Have you ever wondered how much protein, carbs, and fats you need to consume daily? Do you find yourself perplexed by the overwhelming amount of information online about macronutrients? Figuring out your daily macronutrient intake can be intimidating, but it’s an essential step in achieving your fitness goals. In this comprehensive guide, we will break down everything you need to know about calculating your daily macronutrient needs, tracking them, and avoiding common mistakes. So, get ready to learn how to fuel your body effectively for optimal health and performance.
Why Macronutrient Intake Matters

Macronutrient intake matters because it plays a critical role in determining our overall health and well-being. Macronutrients refer to the three major nutrients that our bodies need in large amounts to function optimally – carbohydrates, protein, and fat. Each of these macronutrients serves a specific purpose in our bodies and is essential for various bodily functions.
Carbohydrates: Carbs are the primary source of energy for our bodies. They are broken down into glucose, which is used by our cells to produce the energy required for daily activities. Carbs are found in various foods, including fruits, vegetables, grains, and dairy products.
Proteins: Proteins are the building blocks of our bodies. They are crucial for the growth and repair of our muscles, bones, and other tissues. Protein is found in many animal products, such as meat, eggs, and dairy, as well as in plant-based sources like legumes, nuts, and seeds.
Fats: Fats are another essential macronutrient that our bodies need to function correctly. They are necessary for the absorption of certain vitamins, the production of hormones, and the protection of our vital organs. Fats can be found in foods like avocados, nuts, seeds, and oils.
Healthy macronutrient intake is essential for numerous reasons, including:
– Energy levels: Macronutrients provide our bodies with the energy required for daily activities. When we consume insufficient macronutrients, we may feel fatigued, weak, and tired.
– Muscle growth and repair: Protein is essential for the growth, maintenance, and repair of our muscles. Adequate protein intake is particularly important for those who engage in strength training or other forms of exercise regularly.
– Heart and brain health: Healthy fats like omega-3 fatty acids are essential for maintaining a healthy heart and brain function.
– Digestive health: Carbs and fiber work together to promote healthy digestion and prevent conditions like constipation and diverticulitis.
– Weight management: Eating a balanced diet that includes all three macronutrients can help maintain a healthy weight and prevent weight-related issues like obesity and diabetes.
Macronutrient intake is crucial for achieving and maintaining optimal health. While each macronutrient has its role, consuming them in the right balance is key. Too little or too much of any macronutrient can lead to health problems, so it is essential to find the right balance for your body’s needs.
What are Macronutrients?
When it comes to discussing proper nutrition, the term “macronutrients” often comes up. But what exactly are macronutrients? To put it in simple terms, macronutrients are the nutrients that our bodies need in large amounts to function properly. These include carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. Each of these macronutrients plays a unique and important role in keeping our bodies healthy and energized. However, there are many myths and misconceptions about macronutrients, such as the idea that a low-carb diet is the best way to lose weight. Let’s explore the science behind macronutrients to better understand their importance in our diet.
Why are they important?
Macronutrients, which include carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, are important for overall health and body function. Each macronutrient plays a unique role in the body and consuming them in appropriate amounts is essential for maintaining good health. Here are some of the key reasons why macronutrients are important:
| Macronutrient | Role in the Body |
|---|---|
| Carbohydrates | Provide energy for the body, especially for the brain and nervous system |
| Proteins | Build and repair tissues, including muscles, organs, and skin |
| Fats | Help absorb and transport vitamins and minerals, form cell membranes, and provide energy during periods of low carbohydrate intake |
While each macronutrient has a unique function, it’s important to note that all three are necessary for optimal health. Diets that restrict or eliminate any one macronutrient can lead to deficiencies and negative health consequences. For example, low-carbohydrate diets may lead to fatigue and brain fog due to inadequate energy for the brain, while low-fat diets can result in skin and hair issues due to a lack of essential fatty acids.
It’s also important to note that the quality of macronutrients consumed is important. For example, whole food sources of carbohydrates, such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, provide important nutrients along with energy, while refined carbohydrates, such as white bread and sugar, offer little to no nutritional value. Similarly, plant-based sources of protein, such as legumes and tofu, offer additional nutrients such as fiber and antioxidants, while red and processed meats have been linked to negative health outcomes.
By understanding the importance of macronutrients and consuming them in appropriate amounts and from quality sources, individuals can improve their overall health and well-being. To learn more about common macronutrient myths and facts, visit /myths-facts-macronutrients-weight-loss/. For information on the macronutrient content of vegetarian and vegan diets, check out /veggie-macronutrients/ or /plant-based-macronutrients/.
Determining Your Macronutrient Needs
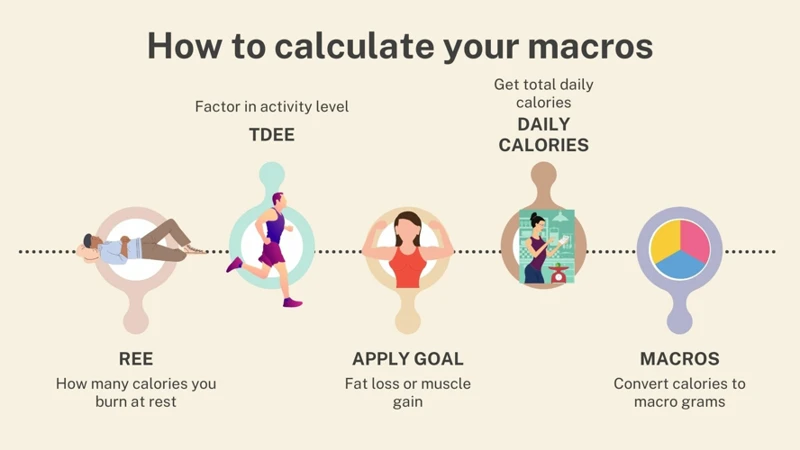
Determining Your Macronutrient Needs
To calculate your daily macronutrient intake, you first need to determine the optimal distribution of carbohydrates, protein, and fat in your diet based on your individual needs and goals.
Factors to Consider
Several factors can influence the optimal macronutrient distribution for each individual. These include age, gender, weight, height, activity level, and overall health status. For example, a young, active male who is looking to build muscle will have different macronutrient needs than an older, sedentary female who is aiming to lose weight. It’s important to take into account your personal goals, lifestyle, and dietary preferences when determining your macronutrient needs.
Calculations
Once you’ve taken these factors into account, you can calculate your daily macronutrient intake using a simple formula. To determine the number of calories you need to consume each day, you can use an online calculator or consult with a registered dietitian. Once you have your daily calorie target, you can calculate your macronutrient needs using the following guidelines:
- Carbohydrates: should make up between 45 and 65 percent of your daily calorie intake
- Protein: should make up between 10 and 35 percent of your daily calorie intake
- Fat: should make up between 20 and 35 percent of your daily calorie intake
To illustrate, let’s say you have determined that you need to consume 2,000 calories per day to achieve your goals. Using the above guidelines, you can calculate your daily macronutrient needs as follows:
- Carbohydrates: 45-65% x 2,000 calories = 900-1,300 calories (225-325 grams)
- Protein: 10-35% x 2,000 calories = 200-700 calories (50-175 grams)
- Fat: 20-35% x 2,000 calories = 400-700 calories (44-77 grams)
It’s important to note that these are general guidelines and individual needs may vary based on unique circumstances. Consulting with a registered dietitian can help you determine the best macronutrient distribution for your individual needs and goals.
Examples
To put these calculations into practice, let’s look at some examples.
- Example 1: A young, active male who weighs 180 pounds, is 6 feet tall, and wants to build muscle might have a daily calorie target of 3,000 calories. Based on his activity level and goals, he might aim for a macronutrient distribution of 50% carbohydrates, 30% protein, and 20% fat. This would translate to approximately 375 grams of carbohydrates, 225 grams of protein, and 67 grams of fat per day.
- Example 2: An older, sedentary female who weighs 150 pounds, is 5’5, and wants to lose weight might have a daily calorie target of 1,500 calories. Based on her activity level and goals, she might aim for a macronutrient distribution of 45% carbohydrates, 30% protein, and 25% fat. This would translate to approximately 168 grams of carbohydrates, 113 grams of protein, and 42 grams of fat per day.
In both of these examples, the macronutrient distribution is tailored to each individual’s needs and goals. By calculating your own macronutrient needs, you can create a customized eating plan that supports your health and fitness goals.
Factors to Consider
When determining your macronutrient needs, there are several factors to take into consideration. It’s important to remember that everyone’s nutritional requirements are different and can vary based on your personal goals, activity level, age, and gender. It’s crucial to assess your individual needs before embarking on any dietary plan. In this section, we’ll explore the key factors to consider when calculating your daily macronutrient intake.
Calculations
Calculations are an important part of determining your daily macronutrient intake. Here are the steps to calculate your macronutrient needs:
- Determine your basal metabolic rate (BMR): Your BMR is the number of calories your body burns at rest to maintain basic functions such as breathing and circulation. There are several formulas to calculate your BMR, such as the Harris-Benedict equation, but the most accurate one is to get a body composition analysis done by a professional.
- Factor in your activity level: The next step is to factor in the calories you burn through physical activity. This is known as your total daily energy expenditure (TDEE). Multiply your BMR by a factor that corresponds to your activity level: sedentary (1.2), lightly active (1.375), moderately active (1.55), very active (1.725), or extra active (1.9).
- Set your calorie target: Once you know your TDEE, you can set a calorie target that aligns with your goals. To lose weight, you need to eat less than your TDEE, while to gain weight, you need to eat more. A safe and sustainable rate of weight loss or gain is 0.5-1% of your body weight per week. This translates to a calorie deficit or surplus of 500-1000 calories per day.
- Determine your macronutrient ratios: Your macronutrient ratio is the proportion of calories you get from each macronutrient. The three main macronutrients are carbohydrates, protein, and fat. The optimal ratios depend on your individual needs, goals, and preferences. A general guideline is to aim for 45-65% of calories from carbohydrates, 10-35% from protein, and 20-35% from fat.
- Calculate your macronutrient targets: To calculate your daily macronutrient intake, you need to convert your calorie target and macronutrient ratios into grams. To do this, multiply your calorie target by the percentage of calories you want to get from each macronutrient, and then divide each result by the calorie value per gram of that macronutrient. Carbohydrates and protein both provide 4 calories per gram, while fat provides 9 calories per gram.
Keep in mind that these calculations are just a starting point and may need to be adjusted based on your progress and feedback from your body. It’s also important to prioritize nutrient-dense whole foods and avoid overly restrictive diets that can lead to nutrient deficiencies and metabolic damage.
Examples
Now that we have discussed the calculations to determine daily macronutrient intake, it’s time to put these calculations into practice with some examples. Remember, these calculations are just a starting point and may need to be adjusted based on individual needs and goals.
Example 1:
Let’s say you are a 30-year-old female, who weighs 150 pounds, is 5’6″ tall, and has a sedentary job. Your BMR would be 1,397 calories. To factor in your activity level, let’s assume you do light exercise 1-3 times per week, making your daily caloric needs around 1,840 calories. Using the calculations discussed earlier, your recommended daily macronutrient intake for weight loss would be:
- Protein: 25% of 1,840 calories = 460 calories = 115 grams
- Fats: 30% of 1,840 calories = 552 calories = 61 grams
- Carbohydrates: 45% of 1,840 calories = 828 calories = 207 grams
Example 2:
Now, let’s consider a 40-year-old male who weighs 180 pounds, is 6’0″ tall, and has an active job. His BMR would be 1,858 calories. Assuming he exercises 4-5 times per week, his daily caloric needs would be about 2,900 calories. Using the calculations mentioned before, his recommended daily macronutrient intake for muscle gain would be:
- Protein: 35% of 2,900 calories = 1,015 calories = 254 grams
- Fats: 25% of 2,900 calories = 725 calories = 81 grams
- Carbohydrates: 40% of 2,900 calories = 1,160 calories = 290 grams
It’s important to remember that these are just rough estimates and may vary based on individual factors, such as metabolism and hormone levels. It’s always best to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian for personalized recommendations.
Calculating and tracking your daily macronutrient intake can be a helpful tool in reaching your health and fitness goals. It can assist in weight loss, muscle gain, and maintaining overall health. Just remember to also focus on eating whole, nutrient-dense foods and listening to your body’s hunger and fullness cues.
Tracking Your Macronutrient Intake
![]()
Keeping track of your macronutrient intake is a crucial part of achieving your health and fitness goals. With a plethora of apps and tools available, tracking your intake has never been easier. In this section, we will discuss the various apps and tools available to track your macronutrient intake and how to use them effectively.
Apps and Tools
There are numerous apps and tools available for tracking your macronutrient intake. Some of the most popular ones include MyFitnessPal, Lose It!, and Cronometer. These apps allow you to input your daily food intake and will calculate your macronutrient intake automatically. Many of these apps also provide useful features such as barcode scanning, recipe builders, and the ability to track your exercise.
How to Use Them
To effectively use these apps, you need to first determine your daily macronutrient needs. Once you have calculated your needs, you can input them into the app, and it will generate a daily macronutrient target for you to hit. You can then input what you eat throughout the day into the app, and it will track your macronutrient intake automatically.
It’s essential to ensure the accuracy of the information you input into these apps. When selecting foods, make sure you are selecting the correct portion size and brand to ensure the most accurate representation. You can also use the barcode scanner to scan the product, which will automatically populate its nutrition information.
When using these apps, it’s crucial to be consistent with your tracking. Ensure that you are tracking every meal or snack you have throughout the day consistently. If you struggle with tracking, setting reminders on your phone can be helpful. Additionally, be mindful of any cheat meals or snacks you have and ensure you log them in the app, as they are also a part of your daily macronutrient intake.
In Conclusion
Tracking your macronutrient intake is an effective way to achieve your health and fitness goals. With the numerous apps and tools available, tracking has never been easier. By determining your daily macronutrient needs, using the appropriate app, and being consistent with your tracking, you can ensure you are on the right track to achieving your goals.
Apps and Tools
When it comes to tracking your daily macronutrient intake, using the right apps and tools can make the process much simpler and more effective. With a plethora of options available, it can be overwhelming to figure out which ones to use. Fortunately, there are several standout apps and tools that can help you seamlessly monitor your meals and snacks. These resources offer features such as barcode scanning, customized tracking, and recipe calculators to ensure you stay on track with your macronutrient goals. Here are some top picks to consider for streamlining your daily nutrition tracking.
How to Use Them
Once you have chosen the macronutrient tracking app or tool that works best for you, it’s important to know how to use it effectively. Here are some steps to ensure accuracy and success in tracking your macronutrient intake:
Step 1: Set up your profile: This includes inputting your personal information such as height, weight, age, and activity level in order to calculate your recommended daily calorie and macronutrient intake.
Step 2: Customize your goals: Depending on your individual goals, you can adjust the macronutrient ratios to fit your specific needs. For example, someone following a low-carb or ketogenic diet may want to increase their fat intake while decreasing their carbohydrate intake.
Step 3: Input your meals and snacks: This is where the app or tool becomes handy. Simply input the foods and beverages you consume throughout the day, including the portion sizes. Most apps have a large database of foods and their nutritional information pre-loaded, making it easy to track your intake accurately.
Step 4: Monitor your progress: Check to see how well you are sticking to your macronutrient goals by reviewing your daily intake summaries and graphs. Some apps even provide personalized recommendations and insights on how to improve your nutrition.
Step 5: Make adjustments: Based on your progress and any changes in your weight or goals, you may need to adjust your macronutrient intake accordingly. Be willing to adapt and make changes as needed to achieve your desired results.
Using a macronutrient tracking app or tool can be an effective way to improve your nutrient intake and reach your fitness goals. By following these steps and staying consistent with tracking, you can make informed decisions about your diet and reach your desired outcome.
| Step 1 | Set up your profile |
| Step 2 | Customize your goals |
| Step 3 | Input your meals and snacks |
| Step 4 | Monitor your progress |
| Step 5 | Make adjustments |
Mistakes to Avoid

Strong attention is needed when it comes to calculating your daily macronutrient intake. However, there are some common mistakes that people usually make, which can negatively affect their progress.
Going Too Low on Calories: One of the biggest mistakes people make is consuming too few calories in an attempt to lose weight. This can put your body into starvation mode and slow down your metabolism. It’s important to consume enough calories to support your body’s functions and daily activities, plus any exercise you may be doing.
Relying Too Much on Fad Diets: Fad diets may promise quick results, but they usually restrict certain food groups or focus on one macronutrient while completely neglecting the others. These diets are often unsustainable and can be harmful to your health in the long run. It’s important to create a sustainable and balanced eating plan that incorporates all three macronutrients and fits your individual needs and preferences.
To avoid these mistakes, it’s essential to understand your body’s needs and create a balanced eating plan that incorporates all three macronutrients. This may require some trial and error and adjustments over time, but it’s worth the effort to promote long-term health and wellness.
Going Too Low on Calories
It’s understandable to think that drastically reducing your calorie intake will lead to quick weight loss. However, this approach can do more harm than good. Cutting too many calories can lead to a number of negative consequences and is a mistake you should avoid. Let’s delve into why going too low on calories is not the solution to achieving a balanced macronutrient intake.
Relying Too Much on Fad Diets
Relying too much on fad diets can be dangerous for your health and may not provide the necessary macronutrients that your body needs to function properly. Fad diets often eliminate entire food groups or severely restrict calorie intake, leading to potential nutrient deficiencies and health issues.
What are fad diets?
Fad diets are temporary, trendy diets that promise quick weight loss or other health benefits but often lack scientific evidence or long-term sustainability. They usually involve strict rules around specific foods or food groups, such as the ketogenic diet that limits carbohydrates or the juice cleanse diet that eliminates solid food and promotes drinking only juice for a period.
Why do people follow fad diets?
People often turn to fad diets because they promise quick results without much effort. They may also be influenced by celebrities or influencers who claim success with a certain fad diet or by social pressures to have a certain body type.
What are the dangers of relying too much on fad diets?
Relying too much on fad diets can lead to nutrient deficiencies and other health issues. For example, the keto diet may lead to low energy levels due to a lack of carbohydrates, and the juice cleanse diet may result in poor digestion and nutrient deficiencies from a lack of fiber and protein.
Additionally, fad diets can be mentally and emotionally taxing as they often involve strict rules and can lead to feelings of guilt or shame when they cannot be followed perfectly.
What is a better approach to achieving a balanced macronutrient intake?
Rather than relying on fad diets, a better approach to achieving a balanced macronutrient intake is to eat a variety of whole foods and plan meals that incorporate all three macronutrients. This will provide your body with the necessary nutrients for optimal health and energy levels while still allowing for flexibility and enjoyment in your food choices. It is important to listen to your body and find a sustainable and enjoyable way of eating that works for you in the long-term.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Promises quick results | May lead to nutrient deficiencies |
| May provide a sense of structure or rules | May be mentally/emotionally taxing |
| Can be influenced by popular culture | Lack of scientific evidence |
Tips for Achieving a Balanced Macronutrient Intake
When it comes to achieving a balanced macronutrient intake, there are various tips one can follow to ensure their diet is nutritious and beneficial for their body. Eating whole foods is one such tip that can be immensely helpful. By whole foods, we mean minimally processed foods that are closer to their natural state. Processing often strips nutrients from foods, making them less beneficial for our health. Opting for fresh fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins such as chicken breast, fish, beans and lentils can be a great way to increase your macronutrient intake while also supplying your body with essential vitamins and minerals.
Another tip is meal planning. Planning your meals ahead of time can help you stay on track with your macronutrient goals. By prepping your meals, you are less likely to make impulsive food choices that may not align with your macronutrient needs. It is also a great way to stay within your calorie range for the day.
In addition to meal planning, it’s also important to listen to your body. Everyone is different, and what may work for one person may not work for another. So, it’s essential to pay attention to how your body responds to different macronutrient ratios and adjust accordingly. For instance, if you’re following a low-carb diet but you’re constantly feeling foggy or lethargic, it may be a sign that your body requires more carbohydrates. Similarly, if you’re following a high-carb diet but you’re struggling to lose weight, you may need to switch to a lower-carb approach.
By following these tips, you can ensure that you achieve a balanced macronutrient intake that supports your overall health and wellness goals. Remember, it’s all about finding what works best for you and making sustainable lifestyle changes that you can maintain in the long run.
Eating Whole Foods
When it comes to achieving a balanced macronutrient intake, one of the most important practices is to focus on consuming whole foods, which are foods that are in their natural, unprocessed state without any added sugars, preservatives or chemicals. By consuming whole foods, you’re able to provide your body with the nutrients it needs to function optimally, without the negative effects that can come from consuming processed foods. But how exactly can you incorporate whole foods into your diet, and why are they so important for achieving a balanced macronutrient intake? Let’s explore these questions in more detail.
Meal Planning
Meal planning is a crucial aspect of achieving a balanced macronutrient intake. By planning out your meals in advance, you can ensure that you’re getting the right amount of protein, carbohydrates, and fats in each meal.
Here are some tips for effective meal planning:
- Start by setting a macronutrient goal for each meal based on your daily target.
- Choose a variety of whole foods that are high in the macronutrients you need. For example, lean protein sources like chicken, turkey, tofu or legumes are great for getting those essential proteins. For carbohydrates, stick to whole grains, fruits and vegetables. Healthy fats found in nuts, seeds and avocados are a great addition to your meals.
- Plan your meals several days or a week in advance to save time and money. Make a shopping list of all the ingredients you need and stick to it when you go to the grocery store.
- Prep your meals in advance, especially for times when you’re busy or on-the-go. This way, you’ll always have a healthy meal ready to grab and eat, which will help you avoid unhealthy fast food options.
- Be mindful of portion sizes and adjust your meals as needed to meet your macronutrient goals.
Remember, meal planning not only helps you achieve your macronutrient goals, but it also helps you save time, money and unnecessary stress around meal times. Start with just a few days of planning to get used to the process and then work up to planning for an entire week. Before you know it, meal planning will become an effortless part of your routine, and you’ll be on your way to achieving a healthy and balanced macronutrient intake.
Listen to Your Body
It’s important to remember that everyone’s body is unique, so listening to your body’s cues is crucial to ensuring a balanced macronutrient intake. Here are a few tips for listening to your body:
- Pay attention to hunger cues: Don’t ignore feelings of hunger, as this could lead to overeating later on. Instead, try to eat smaller meals throughout the day to keep hunger at bay.
- Notice how your body feels after eating: If you feel sluggish or bloated after a meal, take note of what you ate and adjust your intake accordingly.
- Monitor your energy levels throughout the day: If you find yourself feeling tired or lethargic, it may be a sign that you aren’t getting enough of a particular macronutrient. Try adjusting your intake and see if your energy levels improve.
- Don’t restrict yourself too much: While it’s important to stay within your daily macronutrient goals, don’t restrict yourself too much or you may end up feeling deprived. Allow yourself the occasional treat in moderation.
Paying attention to your body and adjusting your macronutrient intake accordingly can help you achieve a balanced and sustainable diet.
Conclusion
In conclusion, calculating and tracking your daily macronutrient intake is crucial for achieving your health and fitness goals. By understanding the role of macronutrients and how they affect your body, you are able to create a diet that supports your needs and promotes optimal health.
It is important to remember that the needs of each individual vary depending on factors such as age, gender, weight, and activity level. Therefore, it is recommended to consult with a registered dietician or healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate macronutrient intake for your personal needs.
Tracking your macronutrient intake can be done through various apps and tools that make the process simple and effective. Utilizing these resources can help keep you accountable and on track towards achieving your goals.
When it comes to achieving a balanced macronutrient intake, it is important to focus on eating whole, nutrient-dense foods and incorporating meal planning as a regular practice. Listening to your body and adjusting your intake as needed is also key to achieving long-term success.
Avoiding common mistakes such as going too low on calories or relying too much on fad diets is crucial for maintaining both physical and mental health. Instead, focus on creating a sustainable lifestyle that supports your overall wellbeing.
In conclusion, calculating and tracking your macronutrient intake may require some effort and dedication, but the benefits to your health and wellbeing are well worth it in the long run. Choose foods that support your needs, listen to your body, and make sustainable changes that promote optimal health and wellness.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do I know if I need to track my macronutrient intake?
If you have specific health or fitness goals and want to ensure you are meeting the right nutritional requirements, tracking your macronutrient intake can be beneficial.
Can I track my macronutrient intake without an app?
While it is possible to track your macronutrient intake manually, using an app can make the process easier and more accurate.
What is the difference between macronutrients and micronutrients?
Macronutrients refer to nutrients that are needed in larger quantities, such as carbohydrates, protein, and fat, while micronutrients are needed in smaller quantities, such as vitamins and minerals.
How important is it to balance my macronutrient intake?
Balancing your macronutrient intake can help you achieve your health and fitness goals and prevent deficiencies or unnecessary weight gain.
Can I adjust my macronutrient intake based on my activity level?
Yes, your macronutrient intake can vary based on your activity level and exercise goals. It is important to adjust your intake accordingly.
Can I consume all of my daily macronutrients in just one meal?
While it is possible to consume all of your daily macronutrients in one meal, it is not recommended as it may not provide your body with sustained energy throughout the day.
How do I determine my daily caloric needs?
Your daily caloric needs depend on various factors such as age, weight, height, gender, and activity level. You can use an online calculator to determine your basic caloric needs.
Do I need to track my micronutrient intake as well?
While tracking your macronutrient intake is important, ensuring you are meeting your daily recommended intake of micronutrients is also crucial for overall health and wellness.
Is it possible to consume too much protein?
Consuming excessive amounts of protein can potentially lead to negative side effects such as kidney damage, digestive issues, and weight gain. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional before drastically increasing your protein intake.
How do I stay motivated to track my macronutrient intake?
Setting achievable goals, finding a supportive community, and focusing on the benefits of tracking your macronutrient intake can help you stay motivated and committed to the process.