Have you ever experienced a sudden drop in energy levels, leaving you feeling exhausted and drowsy? While numerous factors can contribute to this, your diet could possibly be the culprit. What we consume plays a significant role in how we feel and perform throughout the day, and a balanced diet is vital for optimal energy levels. Macronutrients, such as carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, are key players in energy production. In this article, we’ll explore the connection between macronutrients and energy levels, the importance of balancing these nutrients, and how to incorporate them into your daily diet for optimal results.
The Role of Macronutrients in Energy Production
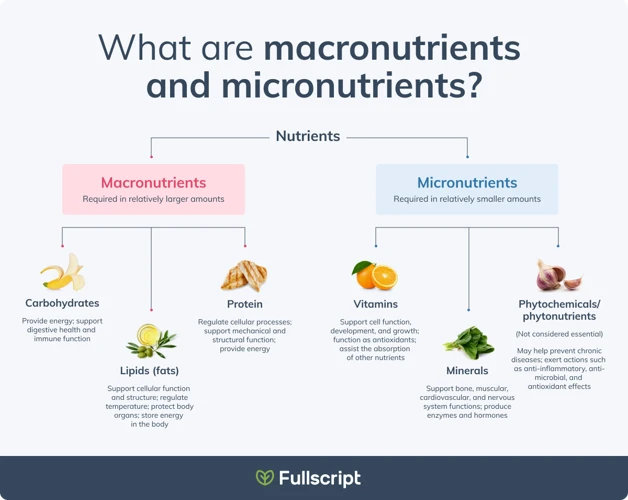
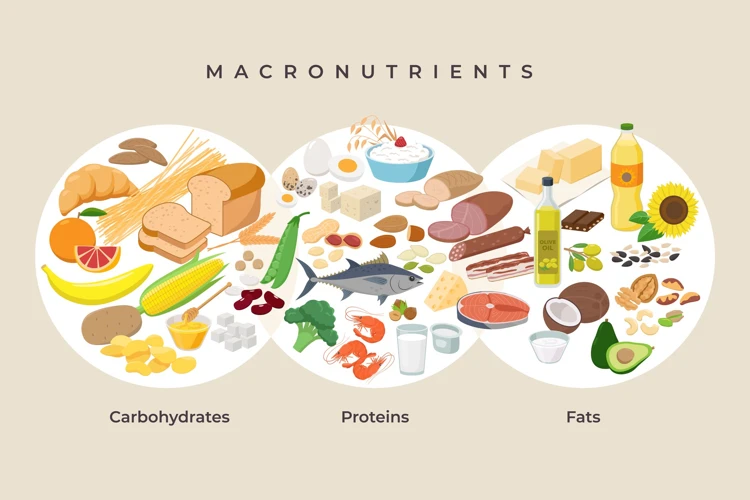
As perplexing as it may seem, one of the most important factors in maintaining high energy levels throughout the day is the types and amounts of macronutrients consumed in your diet. Macronutrients, also known as “macros”, are the main sources of energy for the body, and include carbohydrates, protein, and fats. Understanding how these nutrients affect energy production is crucial for achieving optimal health and wellness. In this section, we will explore the roles of each macronutrient and how they contribute to energy production in the body.
Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are a major source of energy for the body. They provide fuel for our brain and muscles, allowing us to perform daily tasks with ease. [1] Carbohydrates are also necessary for the body to function properly, and they play an important role in digestion, metabolism, and the overall health of the body.
Types of Carbohydrates
There are two types of carbohydrates: simple and complex. Simple carbohydrates are found in fruits and processed foods and are made up of one or two sugar molecules. Complex carbohydrates are found in vegetables, whole grains, and legumes and are made up of many sugar molecules linked together. Complex carbohydrates generally provide more sustainable energy than simple carbohydrates, as they are digested more slowly.
Impact on Energy Levels
Carbohydrates have a direct impact on energy levels. They are broken down into glucose, which is then used as fuel for our cells. When we eat carbohydrates, our blood sugar levels increase, providing an immediate source of energy that can be used by the body. [2] However, if we consume too many simple carbohydrates or refined sugars, our blood sugar levels can spike and then crash. This can lead to a feeling of fatigue and lethargy as the body struggles to regulate its energy levels.
Recommended Intake
Carbohydrate intake varies depending on individual needs and activity levels. The recommended intake for carbohydrates is between 45-65% of total daily caloric intake. [3] It is important to note that not all carbohydrates are created equal, and it is recommended to focus on complex carbohydrates such as whole grains, vegetables, and legumes.
Internal Link: To learn more about daily macronutrient intake, click here.
| Food | Serving Size | Carbohydrate Content |
|---|---|---|
| Brown rice | 1 cup (195g) | 45g |
| Sweet potato | 1 medium (114g) | 22g |
| Black beans | 1/2 cup (86g) | 20g |
| Quinoa | 1 cup (185g) | 39g |
| Blueberries | 1 cup (148g) | 21g |
| Broccoli | 1 cup (91g) | 6g |
It is important to balance carbohydrate intake with other macronutrients such as protein and fat to prevent blood sugar spikes and crashes. Combining complex carbohydrates with protein and healthy fats can lead to sustained energy levels throughout the day.
Internal Link: To learn more about balancing macronutrients in a balanced diet, click here.
Increasing fiber intake through the consumption of complex carbohydrates can also aid in maintaining energy levels. Fiber slows down digestion and provides sustained energy release, preventing blood sugar spikes and crashes. [4]
Internal Link: To learn more about how to increase fiber intake through macronutrients, click here.
It is important to note that carbohydrates are often vilified in popular culture, with many claiming that they lead to weight gain and should be avoided. However, this is a myth. Carbohydrates are an important part of a balanced diet and can contribute to healthy body weight when consumed in moderation and as part of a balanced diet.
Internal Link: To learn more about myths and facts surrounding macronutrients and weight loss, click here.
Protein
Protein is an essential macronutrient needed for a variety of bodily functions such as building and repairing tissue, making enzymes, and producing hormones. It is made up of amino acids, which are the building blocks of protein. There are 20 different amino acids, and the body requires all of them to function properly.
Dietary Sources of Protein
| Protein Sources | Protein Content per 100 grams |
| — | — |
| Chicken Breast | 31 g |
| Tuna | 30 g |
| Turkey Breast | 30 g |
| Lentils (cooked) | 9 g |
| Quinoa (cooked) | 4 g |
| Almonds | 21 g |
| Greek Yogurt | 10 g |
Animal-based protein sources are complete proteins, meaning they contain all of the essential amino acids the body needs. However, it’s important to choose lean sources to avoid excessive saturated fat intake. Plant-based protein sources are often incomplete, so it’s important to combine different sources to get all of the essential amino acids. For example, combining beans and rice, or hummus and pita bread.
The Role of Protein in Energy Production
While carbohydrates are the primary source of energy for the body, protein plays a role in energy production as well. When carbohydrate reserves are low, the body will convert protein into glucose for energy. However, this is not an efficient process and can lead to muscle breakdown if the body does not have enough carbohydrates to use as fuel.
How Much Protein Do You Need?
The amount of protein you need depends on factors such as age, sex, activity level, and overall health. The recommended daily intake is 0.8 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight. Athletes or individuals with high levels of physical activity may need more protein to support muscle growth and repair.
It’s important to have a balance of protein and other macronutrients in your diet for optimal energy levels and overall health. If you’re following a vegetarian or plant-based diet, be sure to include a variety of protein sources to ensure you’re getting all of the essential amino acids. For more information on veggie-based macronutrients or plant-based macronutrients, check out our previous articles on the topic.
Fats
Fats are often demonized as being unhealthy, but the truth is that they have an important role in our body and play a crucial role in energy production. Fats are one of the three macronutrients and are composed of molecules called fatty acids. They are an essential nutrient that our body needs for energy, healthy skin, and proper brain function.
Monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, found in foods such as avocado, nuts, seeds, and fatty fish like salmon, are considered healthy fats, as they can help to lower cholesterol and reduce the risk of heart disease. Saturated fats, which are found in animal products like butter, cheese, and meat, should be consumed in moderation, as they can raise cholesterol levels and contribute to heart disease.
Trans fats, found in processed and fried foods, are the most unhealthy type of fat and should be avoided altogether. They are linked to an increased risk of heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and other chronic health conditions.
While fats are an important source of energy, they are also more calorie-dense than carbohydrates and protein, so it’s important to consume them in moderation. The American Heart Association recommends that adults get 20-35% of their daily calories from fats.
In order to get the most benefit from fats, it’s important to choose healthy sources of fat and incorporate them into a balanced diet alongside other macronutrients like carbohydrates and protein.
For more information about the benefits of a balanced diet that includes all of the essential plant-based macronutrients, read on in this article.
The Importance of Balancing Macronutrients
As we understand the significance of macronutrients, it is essential to ensure we consume them in balanced amounts. The balance of macronutrients depends on several factors such as caloric needs, activity levels, and individual needs. Balancing macronutrients adequately promotes healthy body functioning, and will eventually lead to optimal health. In this section, we will discuss the importance of balancing macronutrients and how to achieve optimal balance in our diets. Understanding this will lead to a healthier lifestyle and prevent the possible risks of unbalanced diets, such as nutrient deficiencies or excess weight gain.
Caloric Needs
To balance macronutrients and improve energy levels, it’s important to consider your caloric needs. Caloric needs vary based on age, gender, weight, height, and activity level. Consuming too few calories can lead to fatigue and a decrease in energy levels, while consuming too many calories can lead to weight gain and also cause fatigue. It’s essential to consider your calorie requirements when balancing your macronutrient intake.
Here’s a table highlighting the recommended daily calorie intake for different genders and activity levels:
| Sedentary Lifestyle | Moderately Active Lifestyle | Active Lifestyle | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Women | 1,800-2,200 calories | 2,000-2,200 calories | 2,400 calories |
| Men | 2,200-2,600 calories | 2,400-2,800 calories | 3,000 calories |
It’s important to note that these values are just an estimate and may vary based on individual needs. For instance, athletes may require more calories to fuel their high-intensity training sessions, while individuals with slower metabolisms may need to consume fewer calories to maintain their weight.
To ensure that you are meeting your calorie and macronutrient needs, it may be helpful to track your food intake using a food diary or nutrition app. This can help you identify areas where you may be lacking in certain macronutrients or consuming too many calories from unhealthy sources.
By taking into consideration your caloric needs and balancing your macronutrient intake, you can maximize your energy levels and overall health. To learn more about plant-based macronutrients, check out our article on plant-based macronutrients.
Activity Levels
One important factor to consider when balancing macronutrients for optimal energy levels is activity levels. The amount and intensity of physical activity you engage in on a daily basis will affect your caloric needs and the type of macronutrients your body uses for fuel. Here are some key points to keep in mind when it comes to activity levels:
- Sedentary – If you have a desk job or engage in very little physical activity throughout the day, your caloric needs will be lower than someone who is more active. This means you may need to consume fewer carbohydrates and fats to maintain a healthy weight and energy level.
- Moderately Active – If you engage in moderate exercise or physical activity for about 30-60 minutes per day, your caloric needs will increase. You’ll also need to consume more carbohydrates to fuel your workouts and replenish glycogen stores in your muscles.
- Highly Active – If you’re an athlete or engage in high-intensity exercise for more than an hour each day, you’ll need even more carbohydrates to keep your body fueled. You may also need to consume more protein to aid in muscle recovery and repair.
It’s important to note that everyone’s activity level and caloric needs will be different. Factors such as age, gender, and body composition can all play a role in determining how much energy you need from macronutrients. Consulting with a registered dietitian or healthcare professional can help you determine your specific needs and create a balanced meal plan that supports your activity level and energy requirements.
Individual Needs
It’s important to consider individual needs when balancing macronutrients for optimal energy levels. Each person has unique dietary requirements based on factors such as age, gender, body composition, and health conditions. Here are some specific factors to take into account:
- Medical Conditions: Individuals with medical conditions such as diabetes or hypertension may require specific nutrient guidelines. For example, those with diabetes may need to limit their intake of carbohydrates to manage blood sugar levels.
- Weight Management: People who are trying to manage their weight may need to adjust their macronutrient ratios accordingly. For instance, those looking to lose weight may need to increase protein intake to promote satiety and preserve muscle mass.
- Vegetarian or Vegan: Individuals who follow vegetarian or vegan diets need to pay special attention to their macronutrient intake to ensure they are getting enough protein and other essential nutrients.
- Food Allergies or Intolerances: People with food allergies or intolerances may need to make adjustments to their macronutrient intake to avoid triggering symptoms.
By taking individual needs into consideration, it’s possible to create a personalized macronutrient plan that supports optimal energy levels and overall health. Consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian to help determine your individual macronutrient needs based on your personal health goals and lifestyle.
Balancing Macronutrients for Optimal Energy Levels
As we discussed earlier, macronutrients play a crucial role in providing us the energy required to perform our daily activities. Balancing the intake of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats is essential for maintaining optimal energy levels throughout the day. But how can we balance these macronutrients in our meals? Let’s delve into some ideas for balancing macronutrients in breakfast, lunch, dinner, and snacks to help you maintain consistent energy levels.
Breakfast
One of the crucial aspects of maintaining optimal energy levels throughout the day is eating a well-balanced breakfast. Here are some tips for balancing macronutrients in your breakfast meals:
| Macronutrient | Food sources | Benefits |
| Carbohydrates | Whole grain bread, oatmeal, fruit | Provides quick energy and regulates blood sugar levels |
| Protein | Eggs, Greek yogurt, nuts/seeds | Helps with muscle repair and growth, keeps you full for longer |
| Fats | Avocado, nut butter, olive oil | Helps with satiety and brain function |
Integrating a balance of carbohydrates, protein, and fats into your breakfast can help keep your blood sugar levels stable and provide essential nutrients for energy production. Including whole grains and fruits can add fiber, which will keep you feeling full for longer periods. Adding a source of protein, like eggs or Greek yogurt, can help with satiety while providing essential amino acids for muscle growth and repair.
It’s essential also not to neglect healthy fats, like those found in nuts, seeds, or avocado. These fats help with cell function in your body and are essential for brain health. Additionally, including healthy fats in your breakfast can help provide satiety and prevent overeating throughout the day.
By incorporating a balance of macronutrients into your breakfast meal, you can start your day with optimal energy levels and set a healthy tone for the rest of your day.
Lunch
When it comes to lunchtime, it can be tempting to opt for convenience foods that are high in refined carbohydrates and sugars, such as fast food or processed snacks. However, these types of food can lead to an energy crash shortly after consumption. To avoid this, it’s important to include a balance of macronutrients in your lunch.
Here are some ideas for a balanced lunch:
- Quinoa salad with grilled chicken or tofu, mixed vegetables, and a vinaigrette dressing
- Whole grain wrap with roasted turkey or hummus, mixed greens, and avocado
- Grilled salmon or tuna burger with a whole grain bun, mixed greens, and a side of sweet potato fries
- Vegetable stir-fry with quinoa or brown rice, tofu or lean meat, and a variety of colorful veggies
- Black bean soup with whole grain crackers and side salad
Incorporating lean protein, whole grains, and plenty of veggies in your lunch can help keep you energized throughout the afternoon. Additionally, it’s important to consider portion sizes and avoid overeating, which can lead to feelings of bloating and lethargy. Additionally, be mindful of added sugars in dressings or condiments, as these can negate the potential energy-boosting benefits of the rest of the meal. By making thoughtful food choices, you can maintain steady energy levels throughout your day.
Dinner
When it comes to dinner, it’s essential to have a balanced combination of macronutrients to ensure optimal energy levels throughout the evening. Here are some ideas for creating a nutritious and energizing dinner:
- Protein: Incorporate a source of lean protein such as chicken, fish, tofu or beans into your dinner. Not only do these sources provide amino acids to support muscle maintenance, but they also help to keep us feeling full and satisfied.
- Carbohydrates: Aim for complex carbohydrates like brown rice, quinoa or sweet potatoes as they provide a slow and steady release of energy. Avoid simple carbohydrates such as white bread or pasta, as they can cause spikes in blood sugar levels and contribute to feelings of fatigue.
- Fats: Healthy fats like avocados, nuts or olive oil are important for maintaining cell health and absorbing important vitamins. However, aim to keep portions in check as fats can be calorie-dense.
Try making a stir fry with brown rice, mixed veggies and grilled chicken, or a quinoa salad with roasted sweet potatoes and black beans. Avoid heavy, fatty or fried foods, as these can cause feelings of lethargy and sluggishness. Remember to also drink plenty of water and avoid alcohol, which can disrupt your sleep and leave you feeling dehydrated in the morning.
Snacks
When it comes to snacks, it’s important to choose options that will provide sustained energy while also balancing macronutrients. Here are some ideas for balanced snack options:
- Apple slices with nut butter: This snack provides carbohydrates and healthy fats from the apple and nut butter respectively. Choosing a natural nut butter without added sugars or oils is ideal.
- Yogurt with berries: Greek yogurt provides protein and a good source of carbohydrates, while berries add additional fiber and antioxidants.
- Carrots and hummus: Carrots are a great source of carbohydrates and fiber, while hummus adds protein and healthy fats.
- Trail mix: A mix of nuts, seeds, and dried fruit provides a good balance of carbohydrates, protein, and healthy fats. Be sure to watch portion sizes, as trail mix can be high in calories.
- Cottage cheese with fruit: Cottage cheese is a good source of protein, while fruit adds carbohydrates and fiber.
By choosing balanced snack options like these, you can help maintain energy levels throughout the day and avoid the crash that comes with consuming high-sugar or heavily processed snacks. Remember to also consider portion sizes and individual caloric needs when selecting snacks.
The Benefits of Eating a Balanced Diet
Eating a well-balanced diet is crucial for overall health and well-being. A diet that includes adequate amounts of carbohydrates, protein, and fats provides the body with the necessary macronutrients to support energy production, cognitive function, and physical performance. However, the benefits of a balanced diet extend beyond these basic functions. Incorporating a variety of whole, nutrient-dense foods into your diet can help reduce fatigue, improve mood, and maintain a healthy body weight. Let’s explore the numerous benefits of consuming a balanced diet in more detail.
Reduced Fatigue
A balanced diet consisting of the right proportions of macronutrients can have a significant impact on reducing fatigue levels. Carbohydrates are the body’s primary source of energy, providing the necessary fuel to get through the day. Protein helps to build and repair muscle tissue, while fats provide long-lasting energy and aid in the absorption of essential vitamins and minerals.
When carbohydrates are consumed, they are broken down into glucose and stored in the muscles and liver as glycogen. When the body requires energy, glycogen is converted back into glucose and used as fuel. Low-carbohydrate diets have been linked to increased fatigue levels, as the body has to work harder to break down fats and protein for energy.
On the other hand, consuming too many simple carbohydrates like sugary drinks and snacks can lead to a sugar crash, leaving you feeling tired and sluggish. A balanced diet consisting of complex carbohydrates such as whole grains, vegetables, and fruits, as well as lean proteins and healthy fats, can help maintain optimal energy levels throughout the day.
It’s important to note that every individual’s caloric needs and activity levels are different, and therefore the ideal macronutrient ratios may vary. Consulting with a registered dietitian can help determine the best balance of macronutrients to meet your individual needs.
A balanced diet that includes the right proportions of macronutrients can help reduce fatigue levels and increase overall energy throughout the day. By incorporating complex carbohydrates, lean proteins, and healthy fats into your meals and snacks, you can ensure that your body has the necessary fuel to power through daily activities.
| Macronutrient | Role | Impact on Energy Levels |
|---|---|---|
| Carbohydrates | Primary source of energy | Consuming complex carbohydrates helps maintain optimal energy levels. Low-carbohydrate diets may lead to increased fatigue levels. |
| Protein | Builds and repairs muscle tissue | Aids in maintaining optimal energy levels. Too much protein in the diet can cause the body to work harder to break it down for energy. |
| Fats | Provides long-lasting energy and aids in nutrient absorption | Consuming healthy fats in moderation helps maintain optimal energy levels. Too much fat in the diet can lead to weight gain and decreased energy levels. |
Improved Mood
A balanced diet that includes the right mix of macronutrients can have a significant impact on an individual’s mood. The foods we eat have the ability to affect our brain chemistry, and this directly affects our emotions, feelings, and behaviors.
Carbohydrates, for instance, have been found to trigger the release of serotonin, a neurotransmitter that helps regulate mood, appetite, and sleep. Protein is also an important macronutrient when it comes to mood regulation, as it contains amino acids that the body uses to make neurotransmitters like dopamine and norepinephrine.
Consuming healthy fats, such as omega-3 fatty acids found in salmon and nuts, have also been linked to improved mood and decreased symptoms of depression. The chart below summarizes the impact of each macronutrient on mood:
| Macronutrient | Impact on Mood |
|---|---|
| Carbohydrates | Trigger release of serotonin, improving mood regulation |
| Protein | Contains amino acids that the body uses to make neurotransmitters, improving mood regulation |
| Fats | Healthy fats, such as omega-3 fatty acids, have been linked to improved mood and decreased symptoms of depression |
It’s also worth noting that skipping meals or not getting enough nutrients can lead to fluctuating blood sugar levels, which can contribute to mood swings, fatigue, and irritability. It’s important to eat a balanced and varied diet to ensure optimal physical and mental health.
Healthy Body Weight
Maintaining a healthy body weight is essential for overall well-being, and balancing macronutrients plays a vital role in achieving this. When we consume excess calories, the body stores the excess energy as fat, leading to weight gain. On the other hand, when we consume fewer calories than we require, the body burns stored fat for energy, leading to weight loss. However, it’s important to achieve this caloric deficit in a healthy and sustainable way.
A balanced diet with the right mix of macronutrients can help us lose or maintain weight in a healthy way. A diet that is too high in carbohydrates can lead to rapid spikes and drops in blood sugar levels, causing us to feel hungry soon after a meal. This can lead to overeating and weight gain over time. On the other hand, a diet that is too low in carbohydrates can cause fatigue and reduced energy levels, making it difficult to maintain an active lifestyle.
Including a moderate amount of carbohydrates, along with adequate amounts of proteins and fats in our diet can help us maintain a healthy weight. Proteins and fats are essential for building and repairing tissues, producing hormones, and maintaining healthy skin and hair. When we consume a balanced mix of macronutrients, we feel fuller for longer periods, reducing our overall calorie intake while still providing us with the energy we need for daily activities.
To achieve a healthy body weight, it’s important to keep track of our caloric intake and ensure that we’re not consuming more calories than we require. By balancing our macronutrients according to our individual needs and activity levels, we can achieve a healthy weight and maintain it in the long term. A healthy body weight not only reduces the risk of chronic diseases but also improves overall energy levels and quality of life.
Some tips for ensuring a balanced diet for a healthy body weight are:
- Include a variety of colorful fruits and vegetables in your meals.
- Choose high-quality protein sources such as lean meats, fish, eggs, and legumes.
- Include healthy fats such as nuts, seeds, and avocados in your diet.
- Avoid processed and packaged foods as much as possible.
- Keep track of your caloric intake and adjust it according to your activity level and weight goals.
By following these tips and balancing our macronutrients, we can achieve and maintain a healthy body weight, leading to overall better health and energy levels.
Conclusion
In conclusion, it is clear that the macronutrients we consume play a vital role in our energy levels. They are the building blocks that our body needs to produce energy, and they must be balanced in order to ensure optimal function.
Carbohydrates are the primary source of energy for the body and should be consumed in moderation to keep energy levels stable. Too many carbohydrates can cause a spike in blood sugar levels, leading to a crash.
Protein is important for muscle growth and repair, and it also helps to keep us feeling full for longer periods of time.
Fats are necessary for cell growth and development, and they help to regulate our hormones. However, consuming too much fat can lead to weight gain and decreased energy levels.
The key to maintaining a healthy balance of macronutrients is to consider our caloric needs, activity levels, and individual needs. We should aim to consume a balanced mix of carbohydrates, protein, and fats at every meal, including breakfast, lunch, dinner, and snacks.
By eating a balanced diet, we can experience a range of benefits, such as reduced fatigue, improved mood, and a healthy body weight. It is important to remember that everyone’s nutritional needs are different, and consulting a healthcare professional can provide valuable guidance.
Overall, understanding the connection between macronutrients and energy levels is crucial for maintaining a healthy and active lifestyle. By incorporating a balanced diet into our daily routine, we can fuel our bodies with the nutrients they need to function at their best.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the different types of carbohydrates?
There are three types of carbohydrates: simple, complex, and fiber. Simple carbohydrates are found in foods like fruits and candy, while complex carbohydrates are found in foods like whole grains and vegetables. Fiber is a type of carbohydrate that is not digested by the body.
Do protein intakes differ depending on the level of physical activity?
Yes, protein needs do vary depending on activity level. Those who engage in regular physical activity may require higher protein intake than sedentary individuals.
Can fats be considered good for us?
Yes, healthy fats (such as monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats) are important for our bodies to function properly. They provide energy and help absorb certain vitamins.
How much of each macronutrient is recommended for daily intake?
This varies depending on age, sex, weight, and activity level. However, generally speaking, a balanced diet should consist of about 45-65% carbohydrates, 10-35% protein, and 20-35% fat.
Are high-protein diets a good way to lose weight?
While high-protein diets may lead to short-term weight loss, they can lead to long-term adverse effects on health. It’s important to maintain a balanced diet that includes carbohydrates and fats for overall health.
Can certain macronutrients affect mood and mental health?
Yes, research shows that consuming a balanced diet that includes whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats can improve mood and reduce symptoms of anxiety and depression.
Why is it important to consider individual needs when balancing macronutrients?
Everybody is different and has unique nutritional needs depending on factors like age, gender, weight, activity level, and health conditions. Balancing macronutrients according to individual needs can optimize energy levels and overall health.
What are the best sources of carbohydrates?
The best sources of carbohydrates are whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and legumes. These foods provide complex carbohydrates, fiber, and essential vitamins and minerals.
Can consuming too much of one macronutrient cause health problems?
Consuming too much of any macronutrient can cause adverse health effects. For example, excessive consumption of saturated fats can increase the risk of heart disease.
Is it necessary to track macronutrient intake for optimal energy levels?
No, it’s not necessary to track macronutrient intake to optimize energy levels. However, being mindful of macronutrient balance and choosing a variety of nutrient-dense foods can help maintain consistent energy levels throughout the day.