The heart is one of the most vital organs in the human body, responsible for pumping blood and delivering essential nutrients and oxygen to all the cells. Heart disease, a condition that affects the heart’s functions, is a growing concern worldwide. It’s a leading cause of death in various countries, and its prevalence continues to rise. Although genetics and age play a role in the development of heart disease, lifestyle factors, such as diet, have a significant influence. A healthy diet can help prevent heart disease and promote overall heart health. But what makes a heart-healthy diet, and what foods should you include in your diet to keep your heart in good shape? This article provides a comprehensive guide on the role of a healthy diet in preventing heart disease, including the best foods and nutrients, lifestyle habits, and meal planning tips.
Understanding Heart Disease and Diet
Heart disease is the leading cause of death worldwide, accounting for approximately 31% of all deaths globally. Despite the prevalence of this disease, there are lifestyle changes that can help prevent it, including dietary modifications. A healthy diet has been shown to reduce the risk of heart disease in both healthy individuals and those with pre-existing conditions. In this section, we will explore the role of diet in heart disease prevention and the best foods and nutrients to include in a heart-healthy diet. Understanding the connection between diet and heart disease is crucial to making informed decisions about what we eat and how we can protect our heart health.
What is Heart Disease?
Heart disease, also known as cardiovascular disease, is a condition that affects the heart and blood vessels. It is a broad term that describes a range of conditions, including coronary artery disease, heart failure, arrhythmias, and heart valve problems. These conditions can lead to serious health complications, such as heart attacks and strokes.
There are several factors that can increase your risk of developing heart disease, including smoking, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, obesity, and a family history of heart disease. While some risk factors cannot be changed, such as family history, others can be managed through lifestyle changes and medical treatment.
It is important to understand the various types of heart disease and their causes, as well as the role of diet in preventing and managing these conditions. A healthy diet can help reduce your risk of heart disease by improving blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and overall heart health.
Research shows that consuming a diet high in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean protein, and healthy fats can help prevent and manage heart disease. Additionally, limiting consumption of processed and fried foods, as well as sugary drinks, can also have a positive impact on heart health.
Role of Diet in Heart Disease
The food we eat plays an important role in determining our heart health. Several studies have shown that a healthy diet can reduce the risk of developing heart disease. On the other hand, an unhealthy diet rich in saturated and trans fats, added sugars, and high in salt can increase the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
A heart-healthy diet should include a variety of nutrient-dense foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. These foods contain nutrients that can help improve cholesterol levels, lower blood pressure, reduce inflammation, and protect against heart disease.
Additionally, a healthy diet can also help in weight management, another important factor in heart disease prevention. Obesity is a risk factor for developing heart disease, so maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular physical activity is crucial for overall heart health.
To understand the role of diet in heart disease better, take a look at the table below:
| Nutrient/ Food Group | Role in Heart Disease Prevention | Food Sources |
|---|---|---|
| Fiber | Reduces cholesterol, regulates blood pressure and blood sugar levels | Whole grains, fruits, vegetables, legumes, nuts and seeds |
| Healthy Fats | Lower LDL cholesterol and reduce inflammation | Fatty fish, olive oil, avocado, nuts and seeds |
| Antioxidants | Protect heart cells from oxidative damage | Berries, dark chocolate, green tea, leafy green vegetables |
| Sodium | Excessive sodium intake can lead to high blood pressure, a major risk factor for heart disease | Avoid processed foods, canned soups, and vegetables, and limit adding salt to meals |
| Sugar | Too much added sugar can contribute to obesity and inflammation, which are risk factors for heart disease | Avoid sugary drinks, processed foods, and sweets |
It is essential to consume a well-balanced diet to reduce the risk of heart disease and promote overall health. A healthy diet also has other benefits for health, including reducing the risk of cancer (read more here), boosting the immune system defense against infections (read more here), promoting brain health and preventing chronic diseases (read more here), and protecting against osteoporosis (read more here).
The Best Foods and Nutrients for Your Heart

When it comes to preventing heart disease, one of the most important steps you can take is to eat a healthy diet. A nutrient-rich diet not only helps to keep your heart healthy, but it can also help to reduce your risk of developing other chronic diseases. In this section, we will explore the best foods and nutrients for promoting heart health. From heart-healthy fats to antioxidant-rich fruits and vegetables, discover the top ways to nourish your body and protect your heart.
Heart-Healthy Foods
Eating a heart-healthy diet is the key to preventing heart diseases. Here are some heart-healthy foods that one should include in their diet:
- Fruits and Vegetables: These are rich in vitamins, minerals, and dietary fiber that can reduce the risk of heart diseases. Some of the heart-healthy options include berries, citrus fruits, leafy greens, broccoli, and carrots.
- Whole Grains: Whole grains are rich in fiber, vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, making them an essential part of a heart-healthy diet. Examples of whole grains include oats, quinoa, brown rice, and whole wheat bread.
- Healthy Fats: Not all fats are bad for the heart; some of them can help improve heart health. Foods rich in healthy fats include nuts, seeds, avocado, olive oil, and fatty fish like salmon and tuna.
- Lean Protein: Eating lean protein sources like skinless chicken, fish, legumes, and nuts can help reduce the risk of heart diseases. These sources of protein are not only low in fat but are also rich in other essential nutrients.
- Low-fat Dairy: Low-fat dairy products like skim milk, low-fat cheese, and yogurt are low in saturated fats and high in essential nutrients like calcium, vitamin D, and protein for a healthy heart.
Including these heart-healthy foods in your diet is an excellent way to prevent heart diseases, but it is also crucial to limit or avoid the intake of foods that can increase the risk of heart diseases.
Foods to Limit or Avoid
While there are many foods that can improve heart health, it’s also important to be mindful of foods that can be harmful. In order to prevent heart disease, it’s recommended to limit or avoid the following types of food:
- Saturated and trans fats: These types of fats can increase cholesterol levels and contribute to plaque buildup in the arteries. Limit your intake of red meat, full-fat dairy products, and fried foods. Also, check food labels for ‘partially hydrogenated oils’, which are a source of trans fats.
- Sodium: Consuming too much sodium can lead to high blood pressure, which increases the risk of heart disease. Limit your intake of processed and packaged foods, which often contain high levels of sodium. Additionally, avoid adding extra salt to your meals and opt for herbs and spices to add flavor instead.
- Sugar: Consuming high amounts of sugar can lead to obesity and other conditions that increase the risk of heart disease. Limit your intake of sugary drinks such as soda, sports drinks and fruit juices, as well as candy and baked goods. Instead, opt for fresh fruits as a natural sweetener.
- Alcohol: Drinking excessive amounts of alcohol can raise blood pressure and contribute to heart disease. It’s recommended that women limit their alcohol intake to one drink per day and men to two drinks per day.
By limiting or avoiding these types of foods, you can improve heart health and reduce the risk of developing heart disease. It’s important to remember that moderation is key, and making small changes to your diet can lead to big improvements in heart health over time.
Key Nutrients for a Healthy Heart
In addition to consuming heart-healthy foods, it is important to ensure that your diet includes a variety of key nutrients that are essential for maintaining the health of your heart. These nutrients can help reduce inflammation, lower cholesterol levels, and improve overall cardiovascular health. Some of the key nutrients that you should focus on including in your diet are:
- Omega-3 fatty acids: Found in fatty fish such as salmon and sardines, as well as in chia seeds and flaxseeds, omega-3 fatty acids have been shown to reduce inflammation and decrease the risk of heart disease.
- Fiber: Soluble fiber, found in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, can help lower cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of heart disease.
- Antioxidants: Found in brightly colored fruits and vegetables such as berries, tomatoes, and leafy greens, antioxidants help protect the heart from damage caused by free radicals.
- Vitamin D: Essential for strong bones, vitamin D may also help keep the heart healthy by reducing inflammation and improving blood vessel function. Good food sources of vitamin D include fatty fish and fortified dairy products.
- Potassium: Found in bananas, sweet potatoes, and leafy greens, potassium helps regulate blood pressure and reduce the risk of stroke.
- Magnesium: Found in nuts, seeds, and leafy greens, magnesium plays a key role in heart health by regulating blood pressure, reducing inflammation, and supporting healthy blood vessel function.
Ensuring that your diet is rich in these key nutrients can help protect your heart from disease and ensure that it functions optimally. However, if you are unable to get enough of these nutrients through your diet alone, you may want to consider taking supplements. It is important to speak with your healthcare provider before starting any new supplement regimen.
Lifestyle Habits for Heart Health
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle is crucial for preventing heart disease. While diet plays a significant role, other lifestyle habits can also impact heart health. Incorporating physical activity, managing stress, and avoiding unhealthy habits can help reduce the risk of heart disease. In this section, we will discuss the lifestyle habits that can promote a healthier heart.
Exercise and Physical Activity
Regular exercise and physical activity are important for maintaining a healthy heart. Not only does exercise help with weight management, but it also helps to lower blood pressure, improve cholesterol levels, and reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Here are some ways to incorporate more exercise and physical activity into your routine:
- Take a brisk walk for at least 30 minutes a day, five days a week
- Try cycling, swimming, or hiking
- Join a fitness class or gym
- Incorporate strength training exercises, like lifting weights or using resistance bands
- Make physical activity a family or social activity by exercising with friends or loved ones
- Use a pedometer or fitness tracker to track your steps and progress
It’s important to consult with a healthcare provider before starting a new exercise regimen, especially if you have a pre-existing health condition. Start slowly and gradually increase your physical activity level over time. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous exercise per week. Remember, every little bit counts, so even small bouts of activity throughout the day can add up to big health benefits.
Stress Management
Stress can have a negative impact on heart health, so it is important to manage stress as part of a heart-healthy lifestyle. Here are some strategies for stress management that can help promote a healthy heart:
- Deep Breathing: Take a few moments to focus on your breath, inhaling deeply and exhaling slowly. This can help reduce stress and lower blood pressure.
- Meditation: Practicing mindfulness meditation can help reduce stress and anxiety levels, as well as improve overall well-being.
- Exercise: Physical activity is not only good for the body, but also for the mind. Regular exercise can help reduce stress and improve mood.
- Social Support: Spending time with friends and family can help reduce stress and promote a sense of well-being.
- Time Management: Learning to manage time effectively can help reduce stress levels and promote a sense of control in one’s life.
- Counseling or Therapy: For some individuals, counseling or therapy can be helpful in managing stress and improving overall mental health.
By incorporating these stress management strategies into your daily routine, you can help promote a healthy heart and a sense of overall well-being.
Other Healthy Habits
In addition to maintaining a healthy diet and engaging in regular exercise, there are several other healthy habits that can help prevent heart disease. These habits include:
| Not Smoking: | Smoking is a major risk factor for heart disease. It damages the lining of the arteries, raises blood pressure, and can lead to the development of blood clots. Quitting smoking can greatly reduce the risk of heart disease. |
| Limiting Alcohol: | Excessive alcohol consumption can increase blood pressure, contribute to the development of abnormal heart rhythms, and lead to weight gain. For men, it is recommended to limit alcohol intake to no more than two drinks per day, and for women, no more than one drink per day. |
| Getting Enough Sleep: | Lack of sleep can lead to high blood pressure, weight gain, and an increased risk of heart disease. Adults should aim to get at least seven to eight hours of sleep per night. |
| Managing Diabetes: | People with diabetes are at a higher risk of developing heart disease. Proper management of blood sugar levels through medication, diet, and exercise can greatly reduce this risk. |
| Reducing Stress: | Chronic stress can contribute to high blood pressure, weight gain, and an increased risk of heart disease. Engaging in stress-reducing activities such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing can help manage stress levels. |
| Maintaining a Healthy Weight: | Carrying excess weight puts a strain on the heart and can lead to high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and diabetes. Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise can greatly reduce the risk of heart disease. |
Incorporating these healthy habits into your lifestyle can help prevent heart disease and promote overall health and well-being. It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional before making any significant changes to your diet or exercise routine, especially if you have existing medical conditions.
Meal Planning for Heart Health
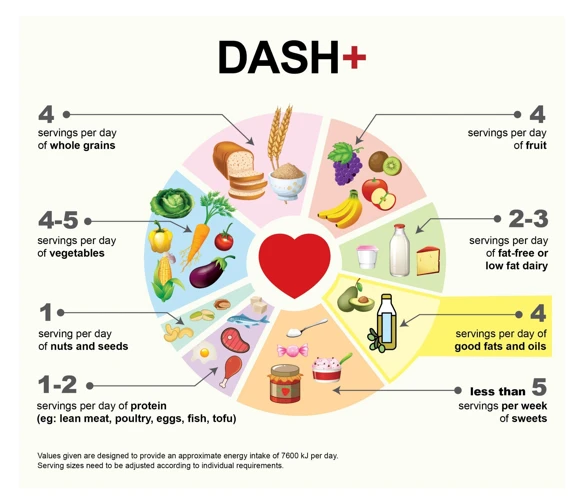
Planning your meals with heart health in mind is an essential step towards preventing heart disease. The foods you eat can significantly impact your overall heart health and can either work towards improving it, or put you at greater risk of heart disease. That’s why it’s crucial to understand which foods are best for your heart and how to incorporate them into your diet. In this section, we will explore some key concepts of meal planning for heart health, including sample meal plans and tips for incorporating heart-healthy foods into your diet. So, let’s dive into the world of heart-healthy eating!
Sample Meal Plan
A heart-healthy meal plan should include a variety of nutritious foods that provide essential nutrients for optimal heart health. Below is a sample meal plan that you can use as a guide:
Breakfast:
- Whole-grain cereal with low-fat milk and mixed berries
- Hard-boiled egg
- Green tea or coffee without added sugar or cream
Lunch:
- Tuna sandwich made with whole-grain bread, canned tuna in water, and light mayonnaise
- Raw veggies such as carrots and celery, paired with hummus
- Nonfat yogurt with a sliced apple for dessert
Snack:
- A small bowl of fresh fruit salad
- A handful of unsalted nuts or seeds
Dinner:
- Roasted chicken breast with rosemary and garlic
- Baked sweet potato with a small amount of butter and a pinch of cinnamon
- Steamed broccoli or green beans
- Slice of whole-grain bread or a small serving of brown rice
Tips:
- Include plenty of fruits and vegetables in your meals and snacks
- Choose lean protein sources such as skinless poultry, fish, and beans
- Opt for whole grains over refined grains, such as whole-grain bread, brown rice, and quinoa
- Avoid or minimize high-fat and high-salt options, such as fried foods, processed meats, and packaged snacks
Remember, this is just a sample meal plan and can be modified to suit your personal tastes and preferences. The key is to include a variety of healthy foods and limit or avoid unhealthy options that can contribute to heart disease.
Tips for Heart-Healthy Eating
Maintaining a heart-healthy diet can seem daunting, but it doesn’t have to be. Here are some tips to help you make better food choices for your heart.
- Eat a variety of fruits and vegetables: Aim for at least five servings of fruits and vegetables per day. Variety is key, so try to eat a range of colors and types to ensure you are getting a full range of nutrients.
- Choose whole grains: Opt for whole grain versions of bread, pasta, rice, and cereals to increase your fiber intake and reduce the amount of refined grains and processed foods in your diet.
- Limit unhealthy fats: Saturated and trans fats should be limited in your diet as they can increase your risk of heart disease. Choose lean proteins like chicken, fish, and beans, and opt for healthy fats like those found in nuts, seeds, and avocados.
- Reduce sodium intake: Too much sodium can raise blood pressure, so try to limit your sodium intake to less than 2,300 milligrams per day. Look for low-sodium options when shopping and avoid processed foods.
- Watch portion sizes: Eating too much of anything, even healthy foods, can lead to weight gain and other health problems. Use measuring cups and food scales to ensure you are eating appropriate portion sizes for your needs.
- Stay hydrated: Drinking enough water can help with digestion, reduce thirst, and support overall health. Aim for six to eight glasses of water per day or more if you are active or in hot weather.
By following these heart-healthy eating tips, you can improve your overall health and reduce your risk of heart disease. Remember that small changes can make a big difference, so start by incorporating one or two of these tips into your daily routine and build from there.
Special Considerations
When it comes to preventing heart disease, a healthy diet is key. However, there are certain populations that may require special considerations when it comes to their diet. This is particularly true for children and seniors, who may have unique nutritional needs. In this section, we will explore how a heart-healthy diet can be tailored to meet the needs of these special populations.
Heart-Healthy Diet for Children
A heart-healthy diet is important for people of all ages, including children. Children who have a healthy diet are more likely to grow up with strong hearts and maintain heart health throughout their lives. Here are some key components of a heart-healthy diet specifically for children:
| Food Group | Examples |
|---|---|
| Whole grains | Brown rice, whole wheat bread, quinoa, oats, barley |
| Fruits and vegetables | Apples, bananas, berries, spinach, broccoli, carrots, sweet potatoes |
| Lean proteins | Chicken breast, fish, tofu, beans, lentils |
| Healthy fats | Nuts, seeds, avocado, olive oil, fatty fish such as salmon |
| Limit or avoid | Sugary drinks, processed snacks, fried foods, high-fat meats, and candy |
Children should also limit their intake of saturated and trans fats, as well as sodium. Encouraging children to participate in meal planning and preparation can also help establish healthy eating habits from a young age. It’s also important for parents to model healthy eating behaviors and make healthy foods readily available at home.
Heart-Healthy Diet for Seniors
As we age, our nutritional needs change as well. The same is true for our heart health. Adopting a heart-healthy diet as a senior can help mitigate the risk of heart disease while providing the appropriate nourishment that seniors need. Here are some tips on how to achieve a heart-healthy diet for seniors:
- Choose lean protein sources: As we age, our bodies require less protein, but we still need to consume protein to maintain and repair tissue. Choosing lean protein sources such as fish, beans, and skinless chicken or turkey can help reduce the risk of heart disease.
- Increase fiber intake: A diet high in fiber can help regulate bowel movements and lower cholesterol, reducing the risk of heart disease. Seniors can increase their fiber intake by consuming whole-grain products, fruits, vegetables, legumes, and nuts.
- Stay hydrated: As we age, our sense of thirst can decline, making us susceptible to dehydration. Staying hydrated is crucial because it helps our bodies circulate blood effectively, reducing the risk of heart disease. Seniors should aim to drink at least eight 8-ounce glasses of water per day.
- Limit salt intake: Excess sodium in the diet can increase blood pressure, increasing the risk of heart disease. Seniors should aim to consume less than 2,300 milligrams of sodium per day.
- Avoid processed and sugary foods: Processed and sugary foods can increase inflammation and cholesterol levels in the body, leading to heart disease. Seniors should avoid foods such as chips, cookies, cakes, and sugary drinks.
- Choose healthy fats: Choosing healthy fats such as olive oil, avocados, nuts, and seeds can help reduce cholesterol levels and lower the risk of heart disease.
- Stay active: In addition to diet, physical activity is also crucial for heart health. Seniors can stay active by engaging in activities such as walking, swimming, and yoga.
It is important to remember that everyone’s nutritional needs are different, and seniors should consult with a healthcare professional before making significant changes to their diet. By incorporating these heart-healthy diet tips, seniors can help protect their heart health while ensuring they are receiving the appropriate nourishment for their bodies.
Conclusion
In conclusion, it cannot be stressed enough how crucial a healthy diet is when it comes to preventing heart disease. By incorporating heart-healthy foods and key nutrients into your diet, limiting or avoiding foods that are detrimental to heart health, practicing regular physical activity, managing stress, and adopting other healthy lifestyle habits, you can significantly reduce your risk of developing heart disease.
It is important to remember that while making dietary and lifestyle changes can seem overwhelming, it is a gradual process that can be achieved through small steps. Start by making small changes to your diet and increasing physical activity gradually. Seek support from a registered dietitian or other healthcare professional to guide you through the process and to ensure that you are meeting your nutritional needs.
In addition, it is important to note that a heart-healthy diet and lifestyle are beneficial for not only preventing heart disease but also for managing and mitigating other chronic conditions such as diabetes, high blood pressure, and obesity.
By making conscious choices regarding your diet and lifestyle habits, you can positively impact your health and reduce your risk of developing heart disease, ultimately leading to a healthier and happier life. So, start taking action today and pave the way to a heart-healthy future.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can a healthy diet prevent heart disease?
Yes, a healthy diet can play a significant role in preventing heart disease.
What kind of diet is best for heart health?
A heart-healthy diet includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean protein, and healthy fats.
What are some heart-healthy foods?
Heart-healthy foods include salmon, nuts, blueberries, leafy greens, and avocado.
Should I limit my consumption of red meat?
Yes, it is recommended to limit your consumption of red meat and opt for lean protein sources instead.
What are some key nutrients for a healthy heart?
Key nutrients for a healthy heart include omega-3 fatty acids, fiber, potassium, and magnesium.
Can exercise and physical activity benefit heart health?
Yes, exercise and physical activity can improve heart health and reduce the risk of heart disease.
What are some lifestyle habits that can improve heart health?
Other lifestyle habits that can improve heart health include stress management, not smoking, and getting enough sleep.
Is it possible to follow a heart-healthy diet as a vegetarian or vegan?
Yes, plant-based diets can sufficiently provide all the necessary nutrients for heart health.
What should I look for when reading food labels?
When reading food labels, look for high amounts of saturated fat, trans fat, and added sugars, and opt for products with low amounts of these ingredients.
Should I consult a healthcare professional before making changes to my diet?
It is recommended to consult a healthcare professional before making significant changes to your diet, especially if you have a history of heart disease or other health conditions.







