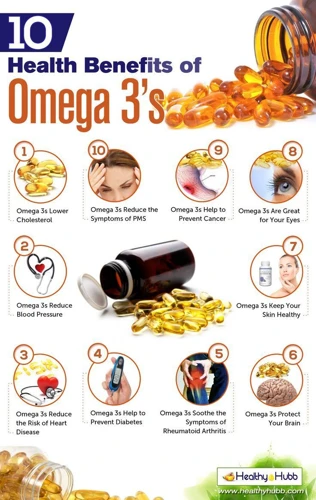
Introduction: What are Omega-3s?
Omega-3s are a type of fatty acid that have been gaining popularity recently due to their numerous health benefits, including their ability to promote skin health. They are a group of polyunsaturated fatty acids that our bodies cannot produce on their own and thus must be obtained through our diet or supplements.
Omega-3s have been found to play an essential role in maintaining healthy skin. They help to keep the skin hydrated, supple, and youthful-looking. These fatty acids work in the body by reducing inflammation and oxidative stress, which are two of the main culprits behind skin aging and skin problems such as acne and dry skin.
Research has shown that people who have a diet that includes a good amount of omega-3s are less likely to suffer from skin related issues such as dryness, wrinkles, fine lines, and even skin cancer. This is why incorporating omega-3s into your diet can be a great way to promote healthy skin that not only looks radiant but is also protected from harmful UV rays.
There are three main types of omega-3 fatty acids: EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid), DHA (docosahexaenoic acid), and ALA (alpha-linolenic acid). EPA and DHA are primarily found in fatty fish such as salmon, tuna, and mackerel, while ALA is found in plant-based foods such as flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts.
By including a variety of omega-3 sources in your diet, you may be able to give your skin the nourishment it needs to stay healthy and vibrant. So, let’s dive deeper into the different types of omega-3s and the food sources that contain them, as well as some tips on how to incorporate them into your diet for optimal skin health. If you want to learn more about how food affects your skin, check out our detailed guide.
The Link Between Omega-3s and Skin Health

When it comes to achieving healthy and glowing skin, there are numerous factors to consider. One of the most crucial elements that often gets overlooked is our diet. What we eat can significantly impact the health of our skin. A growing body of research suggests that incorporating foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids into our diet may have a positive impact on our skin. In this article, we’ll explore the link between omega-3s and skin health, and how you can reap the benefits of this essential nutrient. To learn more about other dietary factors that affect the skin, check out our article on foods that affect skin health.
How Omega-3s Help Your Skin
Omega-3 fatty acids are essential for maintaining the health of the skin. They play a crucial role in keeping the skin cells healthy and functioning correctly. Here are some ways in which these good fats can benefit your skin:
- Reduces Inflammation: Omega-3s have natural anti-inflammatory properties that can help reduce redness and swelling in the skin. This is especially beneficial for those with inflammatory skin conditions such as acne, eczema, and psoriasis. In fact, several studies have found that omega-3 supplementation can reduce the severity of these skin conditions.
- Increases Skin Elasticity: As we age, our skin tends to lose its elasticity, leading to wrinkles and fine lines. Omega-3s can help counteract this process by promoting collagen production. Collagen is a protein that provides structure and elasticity to the skin, and omega-3s help to keep it strong and healthy.
- Hydrates the Skin: Omega-3s help to strengthen the skin’s barrier function, which helps to lock in moisture and prevent dehydration. This is important because dehydrated skin tends to look dull and can become more prone to fine lines and wrinkles.
- Protects Against Sun Damage: Exposure to UV radiation from the sun can damage the skin and lead to premature aging. Omega-3s can help protect the skin from this damage by reducing inflammation and supporting the skin’s natural defenses.
Incorporating omega-3s into your diet can have a significant impact on the health and appearance of your skin. However, it is important to remember that omega-3s are just one part of a comprehensive approach to skin care. Eating a balanced diet, staying hydrated, protecting your skin from the sun, and promoting gut health are all crucial components of healthy skin. For more information on foods that are beneficial for the skin, check out our article on 10 Foods for Healthy Skin.
What the Research Says
Studies have demonstrated that consuming foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids can improve skin health. One study found that individuals who consumed more fish had a lower risk of squamous cell carcinoma, a common type of skin cancer, indicating that incorporating omega-3s into your diet may help lower your risk of skin cancer.
Several small studies have also demonstrated that supplementing with omega-3 supplements may improve skin health. One study showed that supplementing with 2.2 grams of EPA and 1.4 grams of DHA for 10 weeks significantly reduced acne severity in individuals with moderate to severe acne. Another study found that supplementing with 1 gram of omega-3 supplements per day for four months reduced roughness in the skin and helped improve skin hydration.
Other research has suggested that omega-3s may also help reduce inflammation in the body, which can contribute to several skin conditions, including psoriasis and eczema. One study found that supplementing with fish oil, which is high in omega-3s, significantly reduced inflammation in individuals with psoriasis. Another study showed that supplementing with a combination of omega-3s and omega-6s helped improve symptoms of eczema, a common skin condition that causes itchy, inflamed skin.
While additional research is needed to fully understand the effects of omega-3s on skin health, current studies suggest that incorporating these healthy fats into your diet may provide numerous benefits for your skin. To maximize the potential benefits of omega-3s, it is best to consume them as part of a healthy, balanced diet that contains a variety of nutrients that support skin health, such as antioxidants and healthy fats. You can find more information on how to eat for healthy skin in our articles on acne-fighting foods, healthy fats for skin, and antioxidants for skin health.
Types of Omega-3 Fatty Acids

When it comes to understanding the benefits of omega-3s for skin health, it’s important to first take a closer look at the types of omega-3 fatty acids. Omega-3s are essential fatty acids that our bodies cannot produce on their own, yet they play a crucial role in maintaining good health. There are three main types of omega-3s: EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid), DHA (docosahexaenoic acid), and ALA (alpha-linolenic acid). Each of these fatty acids offers unique benefits and can be found in different food sources, from fatty fish to plant-based options. Understanding the differences between these types of omega-3s can help you make more informed decisions about incorporating them into your diet for optimal skin health.
EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid)
EPA, or eicosapentaenoic acid, is one of three main types of Omega-3 fatty acids. It plays an important role in maintaining overall health and has been linked to many benefits for skin health. EPA is particularly important for reducing inflammation in the body, which can help reduce the risk of chronic skin conditions such as acne, psoriasis, and eczema.
Studies have found that EPA may also help to reduce the risk of skin cancer and sunburn. This is because it can help to protect the skin from UV damage and oxidative stress caused by free radicals. Additionally, EPA has been shown to help improve skin hydration, which can help to reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles.
EPA can be found in:
| Food Source | EPA Content per 100g |
|---|---|
| Salmon | 1.2g |
| Sardines | 1.4g |
| Mackerel | 1.5g |
| Anchovies | 1.4g |
| Chia Seeds | 0.2g |
| Flaxseeds | 0.6g |
| Walnuts | 0.2g |
It’s important to note that EPA is most commonly found in fatty fish, making it more difficult for vegetarians and vegans to get enough of this nutrient through their diet alone. In such cases, it may be beneficial to consider taking an Omega-3 supplement that contains EPA.
Incorporating foods rich in EPA into your diet can be a great way to support your skin health. However, it is important to remember that overall skin health is influenced by many factors, including hydration, diet, and sun protection. It is essential to maintain a healthy and balanced lifestyle to achieve optimal skin health.
Hydration, avoiding harmful foods, and supporting gut health through a balanced diet can also help to improve skin health. Additionally, consuming foods high in antioxidants and other beneficial nutrients can also help to reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles. Some foods that are particularly beneficial for skin health include berries, leafy greens, and nuts.
DHA (docosahexaenoic acid)
DHA (docosahexaenoic acid) is one of the three main types of omega-3 fatty acids. It is a major structural component of the skin, making it important for maintaining overall skin health. In fact, DHA makes up around 10% to 15% of the skin’s total fatty acid content.
Studies have shown that DHA can help improve skin hydration and reduce the appearance of aging by promoting collagen production. DHA also has anti-inflammatory properties, which can help reduce skin redness and irritation.
Here are some common food sources of DHA:
| Food | Portion | DHA Content |
| Salmon | 3 ounces (85 grams) | 1,500 – 2,000 mg |
| Mackerel | 3 ounces (85 grams) | 1,200 – 1,500 mg |
| Sardines | 3 ounces (85 grams) | 1,100 – 1,500 mg |
| Tuna | 3 ounces (85 grams) | 200 – 300 mg |
| Trout | 3 ounces (85 grams) | 200 – 500 mg |
| Seaweed | 1 ounce (28 grams) | 60 – 150 mg |
If you’re not a fan of fish, you can also get DHA from algae-based supplements. Make sure to speak with your doctor before taking any supplements, especially if you have a medical condition or are taking medication.
ALA (alpha-linolenic acid)
Alpha-linolenic acid (ALA) is another type of omega-3 fatty acid that is found in plant-based sources. ALA is an essential fatty acid, meaning that our bodies cannot produce it on their own and we must obtain it from our diet.
Sources of ALA
Here are some of the top sources of ALA:
| Source | Serving Size | Amount of ALA |
|---|---|---|
| Chia Seeds | 1 ounce (28 grams) | 4,915 mg |
| Flax Seeds | 1 ounce (28 grams) | 6,388 mg |
| Walnuts | 1/4 cup (28 grams) | 2,542 mg |
| Soybeans | 1 cup (155 grams) | 1,241 mg |
Conversion to EPA and DHA
While ALA is not as effective at improving skin health as EPA and DHA, it can be converted by the body into these more potent forms. However, the conversion rate is quite low, with only about 5% of ALA being converted to EPA and less than 1% being converted to DHA.
Incorporating ALA into Your Diet
To increase your intake of ALA, you can incorporate foods such as chia seeds, flax seeds, and walnuts into your diet. Vegetarians and vegans can also consider taking an algae-based omega-3 supplement, which provides EPA and DHA without the need for fish or fish oil. However, it is important to note that these supplements may not be as effective as those derived from fish oil.
Sources of Omega-3s
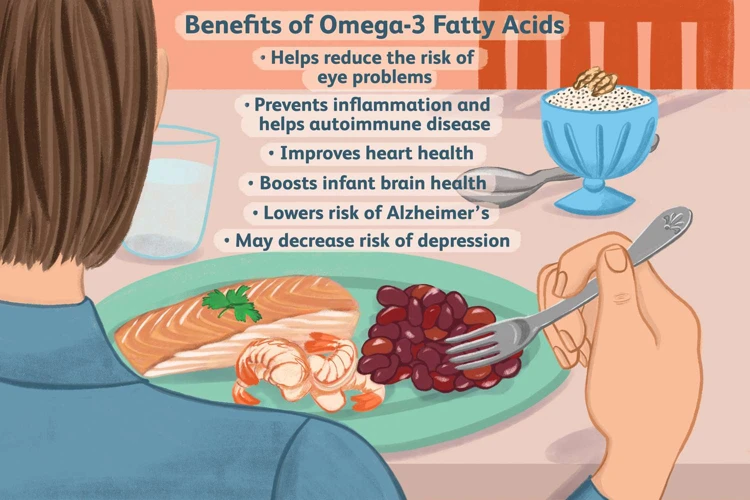
When it comes to incorporating more omega-3s into your diet, there are a variety of sources to choose from. These sources include fatty fish, plant-based options, and supplements. Each of these options has its own benefits and drawbacks, so it’s important to choose the one that works best for you and your lifestyle. Let’s dive into each source in more detail.
Fatty Fish
One of the best sources of omega-3 fatty acids is fatty fish. Here are some types of fatty fish that are particularly high in omega-3s:
- Salmon: This popular fish is a great source of both EPA and DHA omega-3s. In fact, a 3-ounce serving of cooked salmon contains around 1.5 grams of combined EPA and DHA.
- Sardines: These small, oily fish are also rich in EPA and DHA. Just one serving of canned sardines (about 3.75 ounces) provides around 1 gram of combined EPA and DHA.
- Mackerel: Mackerel is another fatty fish that is rich in both EPA and DHA. A 3-ounce serving of cooked mackerel contains around 0.5 grams of EPA and 1 gram of DHA.
- Herring: Herring is another smaller fish that is rich in omega-3s. A 3-ounce serving of pickled herring can contain over 1 gram of combined EPA and DHA.
- Tuna: While not as high in omega-3s as some other fatty fish, canned tuna can still provide a good source of these beneficial fatty acids. A 3-ounce serving of canned light tuna contains around 0.2 grams of combined EPA and DHA.
Incorporating more fatty fish into your diet is a great way to increase your omega-3 intake and support your skin health. Try grilling, roasting, or baking your fish with some herbs and spices for a flavorful and healthy meal.
Plant-Based Sources
Plant-based sources of omega-3s offer a great alternative for vegetarians and vegans who wish to enjoy the benefits of omega-3s. Here are some excellent plant-based sources of omega-3s that you can include in your diet:
- Flaxseeds: These tiny seeds are a great source of ALA. Just two tablespoons of flaxseeds provide more than 100% of the daily recommended intake for ALA.
- Chia seeds: These seeds are another great source of ALA. They also contain fiber, protein, and antioxidants. Simply sprinkle chia seeds on your oatmeal or yogurt for a quick and easy breakfast.
- Walnuts: These nuts are high in ALA and provide a range of health benefits. They make a great addition to salads, oatmeal, or simply as a snack.
- Hemp seeds: These seeds are rich in both ALA and protein. They can be added to smoothies, oatmeal, or salads for a boost of omega-3s and other important nutrients.
- Soybeans: Soybeans are a good source of ALA and are easy to incorporate into meals. Try adding them to stir-fries, salads, or soups.
- Kale: This leafy green vegetable is a good source of ALA and other important nutrients. Try adding kale to your smoothies or salads to increase your omega-3 intake.
It’s essential to keep in mind that while plant-based sources of omega-3s are plentiful, the conversion of ALA to EPA and DHA in the body is not very efficient. It is recommended to consume a variety of plant-based sources of omega-3s to ensure you’re getting enough to meet your body’s needs. Additionally, supplementation may be necessary for some individuals, especially those who don’t consume fish or other seafood.
Supplements
One way to ensure you’re getting enough omega-3s in your diet is through supplements. These supplements come in different forms, including fish oil, krill oil, and algae oil.
Fish oil: This supplement is made from the tissue of fatty fish, such as salmon, mackerel, or cod liver. It is a popular source of omega-3s and is available in both liquid and capsule form. When choosing a fish oil supplement, be sure to look for one that is high in EPA and DHA.
Krill oil: Krill oil is made from tiny krill, a small crustacean that is a food source for many marine animals. It contains both EPA and DHA and is often marketed as being more potent than fish oil. Some people prefer krill oil because it is considered more sustainable than fish oil.
Algae oil: This supplement is made from algae, which is where fish get their omega-3s from in the first place. Algae oil is a good alternative for vegetarians and vegans who don’t consume fish products. It also contains both EPA and DHA.
It’s important to note that while supplements can be a convenient way to boost your omega-3 intake, it’s always best to try to get your nutrients from whole food sources whenever possible. Additionally, if you are taking any medications or have any health conditions, it’s important to talk to your healthcare provider before starting any new supplements.
| Supplement | Source | Omega-3 content |
| — | — | — |
| Fish oil | Fatty fish | EPA and DHA |
| Krill oil | Krill | EPA and DHA |
| Algae oil | Algae | EPA and DHA |
Tips for Incorporating More Omega-3s into Your Diet

If you’re convinced that boosting your omega-3 intake can do wonders for your skin, you’re probably wondering how to go about incorporating more of this nutrient into your diet. Fear not, there are plenty of different ways to get your daily dose of omega-3s. In this section, we’ll highlight a few tips and tricks for upping your omega-3 intake, including meal ideas and recipes to try. With a little creativity and some planning, you can easily make omega-3s a regular part of your diet and see the benefits for your skin. Let’s dive in!
Meal Ideas
Incorporating more omega-3s into your diet can be easy with the right meal ideas. Here are a few to get you started:
- Salmon and greens: Grill a piece of salmon with lemon and butter and serve with a side of sautéed kale or spinach.
- Tuna salad: Mix canned tuna with Greek yogurt, diced celery and red onion, and a tablespoon of flaxseed oil. Serve on a bed of mixed greens.
- Chia seed pudding: Mix chia seeds, almond milk, and a tablespoon of honey in a jar, and let sit for at least an hour. Top with fresh berries for a delicious and healthy breakfast or snack.
- Quinoa bowl: Cook quinoa according to package instructions and add sautéed broccoli, carrots, and bell peppers for some extra nutrients. Top with a hard-boiled egg or some grilled tofu and a drizzle of olive oil.
- Green smoothie: Blend together some spinach, frozen pineapple, and coconut milk for a refreshing smoothie that’s packed with nutrients. Add a tablespoon of flaxseed or chia seeds for even more omega-3s.
These meal ideas are just a starting point. Don’t be afraid to get creative in the kitchen and experiment with different ingredients and flavors to find the omega-3-rich dishes that you enjoy the most!
Recipes to Try
Here are some delicious recipes that are high in omega-3s and great for your skin:
| Recipe | Ingredients | Instructions |
|---|---|---|
| Salmon Quinoa Bowl |
|
|
| Chia Seed Pudding |
|
|
| Kale and Walnut Pesto Pasta |
|
|
These recipes are not only delicious, but they also provide a healthy dose of omega-3s to promote skin health. Give them a try and see how they can benefit your skin!
Other Ways to Support Your Skin Health
When it comes to achieving healthy and glowing skin, omega-3 fatty acids can certainly play a crucial role. But there are other strategies you can incorporate in your routine to support your skin health. In fact, staying hydrated, eating a balanced diet, and protecting your skin from the sun are some of the most important steps you can take. Let’s dive deeper into these other ways to support your skin health.
Stay Hydrated
One of the simplest yet most effective ways to support your skin health is by staying hydrated. When our bodies are properly hydrated, our skin looks plump and radiant, and is less prone to dryness and wrinkles.
Why is hydration important?
Our skin is made up of cells that require water to function properly. When we become dehydrated, our skin cells become depleted and our skin can start to look dull and tired. Additionally, dehydrated skin is more prone to wrinkling and premature aging.
How much water should you drink?
While there is no one-size-fits-all answer to this question, the general rule of thumb is to drink at least eight glasses of water per day. You may need to drink more if you are very active or live in a hot climate.
Tips for staying hydrated
- Carry a refillable water bottle with you wherever you go to encourage yourself to drink more water throughout the day.
- Add a squeeze of lemon or lime to your water for a refreshing twist.
- Eat water-rich foods such as watermelon, cucumbers, and celery.
- Stay away from sugary drinks which can dehydrate you even more.
The bottom line
Staying hydrated is a simple yet effective way to support your skin health. By drinking enough water and incorporating water-rich foods into your diet, you can ensure that your skin stays plump and radiant, and is less prone to premature aging.
Eat a Balanced Diet
Eating a balanced diet is essential for overall health, including the health of your skin. A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can provide the vitamins and minerals necessary for healthy skin. Here are some specific nutrients to focus on:
- Vitamin C: This vitamin is important for collagen production, which helps keep skin firm and smooth. Foods rich in vitamin C include citrus fruits, strawberries, kiwi, bell peppers, and broccoli.
- Vitamin E: This vitamin is an antioxidant that can help protect skin from damage. Good sources of vitamin E include nuts, seeds, and leafy green vegetables.
- Protein: Protein is necessary for the growth and repair of skin cells. Good sources of protein include lean meats, poultry, fish, beans, and lentils.
- Zinc: This mineral is important for skin health and is necessary for wound healing. Zinc can be found in oysters, beef, pork, chicken, beans, and nuts.
- Healthy fats: Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fatty fish like salmon, can help reduce inflammation in the body and may improve skin health. Other sources of healthy fats include nuts, seeds, and avocado.
Remember, a diet that is rich in a variety of nutrients is key for maintaining healthy skin. It’s important to aim for a balanced diet that includes a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
Protect Your Skin from the Sun
When it comes to maintaining healthy skin, protecting it from the sun is crucial. Exposure to the sun’s harmful UV rays can cause skin damage, wrinkles, age spots and even increase the risk of skin cancer. Here are some tips for protecting your skin from the sun:
| Tips for Protecting Your Skin from the Sun |
|---|
| Wear Protective Clothing: When possible, wear long-sleeved shirts, pants, and wide-brimmed hats to protect your skin from the sun’s harmful rays. |
| Use Sunscreen: Choose a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30 and apply it generously to all exposed skin. Reapply every two hours or more frequently if sweating or swimming. |
| Seek Shade: When possible, seek shade during the sun’s peak hours from 10 a.m. to 4 p.m. to minimize exposure to harmful UV rays. |
| Avoid Tanning Beds: Tanning beds emit harmful UV rays that can increase your risk of skin cancer and lead to premature aging of the skin. |
Remember, protecting your skin from the sun is important year-round, not just during the summer months. Be sure to incorporate these tips into your daily routine to help keep your skin looking and feeling its best.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the benefits of omega-3s for skin health are undeniable. These essential fatty acids play a vital role in maintaining the integrity and elasticity of the skin, promoting hydration, and reducing inflammation. Research has shown that a diet rich in omega-3s can improve several skin conditions, such as acne, psoriasis, and eczema.
Incorporating more omega-3s into your diet can be achievable through consuming fatty fish, plant-based sources, or taking supplements. It is important to take steps to protect your skin from the sun and stay hydrated to maximize the benefits of omega-3 consumption.
While omega-3s have shown promise in improving skin health, they are just one part of a holistic approach to skin care. A balanced diet, proper hydration, and protection from the sun are also crucial in maintaining healthy skin.
It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen. However, with the information provided in this comprehensive guide, you can confidently make informed decisions that benefit not only your skin but also your overall health and wellbeing.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the recommended daily intake of omega-3s?
The American Heart Association recommends at least two servings of fatty fish per week, which provides about 500 milligrams of EPA and DHA.
Can omega-3s help with acne?
There is limited research on the effects of omega-3s on acne, but some studies suggest that they may have a beneficial effect on reducing inflammation and improving skin health.
Can omega-3s prevent wrinkles?
While there is no clear evidence that omega-3s can prevent wrinkles, they may help support overall skin health and hydration, which can contribute to a more youthful appearance.
Are plant-based sources of omega-3s as beneficial as fatty fish?
Plant-based sources of omega-3s, such as flaxseeds and chia seeds, provide a different type of omega-3 fatty acid (ALA) than fatty fish (EPA and DHA). While ALA is still beneficial, the body may not convert it as efficiently into EPA and DHA as it does with fish-based omega-3s.
Can omega-3s help with rosacea?
There is limited research on the effects of omega-3s on rosacea, but some studies suggest that they may help reduce inflammation and improve skin hydration.
Can you get too much omega-3s?
It is possible to get too much omega-3s, which can lead to bleeding and excessive blood thinning. It is important to follow recommended daily intake guidelines and speak with a healthcare provider before adding supplements to your diet.
Can omega-3s help with psoriasis?
Some studies suggest that omega-3s may have a beneficial effect on reducing inflammation associated with psoriasis. However, more research is needed in this area.
Are omega-3 supplements necessary if you already eat fatty fish?
If you are able to regularly consume fatty fish, you may not need omega-3 supplements. However, supplements can provide a convenient way to ensure you are meeting your daily intake recommendations.
What are some vegetarian alternatives to fatty fish for omega-3s?
Vegetarian sources of omega-3s include flaxseeds, chia seeds, hemp seeds, walnuts, and algae-based supplements.
Can omega-3s improve overall skin texture?
While there is no clear evidence that omega-3s can specifically improve skin texture, they may support overall skin health and hydration, which can contribute to a more even and smooth complexion.