In the quest for a healthy lifestyle, we are often bombarded with information on the latest diets and weight loss fads. Amidst all the noise, it can be easy to overlook the basics of nutrition. In reality, the key to a healthy diet lies in understanding the importance of macronutrients. These nutrients, which include carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, form the foundation of our diets and play a fundamental role in maintaining optimal health. In this article, we will explore the significance of macronutrients, their role in the body, the consequences of imbalanced intake, and how to incorporate them into our daily meals to achieve a balanced diet.
What are Macronutrients
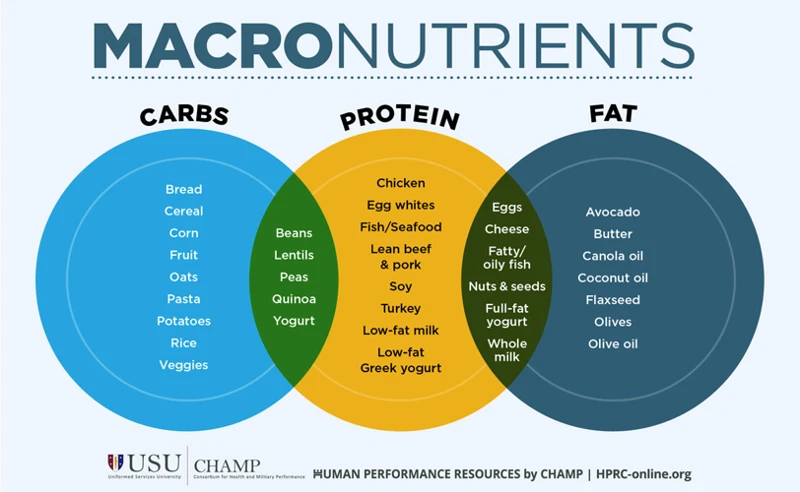
Understanding what macronutrients are is essential to achieving a well-balanced and healthy diet. Macronutrients are the nutrients that the body needs in larger amounts to function properly. These include carbohydrates, proteins and fats. Each macronutrient plays an important role in the body and it’s important to consume them in the right amounts to maintain optimal health. To learn more about the different types of macronutrients and their functions, read on or check out our article on daily macronutrient intake.
Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are one of the three essential macronutrients, along with proteins and fats. Carbohydrates are the body’s primary source of energy and play a crucial role in maintaining overall health and wellness. They are found in a variety of foods, including fruits, vegetables, grains, and dairy products.
Function: The primary function of carbohydrates is to provide energy to the body. They are broken down into glucose and used to fuel the brain, nervous system, and muscles. Additionally, carbohydrates serve as a source of fiber, which helps regulate digestion and promote a feeling of fullness.
Types: There are two types of carbohydrates: simple and complex. Simple carbohydrates, also known as sugars, provide quick energy but can cause blood sugar levels to spike and then crash. Complex carbohydrates, on the other hand, provide sustained energy and are rich in fiber and other essential nutrients. Examples of complex carbohydrates include whole grains, vegetables, and legumes.
Recommended Intake: The recommended intake of carbohydrates varies depending on an individual’s age, sex, weight, height, and activity level. Generally, carbohydrates should make up 45-65% of daily calories, with an emphasis on consuming complex carbohydrates.
Effects of Imbalanced Intake: Consuming too few carbohydrates can lead to low energy levels, irritability, and impaired cognitive function. On the other hand, consuming too many simple carbohydrates can lead to weight gain, insulin resistance, and an increased risk of chronic diseases such as diabetes and heart disease.
Choosing the Right Sources: When selecting carbohydrate sources, it is important to choose those that are high in fiber and other essential nutrients. Examples include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes.
Sample Meal Plan: A sample meal plan that includes carbohydrates could consist of oatmeal with fruit and nuts for breakfast, a quinoa and vegetable salad with grilled chicken for lunch, and a bean and vegetable stew with a side of whole grain bread for dinner.
Carbohydrates play a crucial role in maintaining optimal health and energy levels. Making sure to consume a balance of complex carbohydrates can provide sustained energy throughout the day while also promoting overall wellness.
Proteins
Proteins are an essential macronutrient, made up of amino acids, that play a crucial role in the body’s growth, repair, and maintenance of tissues. Amino acids are the building blocks of protein molecules which are used by the body for a variety of functions.
The benefits of consuming enough protein include:
- Muscle growth and repair: During exercise, protein is required to create and repair muscle tissue. Consuming adequate protein allows for proper muscle recovery and growth (source).
- Healthy bones: Protein is essential for the development and maintenance of bone health. Insufficient protein intake can lead to decreased bone density and an increased risk of fractures.
- Healthy immune system: Protein is important for the production of antibodies, which help fight off infections and illnesses.
- Satiety: Protein is known to be one of the most satiating macronutrients, meaning it leaves you feeling fuller for longer (source).
Good sources of protein include:
- Meat, poultry, and fish
- Dairy products such as milk, cheese, and yogurt
- Eggs
- Nuts and seeds
- Beans and legumes
- Tofu and other soy products
It is important to keep in mind that not all sources of protein are created equal. Some sources, such as red meat, can be higher in saturated fats which can be harmful to cardiovascular health (source). To decrease the risk of heart disease, it’s recommended to choose lean protein sources and consume fatty fish or plant-based sources of omega-3 fatty acids.
While protein is crucial for our health, it’s important to remember that it should be consumed in balance with the other macronutrients like carbohydrates and fats. Consuming too little protein can lead to muscle weakness and loss, while consuming too much protein can lead to weight gain or damage to the kidneys.
Making sure to have a diverse diet rich in all macronutrients can help provide optimal health and energy levels (source).
Fats
Fats serve several important roles in the body. They provide energy, help with the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins (vitamins A, D, E, and K), and help maintain healthy skin and hair. Additionally, certain types of fats, such as omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, are essential for neurological function and reducing inflammation in the body.
However, not all fats are created equal. Saturated fats, found primarily in animal products like meat and dairy, can increase cholesterol levels and increase the risk of heart disease when consumed in excess. On the other hand, unsaturated fats, found in foods like nuts, seeds, and vegetable oils, can help lower cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of heart disease.
It’s important to remember that while fats are a necessary part of a balanced diet, they are also high in calories. Consuming too much fat can lead to weight gain and health problems like heart disease and high cholesterol. It’s recommended that adults aim for 20-35% of daily calories from fats.
To incorporate healthy fats into your diet, try incorporating foods like avocados, nuts, seeds, and fatty fish like salmon or tuna. It’s also important to avoid processed and fried foods that are high in unhealthy fats.
By choosing healthy sources of fats and balancing your intake with other macronutrients like carbohydrates and proteins, you can maintain a healthy and balanced diet.
The Role of Macronutrients in the Body

The human body requires a variety of essential nutrients to function properly, and macronutrients play a crucial role in maintaining a healthy physique. Macronutrients are the nutrients that our bodies need in large amounts to provide energy, build and maintain tissues, and regulate bodily processes. There are three primary macronutrients: carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. Each of these macronutrients plays a unique yet essential role in maintaining our overall health and wellbeing. In this section, we’ll dive into the specific ways that each macronutrient functions in the body, and how they contribute to our overall health. Additionally, we’ll explore the impact of an imbalanced macronutrient intake and how to choose the right macronutrient sources for a healthy diet.
Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are one of the three macronutrients that provide energy to the body. They are found in many foods, including fruits, vegetables, bread, pasta, rice, and sugar. Carbohydrates are an essential fuel for the body and are necessary for proper brain function and physical activity.
There are two types of carbohydrates:
- Simple carbohydrates: These are also known as sugars and are found in foods like table sugar, honey, and fruits.
- Complex carbohydrates: These are also known as starches and are found in foods like bread, pasta, and rice.
Both types of carbohydrates are broken down into glucose in the body, which is then used for energy. Glucose is stored in the muscles and liver as glycogen, which can be used later when the body needs more energy.
Carbohydrates are important for the body for the following reasons:
- Energy: Carbohydrates are the body’s main source of energy. The brain and nervous system rely on glucose to function properly, and the body needs glucose for physical activity and exercise.
- Regulating blood sugar: Complex carbohydrates, like those found in vegetables, whole grains, and legumes, can help regulate blood sugar levels by slowing down the absorption of glucose into the bloodstream.
- Increasing fiber intake: Many high-carbohydrate foods are also high in fiber, which is important for maintaining digestive health and can help lower the risk for certain diseases. Increasing fiber intake can also help with weight management by promoting feelings of fullness.
- Providing essential nutrients: Many carbohydrate-rich foods, especially fruits and vegetables, provide important vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that the body needs to function properly.
- Replacing other macronutrients: Choosing complex carbohydrates over simple sugars can help replace other macronutrients, like fats and proteins, in the diet.
- Fueling exercise: Carbohydrates are an important fuel source for physical activity and endurance exercise. They help delay muscle fatigue and improve performance.
It’s important to note that not all carbohydrates are created equal. Plant-based sources of carbohydrates, like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, are generally healthier choices compared to processed or refined carbohydrates, like cookies and pastries. Choosing complex carbohydrates over simple sugars can also help prevent spikes in blood sugar levels.
It’s recommended that carbohydrates make up 45-65% of daily calorie intake. However, individual needs may vary based on age, gender, activity level, and overall health. It’s important to work with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian to determine the right amount of carbohydrates for an individual’s needs.
Carbohydrates are an important macronutrient that provide the body with energy, regulate blood sugar levels, and provide essential nutrients. Choosing complex carbohydrates from plant-based sources is recommended, and working with a healthcare professional can help determine the right amount of carbohydrates for individual needs.
Proteins
Proteins are essential macronutrients that are composed of amino acids. These amino acids are the building blocks of proteins and are used by the body for various functions such as muscle building, hormone production, and immune system function.
Functions of Proteins:
- Building and repairing muscle tissue
- Producing hormones and enzymes
- Supporting the immune system
- Transporting molecules such as oxygen in the blood
Proteins are made up of 20 different amino acids, nine of which are essential and can only be obtained from the diet. The other 11 can be synthesized by the body.
How Much Protein to Consume:
The amount of protein needed depends on a person’s age, body weight, and activity level. The recommended daily intake for the average sedentary adult is 0.8 grams per kilogram of body weight. However, for athletes or those engaging in regular resistance training, a higher protein intake may be necessary to support muscle growth and repair.
Plant-based Protein Sources:
Plant-based sources of protein include legumes, nuts, seeds, and whole grains. These sources are typically lower in saturated fat and higher in fiber, making them a healthier choice for overall health.
Animal-based Protein Sources:
Animal-based sources of protein include meat, poultry, fish, and dairy products. These sources are high in protein but can also be high in saturated fat, which is linked to an increased risk of heart disease.
Without enough protein, the body cannot function properly and may experience muscle breakdown, weakness, and fatigue. On the other hand, consuming too much protein can put a strain on the kidneys and liver, as they are responsible for metabolizing excess protein.
So, it’s important to find a balance and incorporate a variety of protein sources into your diet. adequate protein intake, along with proper carbohydrate and fat intake, contributes to maintaining a healthy and balanced diet.
Fats
Fats are a type of macronutrient that is essential for many bodily functions. They are a concentrated source of energy, providing 9 calories per gram, and can be divided into two main categories – saturated and unsaturated fats.
| Saturated Fats | Unsaturated Fats |
|---|---|
| Solid at room temperature | Liquid at room temperature |
| Found in animal products such as meat, cheese, and butter | Found in plant-based sources such as avocados, nuts, and olive oil |
| May increase LDL, or “bad” cholesterol | May decrease LDL and increase HDL, or “good” cholesterol |
| May contribute to an increased risk of heart disease | May decrease the risk of heart disease |
While some saturated fats can have negative health effects, unsaturated fats are an important part of a healthy diet. They aid in the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins and provide insulation for the body’s organs. Additionally, they can help reduce inflammation and lower the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease and type 2 diabetes.
It’s important to note that all fats, whether saturated or unsaturated, are high in calories and should be consumed in moderation as part of a balanced diet. Opting for plant-based sources of macronutrients, including fats, can also provide additional health benefits such as increased fiber intake, which can aid in digestion and maintain stable levels of glucose in the blood.
How Much Macronutrients Should You Consume?

To maintain a healthy and balanced diet, it is crucial to consume macronutrients in appropriate quantities. Macronutrients, such as carbohydrates, proteins, and fats provide energy, promote growth and development, and support a host of bodily functions. However, consuming too much or too little of any macronutrient can have adverse effects on the body.
The recommended daily intake of macronutrients depends on several factors, such as age, sex, weight, height, and physical activity level. As per the National Academy of Medicine, adults should consume 45-65% of their total calories from carbohydrates, 10-35% from proteins, and 20-35% from fats.
For example, if you consume a total of 2000 calories per day, you should aim to consume 225-325 grams of carbohydrates, 50-175 grams of protein, and 44-78 grams of fat. These recommendations may vary based on activity levels, such as athletes who require more protein and endurance athletes who may need more carbohydrates for sustained energy during prolonged activities.
It is essential to consume the right balance of macronutrients to maintain stable blood sugar levels, feel satiated throughout the day, and provide the body with the essential nutrients it needs to function optimally. Consuming too many carbohydrates or a high glycemic index diet can lead to fluctuations in blood sugar levels and subsequent energy crashes. In contrast, consuming too little protein can impact muscle and bone health over time. Additionally, consuming too much saturated and trans fats can increase the risk of heart disease and other health problems.
By understanding your daily caloric requirements and the recommended macronutrient ratios, you can make informed decisions about what to eat and how much to consume. A balanced diet including carbohydrates, proteins, and fats from healthy sources can help promote overall health and wellbeing. For instance, consuming plant-based macronutrients can have many health benefits since they are typically nutrient-dense, low in calories, and high in fiber content. So, a diet high in plant-based carbohydrates can be beneficial for weight loss and managing lifestyle diseases.
Thus, striking the right balance of macronutrients can help improve your overall health and wellbeing, and limiting or overconsuming any macronutrient can have detrimental effects on the body. For more information on the types and distribution of carbs in the body, check out our article on carbs in the body. Or if you are interested in plant-based protein sources, see our article on plant-based macronutrients for healthy protein sources.
Effects of Imbalanced Macronutrient Intake
Have you ever heard the phrase, “everything in moderation”? This applies to the three macronutrients: carbohydrates, proteins, and fats as well. When one of them is consumed excessively or too little, it can result in negative effects on your health. These effects can include weight gain or loss, decreased muscle mass, and increased risk for certain diseases. It’s important to understand the consequences of imbalanced macronutrient intake and how to prevent them.
Too Many Carbohydrates
When it comes to consumption of carbohydrates, balance is key. Consuming too many carbohydrates can have negative effects on our health and body composition. Here are some potential consequences of consuming too many carbohydrates:
- Weight gain: Consuming excess carbohydrates contributes to weight gain, as the body stores unused energy in the form of body fat.
- Increased blood sugar: Consuming too many carbohydrates can lead to high blood sugar levels, which can cause a variety of health problems over time.
- Reduced insulin sensitivity: When we consume too many carbohydrates, our body releases large amounts of insulin to help manage the influx of glucose in the bloodstream. Over time, this can reduce insulin sensitivity, making the body less effective at regulating blood sugar levels.
- Elevated triglyceride levels: Too many carbohydrates can also lead to elevated triglyceride levels, which can contribute to the development of heart disease.
It’s important to note that not all carbohydrates are created equal. Simple carbohydrates, such as those found in processed foods and sugary drinks, are more likely to contribute to these negative effects than complex carbohydrates found in whole grains, fruits, and vegetables. Nonetheless, it’s important to be mindful of carbohydrate intake and aim for balance in our diet.
Too Little Protein
Proteins are essential macronutrients that are made up of amino acids which play a key role in building and repairing tissues in the body. When we don’t consume enough protein, it can lead to a number of negative health effects. This can include weakened muscles, slower recovery time after injury or exercise, and decreased immune function.
Insufficient protein intake can cause:
| Health Effects | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Muscle Loss | Protein is necessary for muscle synthesis and repair. Without enough protein, muscles can break down and become weaker. |
| Slower recovery time | Protein is essential for repairing tissues in the body. Without enough protein, it can take longer for the body to recover after exercise or injury. |
| Immune dysfunction | Protein is necessary for the production of antibodies which help fight off infections. Without enough protein, the immune system may not function properly, leading to increased risk of infections and illnesses. |
| Poor growth and development | Protein is essential for growth and development in children. Insufficient protein intake can lead to stunted growth and development. |
| Increased appetite | Protein is important for satiety, meaning it helps us feel full and satisfied after meals. Without enough protein, we may feel hungry more frequently or consume more calories than necessary to feel full. |
It is recommended to consume at least 0.8 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight per day. However, this amount can vary depending on factors such as age, sex, body composition, and activity levels. Individuals who engage in regular exercise or strength training may need to consume more protein to support muscle repair and growth.
Good sources of protein include lean meats, poultry, fish, eggs, dairy products, beans, and legumes. It is important to choose a variety of protein sources to ensure a complete intake of all essential amino acids. Vegetarians and vegans may need to combine different sources of plant-based proteins to achieve the same effect.
Too Much Saturated Fat
Consuming too much saturated fat in the diet can have negative effects on the human body. Saturated fats are typically found in animal products, such as meat and dairy, as well as some plant-based sources like coconut and palm oil. While the body does need some saturated fats for various functions, too much can lead to health problems.
Some potential effects of consuming too much saturated fat include elevated levels of LDL cholesterol, which is often referred to as the “bad” cholesterol. Consuming too much of this type of fat can also increase the risk of heart disease and stroke. Additionally, some studies have suggested a link between a high saturated fat intake and an increased risk of certain types of cancer, such as breast and colon cancer.
To reduce the intake of saturated fats, it is recommended to limit consumption of meat, especially fatty cuts like beef and pork. It is also advisable to choose low-fat dairy products or switch to plant-based milk alternatives like almond, soy, or oat milk. Replacing saturated fats with unsaturated fats, found in foods like nuts, avocados, and olive oil, can also have positive effects on overall health.
It is important to note that not all types of fat are bad for the body. In fact, the body requires some types of fat for proper function. Fats that are high in omega-3 fatty acids, found in foods like salmon and chia seeds, are beneficial for heart health. It is crucial to maintain a balance of different types of fats in the diet to support overall health and wellbeing.
Choosing the Right Macronutrient Sources

When it comes to choosing the right sources of macronutrients, it can be overwhelming with so many options available. However, making the right choices is important to ensure you are getting the right balance of nutrients for your body to function at its best. Below are some tips and guidelines to help you choose the best sources of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats for your optimal health and wellness.
Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are one of the three macronutrients that the body needs in order to function properly. They play a crucial role in providing energy to the body, especially during exercise and other physical activities. Carbohydrates are found in many different foods, including fruits, vegetables, breads, cereals, pasta, rice, and sugar. There are two types of carbohydrates: simple and complex.
Simple carbohydrates are composed of one or two sugar molecules and are quickly broken down by the body, providing a quick source of energy. Examples of foods high in simple carbohydrates are candy, soda, and other sweet treats. While they may provide a quick energy boost, consuming too much simple carbohydrates can lead to a rapid spike in blood sugar levels, followed by a crash. This can leave a person feeling tired and sluggish.
Complex carbohydrates, on the other hand, are composed of many sugar molecules linked together. These molecules take longer to break down, providing a steady source of energy to the body. Complex carbohydrates can be found in foods such as whole grains, vegetables, and beans. They are also high in fiber, which can help regulate digestion and keep a person feeling full for longer periods of time.
The body breaks down carbohydrates into glucose, which is used by cells to produce energy. Excess glucose is stored in the liver and muscles as glycogen, which can be used later when the body needs more energy. However, if there is too much glucose in the blood, the body will convert it into fat and store it in adipose tissue.
Carbohydrates are important for maintaining a balanced diet and providing energy to the body. However, it is important to consume them in moderation and choose complex carbohydrates over simple carbohydrates. A diet high in simple carbohydrates can lead to weight gain, while a diet high in complex carbohydrates can help regulate digestion and maintain a healthy weight.
Proteins
Proteins are an essential macronutrient for the proper functioning of the body. They are the building blocks of muscles, skin, hair, and nails. Protein is made up of amino acids, which are necessary for the synthesis of important molecules like enzymes and hormones. Here are some important roles of protein in the body:
- Growth and repair: Proteins are necessary for the growth and repair of tissues in the body. This is especially important for children and athletes who require more protein for muscle growth and recovery.
- Immune function: Antibodies, which are important for immune function, are made up of proteins. Proteins also play a role in the production of white blood cells, which are important for fighting infections.
- Hormone production: Hormones are proteins that regulate various processes within the body like metabolism, growth and development, and mood.
- Transportation: Proteins are also involved in the transportation of important molecules like oxygen, carbon dioxide, and nutrients.
It is important to consume enough protein in the diet to prevent protein deficiency, which can lead to muscle wasting, fatigue, and weakened immune function. The recommended daily allowance for protein is 0.8 grams per kilogram of body weight. However, athletes and individuals who engage in regular exercise may require up to 1.2-1.7 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight to support muscle growth and recovery.
Good sources of protein include:
- Meat: Beef, chicken, pork, and lamb are all good sources of protein.
- Fish and seafood: Salmon, tuna, shrimp, and other seafood are excellent sources of protein and also provide important omega-3 fatty acids.
- Dairy products: Milk, cheese, and yogurt are good sources of protein, as well as calcium and vitamin D.
- Eggs: Whole eggs are a great source of protein, as well as other important nutrients like choline and vitamin B12.
- Beans and legumes: Black beans, lentils, and chickpeas are all good sources of protein and also provide fiber and other important nutrients.
- Nuts and seeds: Almonds, sunflower seeds, and other nuts and seeds are good sources of protein and also provide healthy fats and important minerals like magnesium and zinc.
Remember to choose lean sources of protein like chicken, fish, and beans to limit intake of saturated fat which can increase the risk of heart disease. By including a variety of protein sources in your diet, you can ensure that you are meeting your daily protein needs while also enjoying a range of delicious foods.
Fats
Fats are an essential macronutrient that provide the body with energy, support cell growth and help protect organs. It is important to note that not all fats are created equal. Some fats, such as trans fats and saturated fats, can be harmful to health while others, such as monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, are beneficial.
Saturated Fats: These types of fats are solid at room temperature and can be found in animal products such as butter, cheese and fatty meats. While small amounts of saturated fats are necessary for body functions, it is important to limit intake as high levels have been linked to increased risk of heart disease and high cholesterol.
Trans Fats: Trans fats are often found in processed foods such as fried foods, baked goods, and snack foods. They are created by adding hydrogen to liquid vegetable oils, which turns them into a solid form. Like saturated fats, high consumption of trans fats can lead to health problems such as heart disease.
Monounsaturated and Polyunsaturated Fats: These healthy fats can be found in foods such as nuts, seeds, avocados, and fish. They have been shown to lower cholesterol levels and decrease the risk of heart disease. Omega-3 fatty acids, a type of polyunsaturated fat, are particularly important for brain function and can be found in fatty fish such as salmon and tuna.
It is important to include a variety of fat sources in a balanced diet, while being mindful of the type and amount consumed. Substituting unhealthy fats for healthy fats can have a positive impact on overall health.
Sample Meal Plan

When it comes to achieving a balanced diet that includes proper macronutrient intake, one of the most effective ways is to plan your meals. This can be especially useful for people who struggle with portion control, emotional eating, or simply lack the time to cook healthy meals throughout the week. Below, we’ll take a look at an example meal plan that covers the main macronutrient categories, so that you can get a clearer idea of how to structure your own meals.
Breakfast: One slice of whole grain toast topped with mashed avocado, one poached egg, and a sprinkle of salt and pepper. Additionally, one small banana and a cup of black coffee.
Snack: One small apple paired with a tablespoon of almond butter.
Lunch: A spinach salad topped with grilled chicken breast, cherry tomatoes, cucumber slices, and a homemade vinaigrette made with olive oil and balsamic vinegar. On the side, quinoa mixed with chickpeas and a sprinkle of feta cheese.
Snack: One serving of plain Greek yogurt mixed with fresh berries and a tablespoon of honey.
Dinner: Grilled salmon fillet served with a side of roasted asparagus and wild rice cooked in chicken broth.
Keep in mind that this meal plan is just one example, and you should adjust the portions according to your needs, goals, and activity level. Alternatively, you can switch up the foods to include your favorite sources of protein, carbohydrates, and fats. The key is to aim for variety, balance, and moderation, and to avoid highly processed or refined foods as much as possible.
Macronutrients and Exercise
As we know, exercise is an important part of a healthy lifestyle, but did you know that macronutrients play a crucial role in fueling our physical activity? It’s not just about how much we eat, but also about what we eat. In this section, we’ll explore the connection between macronutrients and exercise, and how they work together to help us meet our fitness goals. So grab your workout gear and let’s dive in!
Pre-Exercise Carbohydrate Intake
Before engaging in any type of physical activity or exercise routine, it is important to ensure that your body has enough fuel to perform at its best. One of the most important macronutrients for athletic performance is carbohydrates.
Carbohydrates serve as the primary source of energy for your muscles, providing the glucose they need to function properly. When you exercise, your body taps into its glycogen stores, which are essentially stored glucose molecules, to provide energy for your muscles. Consuming carbohydrates before exercising can help ensure that your glycogen stores are topped up and ready to go.
So how much carbohydrates should you consume pre-exercise? The answer to this question depends on the individual and the intensity/duration of the activity they will be engaging in. In general, a moderate to high intensity exercise session (lasting more than 60 minutes) may require anywhere from 30-90 grams of carbohydrates prior to exercise. It is also important to consider the type of carbohydrates being consumed. Complex carbohydrates, such as whole grains and starchy vegetables, are typically more slowly digested and provide a steady source of glucose for your muscles.
Below is a table outlining some examples of pre-exercise carbohydrate intake:
| Activity | Intensity | Amount of Carbohydrates | Example Food Sources |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low-Intensity Exercise | Less than 60 minutes | 15-30 grams | Fruit, yogurt, granola bar |
| Moderate Intensity Exercise | 60-90 minutes | 30-60 grams | Whole grain toast with peanut butter, banana |
| High Intensity Exercise | More than 90 minutes | 60-90 grams | Bowl of oatmeal with banana and honey |
It is important to note that consuming too many carbohydrates pre-exercise can result in discomfort or sluggishness during physical activity. It is always recommended to experiment and see what works best for you and your body. Consulting a registered dietitian can also provide personalized guidance on carbohydrate intake for exercise.
Consuming carbohydrates pre-exercise can help ensure that your muscles have enough glycogen to perform at their best. The amount and type of carbohydrates consumed should be individualized based on the intensity and duration of the physical activity. Experimentation and consulting a registered dietitian can help optimize pre-exercise carbohydrate intake.
Post-Exercise Protein Intake
After an intense workout, the body requires adequate nutrition for repair and recovery. One important macronutrient for post-exercise recovery is protein. Protein helps repair muscle tissue that is damaged during exercise and promotes muscle growth.
How much protein should you consume after exercise?
The amount of protein required after exercise depends on several factors such as body weight, exercise intensity and duration, and overall dietary protein intake. A general guideline is to consume 0.14-0.23 grams of protein per pound of body weight within 30 minutes of completing exercise. This amount of protein can help maximize muscle protein synthesis, which is the process of building new muscle protein.
What are good sources of post-exercise protein?
Some good sources of post-workout protein include:
| Food | Protein Content (per 100 grams) |
|---|---|
| Chicken breast | 31 grams |
| Cottage cheese | 11 grams |
| Greek yogurt | 10 grams |
| Skinless turkey breast | 29 grams |
| Tuna | 30 grams |
When should you consume post-exercise protein?
Consuming protein within 30 minutes of exercise is ideal, but it’s also important to consume protein throughout the day to meet your body’s overall protein needs. Aim to consume protein with each meal and snack to ensure you are meeting your daily protein requirements.
Consuming adequate protein after exercise is important for muscle repair and growth. Aim to consume 0.14-0.23 grams of protein per pound of body weight within 30 minutes of completing exercise and incorporate protein into each meal and snack throughout the day.
The Role of Fats in Endurance Activities
Fats play an important role in the body during endurance activities, such as long-distance running, cycling, or swimming. Endurance exercise requires a steady supply of energy. While carbohydrates are the primary energy source for high-intensity exercise, the body primarily relies on fat for energy during low to moderate-intensity exercise.
Fats are stored in adipose tissue throughout the body and can be broken down into fatty acids and glycerol to be used as an energy source. During endurance activities, the body uses a combination of stored fat and dietary fat to meet energy needs.
Research has shown that a diet high in fats can improve endurance exercise performance by increasing the body’s ability to use fat as fuel. However, it’s important to note that consuming too much fat can lead to digestive issues and may not be suitable for everyone.
Aim to consume a balance of healthy fats, such as those found in nuts, seeds, oily fish, and avocados, to support endurance exercise. Consuming too much saturated and trans fats, found in fried foods, processed snacks, and fatty meats, can increase the risk of heart disease and negatively impact exercise performance.
A balanced diet that includes a variety of healthy fats, carbohydrates, and proteins is essential for supporting endurance exercise performance and overall health.
Conclusion
In conclusion, it’s clear that macronutrients play a crucial role in maintaining a healthy and balanced diet. Carbohydrates provide the body with energy, while proteins help build and repair tissues, and fats are important for insulation and absorption of certain vitamins. However, it’s important to consume these macronutrients in the right balance, as an imbalance can lead to negative effects on the body.
Consuming too many carbohydrates can lead to weight gain and an increased risk of certain diseases, while consuming too little protein can lead to muscle loss and weakness. It’s also important to choose the right sources of macronutrients, as some sources can be high in unhealthy fats and sugars.
Additionally, macronutrient intake can also play a role in physical activity and exercise. Pre-exercise carbohydrate intake can help provide the body with energy, while post-exercise protein intake can aid in muscle recovery and growth.
Overall, a balanced diet that includes the appropriate amounts of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats can lead to improved health and well-being. It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian to develop a personalized nutrition plan that meets your individual needs and goals.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the three main macronutrients?
The three main macronutrients are carbohydrates, proteins, and fats.
What is the role of carbohydrates?
Carbohydrates are a primary source of energy for the body.
What is the role of proteins?
Proteins are essential for building and repairing tissues in the body, as well as for numerous biochemical processes.
What is the role of fats?
Fats are important for energy storage, insulation, and the absorption of certain vitamins.
How much of each macronutrient does the body need?
The amount of each macronutrient the body needs varies based on age, sex, weight, physical activity level, and other factors.
What happens if you consume too many carbohydrates?
Consuming too many carbohydrates can lead to weight gain and an increased risk of chronic diseases such as type 2 diabetes.
What happens if you consume too little protein?
Consuming too little protein can lead to muscle loss, weakened immune function, and other health problems.
What are some good sources of carbohydrates?
Good sources of carbohydrates include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes.
What are some good sources of proteins?
Good sources of protein include lean meats, poultry, fish, eggs, beans, and nuts.
What are some good sources of healthy fats?
Good sources of healthy fats include avocados, nuts and seeds, olive oil, and fatty fish such as salmon.







