In today’s fast-paced world, it’s no secret that stress has become a common occurrence for many people. From work to personal life, the pressures of everyday life can add up quickly and often leave us feeling overwhelmed. However, what many people don’t know is that the solution to reducing stress may be found in the foods we eat. Omega-3 fatty acids have been shown to have a significant impact on stress reduction and can be easily incorporated into our diets. In this article, we will explore the benefits of these essential fatty acids, how they can help reduce stress, and ways to incorporate them into your daily life.
What are Omega-3 Fatty Acids?
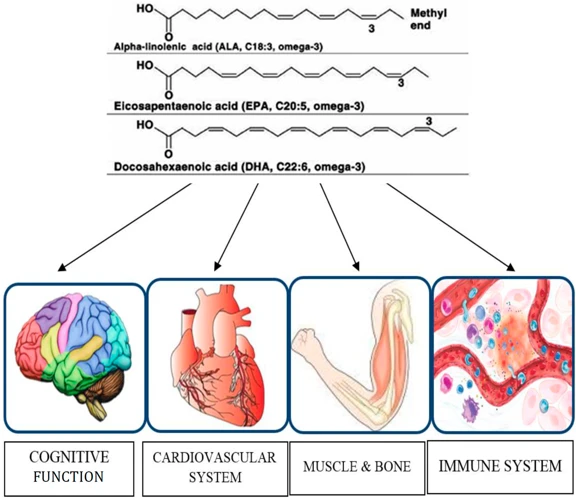
Understanding the nutrients that are beneficial for reducing stress is crucial for maintaining a healthy mind and body. Omega-3 fatty acids are one such nutrient that has been gaining attention in the world of mental health. Omega-3s are a type of polyunsaturated fat that cannot be produced by the body and must be consumed through diet or supplements. These fatty acids play an essential role in brain health, cognitive function, and emotional well-being. In this section, we will discuss the benefits and types of omega-3s – knowledge that will be useful when learning about the role of these fatty acids in stress reduction. To learn about stress-reducing food sources, read our article on foods that reduce stress and anxiety.
Benefits of Omega-3s
Omega-3 fatty acids have numerous benefits for overall health, including heart health, brain function, and reducing inflammation. Incorporating omega-3s into your diet can also have a positive impact on stress levels.
Here are some of the main benefits of omega-3s:
| Benefit | Description |
| Reduces inflammation | Omega-3 fatty acids, especially EPA and DHA, have anti-inflammatory properties that can help reduce inflammation throughout the body, which is linked to many chronic diseases. |
| Improves heart health | Omega-3s can help lower triglycerides, decrease blood pressure, and reduce the risk of heart disease and stroke. |
| Enhances brain function | The brain is made up of nearly 60% fat, and omega-3s are a crucial component of brain cell membranes. Getting enough omega-3s can improve communication between brain cells and may protect against age-related cognitive decline. |
| Reduces anxiety and depression | Studies have shown that omega-3s can help reduce symptoms of anxiety and depression, possibly by increasing the production of neurotransmitters that regulate mood. |
| Improves sleep | Getting enough omega-3s may help regulate the production of the sleep hormone melatonin and improve sleep quality. |
| May improve gut health | Some research suggests that omega-3s can help reduce inflammation in the gut and improve the balance of good bacteria, which may improve overall gut health and reduce the risk of digestive disorders. |
By incorporating omega-3s into your diet, whether through food or supplements, you may be able to enjoy some of these benefits, including a reduction in stress levels. Consider incorporating more omega-3-rich foods into your diet, such as fatty fish like salmon, sardines, and tuna, as well as chia seeds, flaxseeds, and walnuts. Additionally, taking an omega-3 supplement may be beneficial, but it’s important to speak with a healthcare provider first to determine the appropriate dosage for you.
Types of Omega-3s
Omega-3 fatty acids are essential fats that the body cannot produce on its own. There are three main types of omega-3s: Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), and Alpha-linolenic acid (ALA). EPA and DHA are found in fish, while ALA is found in plant sources such as flaxseed and walnuts.
EPA is primarily known for its anti-inflammatory properties. It has been linked to improved cardiovascular health, reduced symptoms of depression, and reduced joint pain. EPA is also believed to reduce symptoms of seasonal affective disorder (SAD), a type of depression that occurs in the winter due to lack of sunlight.
DHA is important for brain function and is a key component of cell membranes in the brain. It is necessary for the growth and development of the brain during infancy, and it may also reduce the risk of cognitive decline in old age. DHA has been linked to improved memory, focus, and attention span.
ALA is the most common type of omega-3 found in the Western diet. It is found in plant-based foods such as flaxseed, chia seeds, and walnuts. ALA is converted into EPA and DHA in the body but in small amounts. It is recommended to consume EPA and DHA directly from fatty fish or supplements.
It’s important to consume a variety of omega-3s as each type has unique health benefits. However, the standard American diet tends to be deficient in these essential fatty acids. It’s recommended to consume fatty fish at least twice a week, or to supplement with fish oil if necessary.
Why Omega-3 Fatty Acids are Important for Stress Reduction
Many people experience stress in their daily lives, which can have a negative impact on their overall well-being. Fortunately, incorporating omega-3 fatty acids into your diet is an effective way to reduce stress levels. Omega-3s are essential nutrients that provide numerous benefits for mental health and brain function. In this section, we will explore the link between omega-3s and stress, the role of omega-3s in brain function, how they can improve mood, and other benefits they offer for mental health. We will also share tips on how you can add more omega-3s to your diet to promote stress reduction. If you’re looking for more ways to manage stress, check out our article on mindful eating and its relaxing properties.
The Link between Omega-3s and Stress
Research has shown a strong link between omega-3s and stress reduction. The body uses these fatty acids to create signaling molecules known as eicosanoids, which have anti-inflammatory effects. Chronic inflammation has been linked to a variety of health problems, including stress and mood disorders. Omega-3s also help regulate cortisol levels, a stress hormone that, when elevated for prolonged periods, can contribute to anxiety and depression.
Additionally, studies have shown that people who consume higher levels of omega-3s tend to have decreased rates of mood disorders and better stress management. In one study, participants who consumed a diet high in omega-3s reported feeling less stressed and anxious compared to those who consumed a diet lacking in these fatty acids.
Omega-3s may also provide stress relief by improving heart health. Stress is known to have a negative impact on the cardiovascular system, and omega-3s have been shown to improve heart function and reduce the risk of heart disease. A healthy heart can better withstand the physical effects of stress, leading to improved stress management overall.
Consuming adequate amounts of omega-3 fatty acids can be an effective way to combat stress and improve overall mental and physical health. It’s important to remember that while omega-3s are beneficial, they should not be used as a sole method of stress management. Other healthy habits, such as regular exercise, proper sleep hygiene, and a balanced diet are also important for managing stress.
The Role of Omega-3s in Brain Function
Omega-3 fatty acids also play a crucial role in brain function and development. In fact, they’re known to be essential for brain health. DHA, one of the types of omega-3s, makes up a significant portion of the brain and is crucial for normal brain development and function.
Research suggests that DHA deficiency may impact normal brain development and may also contribute to neurodevelopmental and psychiatric disorders. Studies also suggest that DHA may have a role in preventing or managing cognitive decline, including Alzheimer’s disease.
Omega-3s have been linked to improved cognitive performance, faster reaction times, and better memory. This may be due to their ability to increase blood flow to the brain, reduce inflammation in the brain, and improve the flexibility and communication between brain cells.
Incorporating omega-3s into your diet can have a beneficial effect on brain function and may contribute to better mental health outcomes. To learn more about other ways to manage stress, check out our articles about stress eating habits, balanced diet for stress management, and the benefits of herbal teas for relaxing properties. Additionally, physical exercise has been found to positively influence stress and mood, while good sleep hygiene influences stress levels and weight. Another approach is to focus on gut health, which can have an impact on stress reduction efforts. Finally, meditation has been shown to be an effective way to manage stress and improve mental health.
How Omega-3s Improve Mood
Omega-3 fatty acids have been found to have a positive impact on mood, and this can be attributed to a number of factors. One of the main ways in which omega-3s improve mood is by reducing inflammation in the body. Inflammation is a natural response to stress, infection, or injury, but chronic inflammation can lead to a number of health problems, including depression and anxiety. By reducing inflammation, omega-3s can help to alleviate these symptoms and promote a more positive outlook.
Omega-3s can also affect the production and function of neurotransmitters in the brain, which are responsible for regulating mood and emotion. For instance, one study found that omega-3 supplementation increased the levels of the neurotransmitter serotonin in the brain, which is associated with feelings of happiness and well-being.
Omega-3s have also been shown to increase the production of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), which is a protein that helps to support the growth and survival of brain cells. Low levels of BDNF have been linked to depression and other mood disorders, so increasing BDNF production through omega-3 supplementation may help to improve mood and alleviate symptoms of these conditions.
In addition to these mechanisms, omega-3s may also have an impact on the gut microbiome, which is increasingly recognized as an important factor in mental health. Research suggests that omega-3s can help to promote the growth of beneficial gut bacteria, which in turn can lead to improvements in mood and overall well-being.
All in all, it is clear that omega-3 fatty acids play an important role in improving mood and promoting mental health. By reducing inflammation, supporting neurotransmitter function, increasing BDNF production, and impacting the gut microbiome, omega-3s offer a multifaceted approach to stress reduction and emotional well-being.
| How Omega-3s Improve Mood: |
|---|
| Inflammation reduction: By reducing inflammation, omega-3s help to alleviate symptoms of depression and anxiety. |
| Neurotransmitters: Omega-3s affect the production and function of neurotransmitters, including serotonin, which is associated with happiness and well-being. |
| BDNF production: Omega-3s can increase the production of BDNF, a protein that supports brain cell growth and survival and is linked to depression and other mood disorders. |
| Gut microbiome: Omega-3s may impact the gut microbiome, promoting the growth of beneficial gut bacteria and leading to improvements in mood and overall well-being. |
Other Benefits of Omega-3s for Mental Health
Omega-3 fatty acids are not only important for stress reduction but they also offer several other benefits for mental health. Here are some of the ways in which omega-3s can contribute to a healthy mind and improved cognitive function:
- Reduced risk of depression: Studies have shown that people with a diet high in omega-3s tend to have lower rates of depression. Omega-3s can help regulate mood and are believed to play a role in the production of serotonin – a neurotransmitter known for its mood-boosting effects.
- Improved memory and cognition: Omega-3s are essential for brain function and can support cognitive processes such as memory, learning, and attention. Some studies have even suggested that omega-3s could help protect against age-related cognitive decline.
- Lower risk of Alzheimer’s disease: Research has found that consuming omega-3s could be associated with a reduced risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease. This may be due to the anti-inflammatory properties of omega-3s and their ability to protect brain cells.
- Reduced symptoms of ADHD: Some studies have suggested that omega-3 supplementation could lead to a reduction in symptoms of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). Omega-3s may support the development and function of the nervous system, which could benefit children with ADHD.
- Improved sleep quality: A diet rich in omega-3s has been linked to better sleep quality. This may be due to the role that omega-3s play in regulating levels of the hormone melatonin, which is involved in sleep-wake cycles.
Incorporating omega-3 fatty acids into your diet can offer significant benefits for your mental health and well-being. Whether it’s reducing the risk of depression, improving memory and cognition, or supporting better sleep quality, omega-3s are an essential component of a healthy and balanced diet.
How to Incorporate Omega-3s into Your Diet
When it comes to improving our diet, it’s important to pay attention to which nutrients we’re consuming. One such nutrient that is often lacking in the standard Western diet is omega-3 fatty acids. Incorporating these healthy fats into your diet is essential, especially when it comes to stress reduction. But you may be wondering, how exactly can you add more omega-3s to your meals? Let’s explore some options.
Food Sources of Omega-3s
Omega-3 fatty acids are essential nutrients that have a wide range of health benefits, including reducing stress and promoting mental well-being. While supplements can be an easy way to get your daily dose of omega-3s, it’s always best to get nutrients from whole foods whenever possible. Here are some of the top food sources of omega-3s:
| Fatty Fish | Flaxseeds | Chia Seeds | Walnuts |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fatty fish like salmon, tuna, mackerel, and sardines are some of the richest sources of omega-3s. These fish contain two types of omega-3s: eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA). | Flaxseeds are a great vegetarian source of omega-3s. They are high in alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), a type of omega-3 that can be converted into EPA and DHA in the body. | Chia seeds are another vegetarian source of omega-3s that are high in ALA. They can be sprinkled on top of oatmeal, yogurt, or smoothie bowls for a tasty and nutritious boost. | Walnuts are a delicious and easy way to get your omega-3s. They are high in ALA and can be added to salads or eaten as a snack. |
| Other types of seafood, such as shrimp and scallops also contain omega-3s, although in smaller amounts compared to fatty fish. | Other sources of vegan omega-3s include hemp seeds, soybeans, and canola oil. However, these sources contain ALA rather than EPA and DHA. | Eggs enriched with omega-3s can also be a good source of this nutrient. Look for eggs that are labeled as containing omega-3s on the package. | Avocado is another plant-based source of omega-3s. While not as high in this nutrient as some other foods, it can still contribute to your overall intake. |
Including these omega-3-rich foods in your diet can be an easy and delicious way to support your mental health and reduce stress.
Supplements
Omega-3 supplements are a popular way to increase intake of these beneficial fatty acids. There are several types of omega-3 supplements available including fish oil, krill oil, algae oil, and flaxseed oil. Each type of supplement has varying levels of the different types of omega-3s, so it is important to choose a supplement that contains high levels of EPA and DHA, the most important omega-3 fatty acids for stress reduction.
One benefit of taking omega-3 supplements is that they are convenient and easy to incorporate into your routine. Unlike some food sources of omega-3s, supplements are available year-round and do not require preparation or cooking. Additionally, supplements can be taken in a variety of forms such as pills, gummies, or liquids, which makes it easy to find a form that works best for you.
When choosing an omega-3 supplement, it is important to do your research and look for a high-quality product. Look for supplements that have been third-party tested for purity and potency, and that have been certified by organizations such as the International Fish Oil Standards Program (IFOS) or the United States Pharmacopeia (USP).
It is also important to talk to your healthcare provider before starting an omega-3 supplement regimen. Supplements can interact with medications, and your healthcare provider can help you determine the right dosage and form of supplement for your individual needs. It is generally recommended to start with a low dose of omega-3 supplements and gradually increase the dosage over time.
Taking omega-3 supplements can be a beneficial way to increase intake of these important fatty acids for stress reduction and overall mental health. However, it is important to choose a high-quality product and consult with your healthcare provider before starting a supplement regimen.
Recommended Dosages
When it comes to the recommended dosages of omega-3 fatty acids, it is important to note that it can vary depending on multiple factors, such as age, gender, and health condition. However, *in general*, the American Heart Association recommends consuming at least two servings of fatty fish per week, which contain omega-3s, and this equates to about 500 milligrams of EPA and DHA per day. EPA and DHA are two types of omega-3s that have been heavily researched for their potential health benefits.
If you decide to take omega-3 supplements, it is important to follow the recommended dosage on the label of the product that you choose. Typically, the recommended dosage ranges from 250 to 1000 milligrams of EPA and DHA per day, but *always* consult with your healthcare provider to determine the appropriate dosage for your specific health needs.
It is important to note that too much omega-3 fatty acids can result in unwanted side effects, such as an increased risk of bleeding, so it is essential to follow the recommended dosages and not to exceed them without medical supervision.
Incorporating omega-3 fatty acids into your diet or taking supplements in the recommended dosages can have potential benefits for your health and stress reduction, but it is important to consult a healthcare provider before starting any supplement regimen.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Omega-3 fatty acids have been found to play a crucial role in reducing stress levels and improving mental health. These essential fatty acids have both physical and mental benefits, making them a valuable addition to any diet.
Research has shown that Omega-3s can reduce inflammation and help regulate the body’s stress response, resulting in lower levels of anxiety and depression. Furthermore, these fatty acids are vital for brain function and can enhance cognitive performance, as well as improve mood and memory.
Incorporating Omega-3s into your diet can be done through consuming foods such as fatty fish, nuts, and seeds, or by taking supplements. It is essential to ensure that you are getting the recommended dosage of Omega-3s to achieve maximum health benefits.
Overall, the importance of Omega-3 fatty acids in stress reduction and mental health cannot be understated. By adding these essential fatty acids to your diet, you can experience improved brain function, reduced stress and anxiety, and a better overall mood. So, make sure to incorporate Omega-3s into your diet and experience the benefits for yourself.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why are omega-3 fatty acids important?
Omega-3s are important for overall health, especially for brain and heart function. They also have anti-inflammatory properties and may help reduce the risk of chronic diseases.
Can omega-3s reduce stress?
Yes, studies have shown that omega-3s can help reduce stress levels and improve mood.
What are some food sources of omega-3s?
Fatty fish such as salmon, mackerel, and sardines are good sources of omega-3s. Other sources include flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts.
Can supplements provide the same benefits as food sources of omega-3s?
Yes, supplements can provide the same benefits as food sources. However, it’s important to choose high-quality supplements from reputable brands.
How much omega-3 should I consume daily?
The recommended daily intake of omega-3s varies depending on age and gender. Generally, adults should aim for at least 250-500mg per day.
Are there any risks or side effects of consuming omega-3s?
While omega-3s are generally safe, high doses can increase the risk of bleeding and interact with certain medications. It’s important to talk to your doctor before taking supplements.
Can omega-3s be used as a treatment for depression?
While omega-3s have been shown to improve mood, they shouldn’t be used as a stand-alone treatment for depression. It’s important to seek professional help for mental health issues.
Can vegetarians and vegans consume enough omega-3s through their diet?
Yes, vegetarians and vegans can consume enough omega-3s through plant-based sources such as flaxseeds, chia seeds, and algae-based supplements.
Is it safe to take omega-3 supplements during pregnancy?
Yes, omega-3 supplements are generally safe during pregnancy and can even benefit fetal brain development. However, it’s important to talk to your doctor before taking any supplements during pregnancy.
Can omega-3s help with cognitive function in older adults?
Yes, studies have shown that omega-3s can help improve cognitive function in older adults, especially in terms of memory and attention.