exercise to ensure that their glycogen stores are adequately replenished and to maintain energy levels. Consuming carbohydrates during endurance exercise can delay fatigue, enhance performance, and improve mental function.
However, it is important to choose the right types of carbohydrates. Complex carbohydrates, such as whole grains, fruits, and vegetables, are ideal sources of carbohydrates because they provide a steady release of energy throughout exercise. Simple carbohydrates, such as candy and soft drinks, provide a quick burst of energy but can lead to a crash later on.
Incorporating fiber into the diet is also important for athletes. Fiber helps to regulate digestion and prevent blood sugar spikes, which can lead to a decrease in energy levels. Good sources of fiber include whole grains, fruits, and vegetables.
Athletes who follow a vegetarian or vegan diet should also be mindful of their carbohydrate intake. Good sources of carbohydrates in a plant-based diet include grains, legumes, and fruits. For more information about carbohydrate sources for vegetarians and vegans, see our article on carbohydrate sources for vegetarians and vegans.
To summarize, carbohydrates are a vital source of energy for athletes during exercise. Consuming complex carbohydrates and incorporating fiber into the diet can help regulate energy levels during exercise. Additionally, athletes should be mindful of their carbohydrate intake and choose appropriate sources of carbohydrates for their diet.
Carbohydrates and Endurance
Endurance athletes require a significant amount of energy to sustain their physical activity for prolonged periods of time. Carbohydrates play a crucial role in providing this energy. Carbohydrates are the primary fuel source for moderate to high-intensity endurance exercise, and their depletion can lead to fatigue and decreased performance.
To improve endurance performance, athletes should aim to consume a diet high in complex carbohydrates, such as whole grains, fruits, and vegetables. These types of carbohydrates provide a sustained release of energy, which can help maintain blood glucose levels during exercise. Additionally, carbohydrate loading can be beneficial for endurance athletes before a competition, allowing for increased glycogen stores in the muscles.
During endurance exercise, athletes may also benefit from carbohydrate supplementation, such as sports drinks, gels or bars, to maintain blood glucose levels and delay fatigue. The American College of Sports Medicine recommends consuming 30-60 grams of carbohydrates per hour of endurance exercise.
It’s also important to keep in mind that fiber, which is a type of carbohydrate, can provide numerous health benefits for athletes. Fiber can help regulate digestion and maintain heart health. Good sources of fiber include whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and legumes. Athletes should aim to consume at least 25-30 grams of fiber per day from these sources.
For endurance athletes, carbohydrate intake is essential for optimal performance. Incorporating complex carbohydrates into the diet, carbohydrate loading before competition, and carbohydrate supplementation during exercise can all contribute to improved endurance performance. Additionally, consuming fiber-rich carbohydrates is important for overall health and wellbeing. For more information on fiber-rich carbohydrate sources, visit our article on Fiber and Carbohydrate Sources.
Carbohydrates and Recovery
After a strenuous workout, the body requires proper recovery to repair and rebuild the muscles. Carbohydrates play a crucial role in this recovery process. Here are some reasons why:
- Restock Glycogen: During exercise, the body depletes its glycogen stores, which are the body’s primary source of energy. Consuming carbohydrates after exercise helps to restock glycogen stores.
- Reduce Muscle Damage: Consuming carbohydrates after exercise helps to reduce muscle damage caused by intense workouts.
- Promote Protein Synthesis: Consuming carbohydrates after exercise helps to promote protein synthesis, which is the process of building muscle.
It’s important to note that the timing of carbohydrate consumption is crucial for optimal recovery. After exercise, the body is in a state where it can quickly absorb and utilize carbohydrates. Consuming carbohydrates within 30 minutes of finishing exercise can help to maximize their benefits.
In addition to carbohydrates, it’s also important to consume protein for muscle recovery. A combination of carbohydrates and protein can help to enhance muscle recovery and promote muscle growth.
Types of Carbohydrates for Athletes
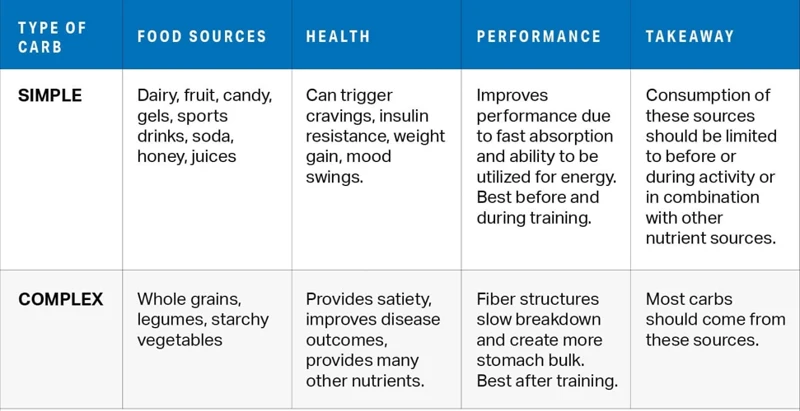
As an athlete, it is important to understand the types of carbohydrates that can benefit your performance. Carbohydrates are the primary source of energy for the body, providing fuel for muscles and the brain. However, not all carbohydrate sources are created equal. There are complex and simple carbohydrates, each with their own unique qualities and benefits. The role of fiber in carbohydrate consumption cannot be overlooked. By understanding the different types of carbohydrates available, athletes can make informed decisions about their dietary intake and ultimately improve their overall performance.
Complex Carbohydrates
Complex carbohydrates are an essential source of energy for athletes. Unlike simple carbohydrates, which are broken down quickly and provide a temporary boost of energy, complex carbohydrates are broken down slowly and provide a sustained release of energy. These carbohydrates are made up of long chains of sugars and are found in foods such as whole grains, legumes, vegetables, and fruits.
Benefits of Complex Carbohydrates
The consumption of complex carbohydrates has numerous benefits for athletes. Firstly, these carbohydrates provide a more consistent and longer-lasting source of energy as compared to simple carbohydrates. This makes them ideal for endurance sports such as long-distance running, swimming or cycling.
Secondly, complex carbohydrates may increase the body’s glycogen stores. Glycogen is a form of glucose that is stored in the liver and muscles, and serves as a primary energy source during exercise. Consuming a diet high in complex carbohydrates may help athletes maintain high levels of glycogen stores and therefore, improve their athletic performance.
Thirdly, unlike simple carbohydrates which can cause an energy crash soon after consumption, complex carbohydrates provide a gradual and sustained energy release. This can help athletes maintain a consistent energy level throughout their workout or competition and avoid the “bonk” or “hit the wall” feeling.
Sources of Complex Carbohydrates
As mentioned earlier, complex carbohydrates are found in a wide variety of foods, including:
- Whole grains: whole wheat bread, brown rice, quinoa, oats, barley, buckwheat, millet, and teff.
- Legumes: lentils, beans, chickpeas, and peas.
- Vegetables: broccoli, cabbage, cauliflower, spinach, zucchini, sweet potato, carrots, and beets.
- Fruits: apples, berries, kiwi, oranges, grapefruit, bananas and pears.
Incorporating complex carbohydrates into the athlete’s diet can be done through various delicious and nutritious meal options. For breakfast, a bowl of oatmeal with berries and nuts can provide a great start to the day. For lunch, a quinoa and vegetable salad with roasted sweet potatoes and brown rice is a great option. Brown rice can be combined with some grilled chicken or tofu and steamed vegetables for a nutritious dinner.
It is clear that complex carbohydrates are an essential component of an athlete’s diet. Their numerous benefits and healthy food sources make them an excellent choice for athletes looking to improve their athletic performance.
Simple Carbohydrates
Simple carbohydrates are molecules composed of one or two sugar molecules that are broken down and absorbed quickly by the body. They are also known as ‘quick-digesting’ or ‘fast-acting’ carbohydrates. While simple carbohydrates can provide a quick burst of energy, they are not recommended as a primary source of carbohydrates for athletes because their effects are short-lived and they can cause energy crashes.
Some sources of simple carbohydrates include:
- Sugar: Table sugar (sucrose) and high-fructose corn syrup are examples of added sugars that are often found in processed foods, such as candy, soda, and baked goods.
- Fruit and fruit juice: Fruit and fruit juice contain natural sugars, such as fructose, that provide quick energy. However, it is important to note that many fruit juices have added sugars, so it is important to choose 100% fruit juice.
- Milk and dairy products: Milk contains lactose, a simple sugar that is quickly broken down and absorbed by the body.
- Sports drinks: Many sports drinks contain simple sugars, such as glucose and sucrose, that can provide a quick source of energy during exercise.
While simple carbohydrates can be useful for providing a quick source of energy during exercise, athletes should primarily focus on consuming complex carbohydrates as their main source of fuel. Complex carbohydrates are broken down and absorbed more slowly, providing a steady and sustained source of energy. Additionally, complex carbohydrates provide important nutrients, such as fiber, that are essential for overall health and well-being.
When choosing carbohydrates, athletes should focus on sources that are high in complex carbohydrates, such as whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and legumes. These sources will provide a steady source of energy and important nutrients to support athletic performance and overall health.
Importance of Fiber
Fiber is a type of carbohydrate that the body cannot fully digest. Even though it is not broken down like other carbs, it still plays a crucial role in athletic performance. Here are some reasons why athletes should prioritize their fiber intake:
- Aids in digestion: Fiber helps regulate digestion and prevent constipation, which can be uncomfortable and interfere with athletic performance.
- Slows down carbohydrate absorption: When paired with carbs, fiber slows down the body’s absorption of them, preventing blood sugar spikes and crashes.
- Increases feelings of fullness: High-fiber foods take longer to digest, so they keep you feeling full for longer periods of time. This can help athletes avoid overeating and control their weight.
- Supports heart health: Multiple studies have shown that a diet high in fiber can lower cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of heart disease.
- Source of energy: While the body cannot directly use fiber for energy, the bacteria in the intestines can ferment it and turn it into short-chain fatty acids, which can be used as fuel for the body during exercise.
That being said, not all sources of fiber are created equal when it comes to athletic performance. High-fiber foods that are also high in fat can be harder to digest and lead to digestive discomfort during exercise. To get the most benefits from fiber, athletes should focus on getting their fiber from whole, nutrient-dense foods like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes.
How to Incorporate Carbohydrates into Your Diet
If you’re an athlete looking to enhance your performance, you’ve likely heard the buzz about carbohydrates. But with so much conflicting information out there, it can be difficult to know how to incorporate these nutrients into your diet in a way that will truly benefit your athletic performance. That’s why we’ve put together this comprehensive guide on the best types of carbohydrates for athletes, as well as how and when to consume them to maximize your results. Keep reading to learn more about how to fuel your body for peak performance.
Carbohydrate Intake for Different Types of Athletes
It is important to note that carbohydrate needs for athletes vary based on their activity level and sport. Below are some guidelines to help determine appropriate carbohydrate intake for different types of athletes:
- Endurance athletes: Athletes who participate in endurance events such as marathons, triathlons, and long-distance cycling require a higher amount of carbohydrates in their diet. These athletes should aim for 8-10 grams of carbohydrates per kilogram of body weight per day.
- Strength athletes: Strength athletes such an weightlifters and bodybuilders generally require fewer carbohydrates in their diet compared to endurance athletes. They should aim for 5-6 grams of carbohydrates per kilogram of body weight per day.
- Team sport athletes: Athletes who participate in team sports such as soccer and basketball should consume carbohydrates based on their individual energy requirements. These athletes should aim for 6-8 grams of carbohydrates per kilogram of body weight per day.
- Sprint athletes: Sprint athletes such as runners and swimmers require moderate amounts of carbohydrates in their diet. They should aim for 6-8 grams of carbohydrates per kilogram of body weight per day.
It is important to note that these are general guidelines and it is important for athletes to work with a registered dietitian to determine individual carbohydrate needs based on their specific activity level, body composition and goals.
Pre-Exercise Carbohydrate Consumption
When it comes to pre-exercise carbohydrate consumption, it is crucial for athletes to fuel their bodies with the right amount of carbohydrates to maximize their performance. Here are some tips to keep in mind:
- Timing: It is recommended that athletes consume a meal high in carbohydrates 3-4 hours before exercise to allow for proper digestion and absorption. If there isn’t enough time for a full meal, a carbohydrate-rich snack 30 minutes to an hour before exercise can also be beneficial.
- Amount: The amount of carbohydrates an athlete should consume before exercise depends on their weight and the intensity and duration of the activity. A general guideline is to consume 1 gram of carbohydrates per kilogram of body weight. For example, a 150-pound athlete would need approximately 68 grams of carbohydrates before exercise.
- Type: Complex carbohydrates, such as whole grain breads and pastas, brown rice, and sweet potatoes, are recommended as they provide sustained energy. Simple carbohydrates, like candy and soda, should be avoided as they can cause a rapid spike in blood sugar levels, leading to a crash in energy later on.
- Hydration: It’s important for athletes to also stay hydrated before exercise. Consuming a carbohydrate-rich drink can help with both carbohydrate intake and hydration.
By following these guidelines for pre-exercise carbohydrate consumption, athletes can ensure that their bodies are properly fueled for optimal performance.
During Exercise Carbohydrate Consumption
During exercise, the body’s demand for carbohydrates increase as glycogen stores are utilized for energy. It is important to consume carbohydrates during exercise to maintain energy levels and performance.
The following table provides guidelines for carbohydrate consumption during exercise:
| Duration of exercise | Carbohydrate intake per hour |
|---|---|
| Less than 1 hour | Not necessary |
| 1-2.5 hours | 30-60 grams |
| 2.5-3 hours | 60-90 grams |
| Greater than 3 hours | 90 or more grams |
It is important to note that individual carbohydrate needs may vary depending on factors such as body weight, exercise intensity, and environmental conditions. Consuming carbohydrates in liquid form, such as sports drinks or gels, can be more easily digested and absorbed during exercise.
Incorporating carbohydrates into your diet during exercise can help maintain energy levels and improve athletic performance. It is important to experiment with different types and amounts of carbohydrates to determine what works best for your individual needs.
Post-Exercise Carbohydrate Consumption
After a strenuous workout, it’s important to refuel your body with the right nutrients, including carbohydrates, which help replenish your glycogen stores and aid in muscle recovery. Here are some guidelines for post-exercise carbohydrate consumption:
| Timing | Carbohydrate Intake | Food Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Immediately after exercise | 0.5-0.7 grams per pound of body weight | Fruit, sports drinks, smoothies with fruit and yogurt, bagels with peanut butter |
| Within 2 hours after exercise | 1-1.2 grams per pound of body weight | Pasta with tomato sauce, rice and bean bowl, turkey sandwich on whole grain bread, sushi roll with brown rice |
Consuming carbohydrates immediately after exercise is important to start the recovery process and ensure glycogen stores are replenished. Aim for 0.5-0.7 grams of carbohydrates per pound of body weight. This can be easily achieved by eating fruits like bananas, apples or oranges, consuming sports drinks or having a smoothie with fruit and yogurt. Bagels with peanut butter are also a good option.
Within 2 hours after exercise, it’s recommended to consume 1-1.2 grams of carbohydrates per pound of body weight. This can be achieved by having meals that are rich in complex carbohydrates like pasta with tomato sauce, a rice and bean bowl, a turkey sandwich on whole grain bread, or sushi roll with brown rice. These meals are ideal as they provide complex carbohydrates, protein, and other essential nutrients that will help rebuild and repair muscles.
After exercise you should focus on consuming carbohydrates that are easy to digest and help replenish glycogen stores. Additionally, it’s important to consume a balance of other nutrients to help with muscle repair and growth.
Conclusion
After delving into the role of carbohydrates in athletic performance, it is clear that these macronutrients are crucial for athletes of all levels. Carbohydrates not only provide the energy needed for intense workouts and endurance events, but they also play a role in recovery and muscle repair.
Whether you are a recreational athlete or a professional competitor, understanding the different types of carbohydrates and how to incorporate them into your diet is key for optimizing performance. Complex carbohydrates found in foods such as whole grains, fruits, and vegetables should make up the majority of carbohydrate intake. Simple carbohydrates like sugary snacks and drinks should be limited and only consumed during exercise when quick energy is needed.
Fiber is also an important component of a carbohydrate-rich diet for athletes. It can improve digestion and overall health, leading to better athletic performance.
Furthermore, it is important for athletes to consider their individual carbohydrate needs based on their sport, body size, and activity level. Proper carbohydrate intake should be timed around exercise, with consumption both before, during, and after workouts. This can help athletes optimize their performance, improve endurance, and speed up recovery time.
In conclusion, it is clear that carbohydrates are a vital macronutrient for athletes. Understanding the role of carbohydrates in athletic performance and incorporating the right types and amounts of carbohydrates into your diet can lead to measurable improvements in overall performance and health.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the role of carbohydrates in athletic performance?
Carbohydrates are the primary source of energy for the body during exercise, making them crucial for optimal athletic performance.
What are carbohydrates?
Carbohydrates are macronutrients that are found in foods such as grains, fruits, and vegetables.
How does the body use carbohydrates for energy?
The body converts carbohydrates into glucose, which is used as fuel by the muscles during exercise.
Can a low-carbohydrate diet improve athletic performance?
No, a low-carbohydrate diet can actually have a negative impact on athletic performance as the body will have reduced stores of glycogen, leading to fatigue and decreased energy levels.
What are some examples of complex carbohydrates?
Complex carbohydrates are found in foods such as brown rice, whole grain bread, and oatmeal.
What are some examples of simple carbohydrates?
Simple carbohydrates are found in foods such as fruit, honey, and sugar.
Why is fiber important for athletes?
Fiber helps to regulate digestion and can also help to lower cholesterol levels, making it an important component of a healthy diet for athletes.
How can athletes incorporate carbohydrates into their diet?
Athletes can incorporate carbohydrates into their diet by eating a variety of complex and simple carbohydrates, as well as adding fruits, vegetables, and whole grains to their meals.
How much carbohydrate intake is recommended for endurance athletes?
Endurance athletes should aim to consume between 6-10 grams of carbohydrates per kilogram of body weight per day in order to maintain glycogen stores and support athletic performance.
When is the optimal time to consume carbohydrates before, during, and after exercise?
Before exercise, athletes should consume carbohydrates 1-4 hours prior to the workout. During exercise, carbohydrates should be consumed every 15-30 minutes. After exercise, carbohydrates should be consumed within 30 minutes to help replenish glycogen stores.