The human brain is a complex and incredible organ that controls all of our daily functions, from the most basic to the most complex. It is responsible for our ability to think, learn, feel, and interact with the world around us. However, in order for the brain to function at its best, it requires a variety of essential nutrients, known as micronutrients. These micronutrients play a vital role in maintaining brain health and function, and deficiencies can lead to a range of cognitive and mental health problems. In this article, we will explore the critical role of micronutrients in brain function and mental health and highlight the most important vitamins, minerals, and amino acids that support brain health.
The Importance of Brain Health
The brain is the control center for every aspect of our body’s function, and therefore its health and proper functioning are crucial for our overall well-being. The importance of brain health cannot be overstated, as it impacts everything from our ability to think and remember to our moods and behaviors. The human brain contains billions of cells that communicate with each other using electrical and chemical signals. These signals depend on the presence of various micronutrients such as vitamins, minerals, and amino acids.
Micronutrients play a vital role in the maintenance of brain health and function. They are the essential nutrients required by our bodies in small quantities to perform various physiological functions. These micronutrients are not produced by the body but can be obtained through a balanced diet, and supplement intake if necessary. Not consuming enough of them, even for a short period, or persistent deficiencies, can lead to adverse effects on the brain’s health and functionality.
According to importance-micronutrients-balanced-diet, a balanced diet consisting of all essential micronutrients is essential for maintaining good mental health. Some micronutrients have been linked with a lower risk of cognitive decline in adults, such as vitamins B6, B12, and folic acid. These micronutrients are essential in keeping the brain functioning properly and protecting it from damage.
Deficiencies in micronutrients such as iron, magnesium, zinc, and selenium can cause cognitive impairment, affecting concentration, attention span, and memory in the short term. Long-term effects can lead to more severe conditions such as depression, anxiety, and even Alzheimer’s disease. As mentioned in micronutrient-deficiencies-effects, the deficiency of micronutrients in individuals can have serious impacts on brain health, and it is necessary to ensure that we are consuming adequate amounts through our daily diet or supplements.
Micronutrients play a crucial role in maintaining brain health and functionality by regulating the electrical and chemical signals of brain cells. Deficiencies in micronutrients have been linked to cognitive impairment in the short and long term. It is therefore essential to maintain a balanced diet and supplement our intake where necessary to ensure we are consuming adequate amounts of micronutrients.
What are Micronutrients?
Micronutrients are a type of nutrient that is required by the body in small amounts, yet are essential for maintaining good health and optimal overall functioning. Unlike macronutrients such as carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, which provide energy, micronutrients do not provide energy, but rather aid in various functions in the body including growth, development, and repair of tissues. These vitamins, minerals, and amino acids are crucial for the proper functioning of the body and should be consumed every day for optimal health.
Micronutrients can be broken down into three categories: vitamins, minerals, and amino acids. Vitamins are organic compounds that the body needs but can’t produce itself. These essential micronutrients must be consumed through the diet or through supplements. The vitamin B complex, Vitamin D, and Vitamin E are some of the most important vitamins to maintain brain health and mental health.
Minerals are inorganic substances that perform multiple roles in the body. They help to build strong bones, transmit nerve impulses, maintain normal heart rhythm, and more. Some of the most important minerals for brain health include iron, magnesium, zinc, and selenium.
Amino acids are organic compounds that combine to form proteins. They are essential for building and repairing tissues in the body, including the brain, as well as for the production of hormones and neurotransmitters. Tryptophan, tyrosine, and glutamine are some of the most vital amino acids for brain and mental health, as they play a major role in the synthesis of neurotransmitters including serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine.
Micronutrients are essential for maintaining good health and brain function. They are required in small amounts, but play a significant role in maintaining overall well-being. Although a balanced diet can provide all of the necessary vitamins, minerals, and amino acids, many people may need to take supplements to meet their daily requirements. These micronutrients can have incredible benefits for the immune system, skin, hair, and nails; and can even play a role in preventing chronic diseases.
Vitamins for Brain Health
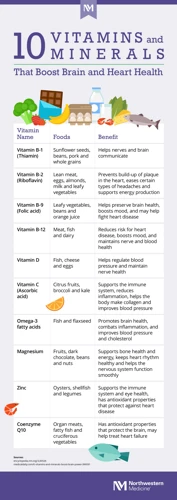
Vitamins are essential micronutrients for brain health. They play a crucial role in maintaining brain function and mental health.
Vitamin B Complex: This group of vitamins plays a vital role in brain health. They help in the production of neurotransmitters that regulate mood and cognitive function. Vitamin B6, in particular, is essential for the synthesis of serotonin, which regulates mood and sleep. Deficiency in vitamin B12 can lead to memory loss and cognitive decline, especially in older adults.
Vitamin D: Vitamin D is known as the sunshine vitamin because our bodies produce it when our skin is exposed to sunlight. It is essential for brain health as it helps in the synthesis of neurotransmitters that regulate mood and cognitive function. Deficiency in vitamin D has been linked to depression, anxiety, and cognitive decline.
Vitamin E: Vitamin E is a potent antioxidant that protects brain cells from damage caused by free radicals. It also plays a crucial role in cognitive function, memory, and mood. Studies have shown that low levels of vitamin E are associated with an increased risk of dementia and cognitive decline.
In addition to vitamins, minerals also play a vital role in brain health.
Iron: Iron is essential for the production of hemoglobin, a protein in red blood cells that helps in the transport of oxygen to the brain. Low levels of iron can lead to brain fog, fatigue, and poor cognitive function.
Magnesium: Magnesium is an essential mineral that helps regulate neurotransmitters and improve cognitive function. It is also involved in the production of energy and helps reduce stress and anxiety.
Zinc: Zinc is a micronutrient that is involved in the regulation of neurotransmitters that affect mood and cognitive function. Deficiency in zinc has been linked to depression and anxiety.
Selenium: Selenium is a trace mineral that is essential for brain health. It is a potent antioxidant that protects the brain from damage caused by free radicals. Studies have also shown that selenium can improve mood and cognitive function.
A diet rich in vitamins, minerals, and amino acids is essential for maintaining brain function and mental health. It is essential to consume a variety of nutrient-dense foods to ensure adequate intake of these micronutrients. Taking supplements should be done with caution, and it is recommended to consult a healthcare professional before starting any supplement regimen. Adequate intake of micronutrients plays a significant role in maintaining overall health and preventing chronic diseases. For more information on the role of micronutrients in health, check out our article on top 10 micronutrients in the diet.
Vitamin B Complex
Vitamin B complex is a group of essential micronutrients that play a vital role in maintaining brain health and mental wellbeing. This group of vitamins includes eight different B vitamins, all of which are water-soluble and cannot be stored in the body to a significant extent, so they have to be obtained from diet or supplements.
These vitamins are known for their role in supporting energy metabolism, but they are also critical for the functioning of the nervous system. Vitamin B1 (thiamin), for example, is necessary for the synthesis of neurotransmitters like acetylcholine, which is essential for learning and memory. Vitamin B6 (pyridoxine) is involved in the process of making serotonin and norepinephrine, two neurotransmitters that play a role in regulating mood, while vitamin B9 (folate) contributes to the synthesis of neurotransmitters and the maintenance of myelin sheath, a protective layer that surrounds nerve fibers.
Deficiencies in B vitamins have been associated with neurological and psychological symptoms, such as fatigue, anxiety, depression, irritability, cognitive impairment, and even dementia. It is essential to consume enough of these vitamins on a daily basis to support brain function and prevent deficiency-related health issues.
Natural sources of B vitamins include whole grains, meat, fish, legumes, nuts, seeds, and dark leafy greens. However, some individuals, including vegans and vegetarians, may be at risk of not getting adequate amounts of these nutrients from their diet. In these cases, supplements may be necessary to meet the body’s needs.
To sum up, Vitamin B complex is not only vital for energy metabolism but also for brain health and mental wellbeing. Adequate consumption of this group of essential micronutrients has been linked to improved cognitive function, mood regulation, and a lower risk of neurological and psychological disorders. To learn more helpful information about micronutrient benefits and their importance, you can visit this article.
Vitamin D
Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin that plays a vital role in brain function and mental health. It acts as a hormone and helps in the absorption of calcium, which in turn improves bone health. In addition to this, research suggests that Vitamin D may also play a crucial role in brain development, neurotransmission, and neuroplasticity.
Deficiency of Vitamin D has been associated with depression, anxiety and other mental health problems. A study published in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism found that individuals with low levels of Vitamin D were at a higher risk of developing depression.
The best source of Vitamin D is sunlight. Our body can produce Vitamin D when it is exposed to sunlight. Foods such as fatty fish, egg yolks, mushrooms, and fortified foods such as milk and cereals are also good sources of Vitamin D. However, it can be difficult to get the recommended daily intake of Vitamin D through diet alone.
Supplementation may be necessary for individuals who are deficient in Vitamin D. The recommended daily intake of Vitamin D varies for different age groups and health conditions. It is important to consult a healthcare professional before taking any supplements to ensure the right dosage and to avoid any potential drug interactions or side effects.
Adequate intake of Vitamin D is crucial for brain function and mental health. It is important to incorporate dietary sources of Vitamin D and get enough sunlight exposure to maintain optimal levels of this important micronutrient. Supplementation should only be considered if advised by a healthcare professional.
Vitamin E
Vitamin E is a powerful antioxidant that plays a critical role in maintaining good brain health. It is a fat-soluble nutrient that protects cell membranes from oxidative damage caused by free radicals, which are unstable molecules that can damage brain cells if left unchecked.
Research has shown that Vitamin E has a neuroprotective effect and may help prevent cognitive decline and improve overall brain function. Additionally, it has been suggested that Vitamin E may help reduce the risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease, a type of dementia that affects memory, thinking, and behavior.
Sources of Vitamin E include nuts, seeds, vegetable oils, and leafy green vegetables. The recommended daily intake for adults is about 15 milligrams per day.
It is essential to consume sufficient levels of Vitamin E in the diet as a deficiency can lead to nerve damage and other neurological conditions. However, excessive amounts of Vitamin E intake can be harmful and may cause bleeding, high blood pressure, or even stroke.
Vitamin E is a vital micronutrient that plays a crucial role in maintaining good brain health. It has potent antioxidant properties that protect the brain from oxidative damage, and studies have suggested that it may help reduce the risk of cognitive decline and Alzheimer’s disease. It is important to include Vitamin E sources in the diet in adequate amounts (micronutrients), and consult with a healthcare professional if considering taking supplements.
Minerals for Brain Health
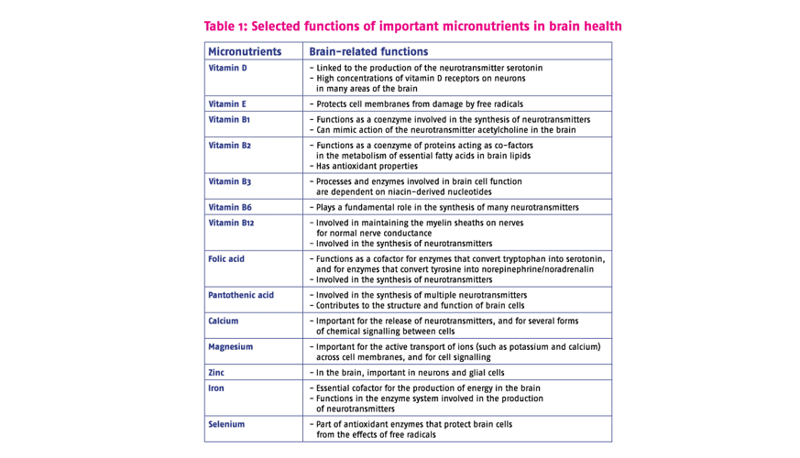
Minerals play an important role in maintaining brain function and mental health. They act as cofactors for enzymes that regulate various metabolic processes in the brain. Some of the essential minerals for brain function include iron, magnesium, zinc, and selenium.
Mineral intake is a crucial part of a healthy diet for maintaining brain function and mental health. It is important to consume a variety of nutrient-dense foods rich in minerals to ensure optimal cognitive performance. Understanding the interplay between various micronutrients is key to maintaining a healthy brain and promoting mental well-being. To learn more about micronutrients and their importance, check out the article on Understanding Vitamins, Minerals, and Micronutrients Explained.
Iron
Iron is an essential micronutrient that plays a vital role in brain function and mental health. This mineral is required for the production of hemoglobin in red blood cells, which is responsible for carrying oxygen to the brain and other parts of the body. Iron deficiency can lead to anemia, which is associated with fatigue, weakness, and decreased cognitive function.
Studies have shown that iron deficiency can also have negative effects on mood and mental health. Iron is required for the synthesis of several neurotransmitters, including serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine. Low iron levels have been linked to depression, anxiety, and other mood disorders.
It is important to note that excessive iron intake can also be harmful to the brain and overall health. Too much iron can lead to oxidative stress, which can cause damage to brain cells and increase the risk of chronic diseases.
It is crucial to maintain a balance of iron intake for optimal brain function and mental health. Foods rich in iron include red meat, poultry, fish, beans, lentils, tofu, and fortified cereals. It is also important to consume foods rich in vitamin C to enhance iron absorption.
Iron is a micronutrient that plays a significant role in brain function and mental health. Its deficiency can lead to anemia, fatigue, weakened cognitive abilities, and mental health issues. However, excessive intake can also have negative consequences. Clients are recommended to maintain a balance of iron intake through a healthy and balanced diet. If you want to learn more about micronutrients and their impact on other aspects of health, check out our articles on micronutrients and immunity health and micronutrient intake and chronic diseases.
Magnesium
Magnesium is another micronutrient that plays a crucial role in maintaining brain health. It helps in regulating the function of various neurotransmitters, including dopamine and serotonin, which are essential for regulating mood, sleep, and emotional well-being.
According to research, magnesium deficiency has been linked to various mental health disorders such as depression, anxiety, and ADHD. Supplementation of this micronutrient has been shown to alleviate symptoms in some patients suffering from these conditions.
Magnesium has also been found to reduce inflammation in the brain and improve cognitive function. It acts as a natural calcium blocker, preventing excess calcium from entering the brain cells, which can be toxic and cause cell damage. Magnesium also helps in maintaining proper blood flow to the brain, which is essential for optimal brain function.
However, it’s important to note that supplementation should be done under the guidance of a healthcare professional, as high doses of magnesium can lead to adverse effects. It’s usually recommended to consume magnesium from dietary sources, such as green leafy vegetables, nuts, seeds, and whole grains.
In addition to its benefits for brain health, magnesium is also important for maintaining healthy skin, hair, and nails. It is involved in the synthesis of collagen and keratin, which are essential for maintaining the health and elasticity of the skin and hair. Magnesium also plays a role in the growth and maintenance of healthy nails.
Magnesium is an important micronutrient for maintaining brain health and overall well-being. It is important to ensure adequate intake of this mineral through a balanced diet or supplement under the guidance of a healthcare professional. Additionally, it can also benefit the health of the skin, hair, and nails.
Zinc
Zinc is a mineral that plays a crucial role in brain function and mental health. It is involved in the production and regulation of various neurotransmitters, including serotonin and dopamine, which are crucial for regulating mood, behavior, and cognition. Zinc deficiency has been linked to a range of mental health disorders, including depression, anxiety, and ADHD.
Research has shown that zinc supplementation may be useful in the treatment of depression and other mental health disorders. A study published in the Journal of Affective Disorders found that zinc supplementation was effective in reducing depressive symptoms in patients with major depression. Another study published in the Journal of Psychopharmacology found that zinc supplementation improved cognitive function in patients with ADHD.
In addition to its role in brain function, zinc is also essential for maintaining healthy skin, hair, and nails. It is involved in the production of collagen, a protein that gives skin its elasticity and helps prevent the formation of wrinkles. Zinc is also important for maintaining healthy hair and nails, as it is involved in the production of keratin, a protein that makes up the structure of hair and nails.
While zinc deficiency is relatively uncommon in developed countries, it can occur in people who follow a vegetarian or vegan diet, as plant-based foods are not as rich in zinc as animal-based foods. Good dietary sources of zinc include oysters, beef, chicken, nuts, and legumes.
Zinc is an important micronutrient that plays a vital role in brain function and mental health, as well as the health of our skin, hair, and nails. If you have concerns about your zinc intake, it may be helpful to speak with a healthcare provider or registered dietitian, who can help you determine whether supplementation or dietary changes are necessary.
Selenium
Selenium:
Selenium is an essential mineral that plays a vital role in the proper functioning of the brain. It is a powerful antioxidant that protects the brain from oxidative damage, which can lead to cognitive decline and may contribute to the development of neurological disorders like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease.
Studies have shown that low levels of selenium are associated with an increased risk of depression and other mood disorders. Selenium helps to regulate the production of thyroid hormones, which play a crucial role in regulating our mood and behavior. Low levels of selenium can lead to an imbalance in thyroid hormone production, which can cause mood swings, depression, and anxiety.
Selenium also plays a critical role in DNA synthesis and repair, which is essential for maintaining the integrity of the nervous system. The brain is particularly vulnerable to oxidative damage, which can cause inflammation and damage to brain cells. Selenium helps to protect the brain from this damage and promotes the regeneration of new cells.
In addition to its role in brain health, selenium is also important for maintaining healthy skin, hair, and nails. It helps to protect the skin from damage caused by free radicals, which can cause premature aging and skin cancer. Selenium also promotes healthy hair growth and can help prevent hair loss.
Foods that are rich in selenium include Brazil nuts, fish, poultry, and eggs. It is also available in supplement form, but it’s important to speak with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplements.
Selenium is an essential micronutrient that plays a critical role in maintaining optimal brain function and overall health. By including selenium-rich foods in your diet or taking a supplement, you can support your brain health and reduce the risk of developing neurological disorders. Additionally, selenium supports healthy skin, hair, and nails, making it an important nutrient for overall wellbeing.
Amino Acids for Brain Health
Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins, and they also have important roles in brain function and mental health. There are several amino acids that have been linked to brain health and cognitive function.
Tryptophan is an essential amino acid that cannot be produced by the body and must be obtained through the diet. It is a precursor to the neurotransmitter serotonin, which is important for regulating mood and sleep. Low levels of serotonin have been linked to depression and anxiety. Foods high in tryptophan include turkey, chicken, tofu, nuts, and seeds.
Tyrosine is another essential amino acid that plays a role in dopamine production. Dopamine is a neurotransmitter that is important for motivation and reward. Studies have shown that tyrosine supplements may improve cognitive function and memory in stressful situations. Foods high in tyrosine include eggs, poultry, fish, and nuts.
Glutamine is a non-essential amino acid that is important for the synthesis of the neurotransmitter GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid). GABA is an inhibitory neurotransmitter that helps to calm the brain and reduce anxiety. Low levels of GABA have been linked to anxiety disorders. Foods high in glutamine include beef, chicken, fish, spinach, and cabbage.
It is important to note that eating a balanced diet that includes a variety of protein sources can provide all of the necessary amino acids for brain health. Some supplements that contain amino acids may interact with medications, so it is important to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any supplement regimen.
Amino acids play an important role in brain function and mental health. Tryptophan, tyrosine, and glutamine are just a few examples of amino acids that have specific functions in the brain. Eating a balanced diet that includes protein sources can provide all of the necessary amino acids for brain health, and supplementation should only be done under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
If you want to learn about the role of micronutrients in other parts of the body, check out our article on micronutrients for skin, hair, and nails.
Tryptophan
Tryptophan is an essential amino acid that plays a crucial role in the production of serotonin, a neurotransmitter that regulates mood, appetite, and sleep. It is also a precursor to melatonin, a hormone that regulates sleep-wake cycles.
One of the main food sources of tryptophan is turkey, but it is also found in chicken, beef, fish, eggs, and dairy products. Additionally, plant-based sources such as pumpkin seeds, soy products, and nuts can also provide an adequate amount of tryptophan to the body.
In addition to its role in mood regulation and sleep, tryptophan also plays a role in cognitive function. It has been shown to improve memory, attention, and decision-making, especially in elderly individuals. Tryptophan also has neuroprotective properties and has been suggested to have a potential therapeutic benefit for neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s.
Some studies suggest that tryptophan supplementation may be useful in treating depression and anxiety. However, more research is needed in this area to establish its efficacy and safety.
It is important to note that tryptophan’s effects on brain function and mental health are dependent on various factors, such as genetics, diet, and lifestyle. It is recommended to consume an adequate amount of tryptophan from food sources as opposed to supplements.
Tyrosine
Tyrosine is an amino acid that plays a crucial role in brain function and mental health. It is a precursor to several neurotransmitters, including dopamine, norepinephrine, and epinephrine, which are essential for mood regulation, stress response, and cognitive function.
Research suggests that tyrosine supplementation can improve cognitive performance and memory in stressful situations. This is because stress depletes the brain’s supply of neurotransmitters, leading to fatigue and impaired cognitive function. However, tyrosine can help replenish the brain’s neurotransmitter levels, leading to improved mental performance under stress.
Tyrosine has been shown to have anti-depressant effects, particularly in individuals with low dopamine levels. Dopamine is often referred to as the “pleasure neurotransmitter” because of its role in reward and motivation. Low dopamine levels have been linked to depression, and tyrosine supplementation can help increase dopamine levels, leading to improved mood and reduced symptoms of depression.
While tyrosine is naturally found in protein-rich foods such as chicken, turkey, and fish, supplementation may be necessary to achieve therapeutic effects. It is generally considered safe when taken in recommended doses, but individuals with certain conditions, such as hyperthyroidism or melanoma, should consult their healthcare provider before taking tyrosine supplements.
Tyrosine is an important micronutrient for brain function and mental health. Its role in neurotransmitter synthesis and regulation makes it a valuable tool for improving cognitive function, reducing stress, and alleviating symptoms of depression.
Glutamine
One essential amino acid that plays a significant role in brain health is glutamine. Glutamine is a non-essential amino acid, which means it can be synthesized by the body on its own. It is the most abundant amino acid in the body and is involved in various physiological functions.
Research suggests that glutamine is vital for brain function and can improve cognitive functions, including memory and focus. It acts as a neurotransmitter and is involved in the production of another important neurotransmitter, GABA. GABA has a calming effect on the brain and helps reduce anxiety and stress.
Studies have shown that glutamine supplementation can help reduce symptoms of depression in individuals. It has also been found to be helpful in treating addiction and substance abuse disorders by reducing cravings and improving brain function.
Glutamine is also important for maintaining the integrity of the blood-brain barrier, a protective barrier that separates the brain from toxins and harmful substances. It helps prevent the entry of harmful compounds and toxins into the brain, which can cause significant damage.
Foods that are high in glutamine include meat, fish, eggs, and dairy products. However, in some cases, dietary supplements may be required to meet the body’s demands for glutamine.
Glutamine is an important amino acid that plays a vital role in brain health and mental well-being. Its impact on cognitive function, neurotransmitter production, and the maintenance of the blood-brain barrier makes it a crucial nutrient for optimal brain health.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the role of micronutrients in brain function and mental health cannot be understated. Vitamins such as B Complex, D, and E all play a crucial role in the proper functioning of the brain. B complex vitamins are known for their ability to support the nervous system and improve cognitive function, while vitamin D deficiency has been linked to a higher risk for depression and other mental health disorders. Vitamin E, on the other hand, is a potent antioxidant that helps protect the brain from oxidative damage.
When it comes to minerals, iron is responsible for helping transport oxygen to the brain, which is necessary for optimal cognitive function. Magnesium is involved in over 300 enzymatic processes in the body, including those related to brain function. Zinc is critical for synaptic plasticity, which is essential for learning and memory. And finally, selenium has been shown to have neuroprotective effects and can help prevent cognitive decline.
Lastly, amino acids such as tryptophan, tyrosine, and glutamine all play a role in optimizing brain health. Tryptophan helps the body produce serotonin, which is a neurotransmitter involved in mood regulation. Tyrosine is a precursor to dopamine, another neurotransmitter important for motivation and pleasure. And glutamine helps protect against the toxic effects of ammonia, which can impair brain function.
Overall, a diet rich in a variety of micronutrients is essential for maintaining optimal brain function and promoting mental health. While supplementation can be beneficial for individuals with nutrient deficiencies, the best way to obtain these essential micronutrients is through a well-balanced diet that includes a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. By prioritizing our micronutrient intake, we can support our brain function and overall mental wellbeing.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the role of micronutrients in brain function and mental health?
Micronutrients, such as vitamins, minerals, and amino acids, play a crucial role in brain function and mental health by supporting neurotransmitter production, preventing oxidative stress, and reducing inflammation in the brain.
What are the best vitamins for brain health?
Some of the best vitamins for brain health include vitamin B complex, vitamin D, and vitamin E. These vitamins support cognitive function, reduce brain fog, and enhance mental clarity.
How do minerals impact brain function?
Minerals, such as iron, magnesium, and zinc, are essential for brain function as they help to improve memory and cognitive function, reduce stress and anxiety, and promote healthy neurotransmitter levels.
What amino acids are essential for brain function?
The three essential amino acids for brain function are tryptophan, tyrosine, and glutamine. These amino acids help to support healthy neurotransmitter levels, improve mood, and reduce anxiety and depression.
Can micronutrient deficiencies lead to mental health problems?
Yes, micronutrient deficiencies, particularly in vitamins and minerals, can lead to mental health problems such as anxiety, depression, and cognitive impairment. These deficiencies can disrupt brain function and impair neurotransmitter production.
Are there any dietary sources of micronutrients that can improve brain function?
Yes, there are several dietary sources of micronutrients that can improve brain function, including leafy greens, nuts and seeds, fish, and lean protein. These foods contain high levels of essential vitamins, minerals, and amino acids that support brain health.
What micronutrients should vegetarians and vegans be mindful of to support brain health?
Vegetarians and vegans should be mindful of certain micronutrients, such as vitamin B12, iron, and zinc, which are typically found in animal products. These nutrients are essential for brain function and can be obtained through plant-based alternatives or supplements.
Can taking micronutrient supplements improve mental health?
Yes, taking micronutrient supplements, such as multivitamins or targeted nutrient supplements, can improve mental health by providing essential vitamins, minerals, and amino acids that support brain function. However, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any supplement regimen.
Are there any side effects of taking micronutrient supplements?
While micronutrient supplements are generally safe, there can be side effects such as upset stomach, nausea, and diarrhea. It is important to follow recommended dosages and consult with a healthcare professional before starting any supplement regimen.
Can improving micronutrient intake also improve physical health?
Yes, improving micronutrient intake can also improve physical health by supporting immune function, reducing inflammation in the body, and promoting healthy aging. A diet rich in essential vitamins, minerals, and amino acids can also improve energy levels and athletic performance.







