Digestive issues are a common problem that plagues many individuals. From bloating and discomfort to more serious concerns, it can be an ongoing battle to maintain a healthy gut. With the rise of gut health awareness, many are turning to probiotics as a means of relief. But what exactly are probiotics, and how do they work? In this article, we’ll be exploring the role of probiotics in digestion, their food sources, and how you can start incorporating them into your diet. So, let’s dive in and discover the power of these mysterious microorganisms.
What are Probiotics?
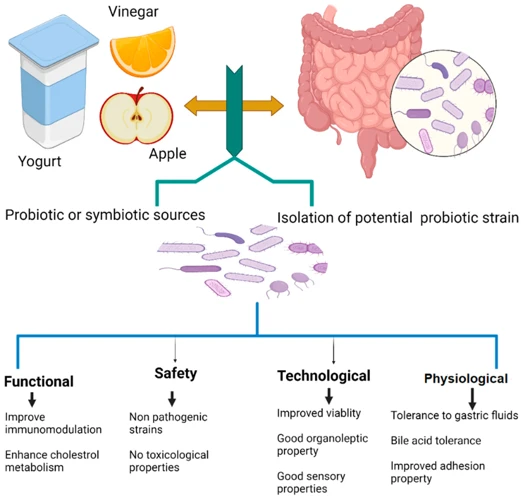
Probiotics are live microorganisms that have numerous health benefits, especially for your digestive system. They are commonly known as “good bacteria” or “friendly bacteria” and can be found naturally in your gut or in certain foods and supplements.
Probiotics are defined by the World Health Organization (WHO) as “live microorganisms that, when administered in adequate amounts, confer a health benefit on the host.” In order for a microorganism to be considered a probiotic, it has to meet several criteria, including being safe for human consumption, having the ability to survive and remain active in the human digestive tract, and providing a health benefit to the host.
Probiotics work by balancing the levels of bacteria in your gut. When there is an imbalance of “bad bacteria” in your digestive system, it can lead to a variety of digestive issues such as bloating, gas, and constipation. By introducing good bacteria into your gut, probiotics can help improve the balance of bacteria and promote better digestion.
Additionally, probiotics can help strengthen the intestinal lining, which can prevent harmful substances from leaking through and entering the bloodstream. This can help reduce inflammation in the body, as well as improve overall immune function.
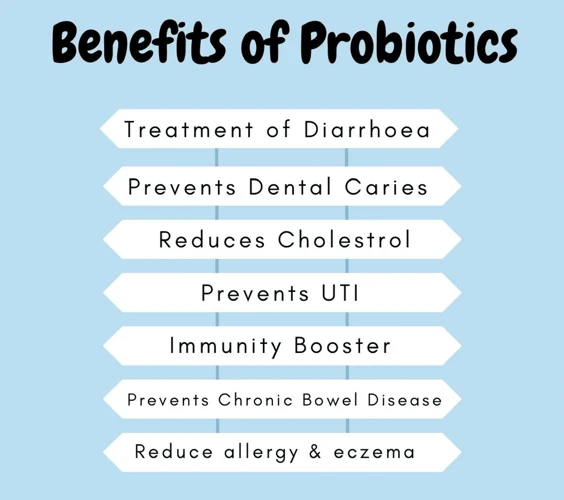
Probiotics are important for digestion because they can help improve the overall health of your gut. When your gut is healthy, it can better absorb nutrients from the foods you eat, which can lead to better overall health.
Many digestive issues such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), and diarrhea have been linked to an imbalance of bacteria in the gut. By taking probiotics, you can help improve the balance of bacteria and reduce the risk of developing these and other digestive issues.
Probiotics can help improve digestion of lactose, the sugar found in milk and other dairy products. This can be especially helpful for those who are lactose intolerant and have difficulty digesting dairy products.
Probiotics are essential for maintaining a healthy digestive system. They work by balancing the levels of bacteria in your gut, strengthening the intestinal lining, and improving nutrient absorption. Incorporating probiotic-rich foods into your diet or taking probiotic supplements can help improve your digestion and overall health.
The Definition of Probiotics
As we delve into the world of probiotics, it’s important to understand their definition and how they work. Probiotics, according to experts, are live microorganisms that offer numerous health benefits when consumed. They are often referred to as “good bacteria” as they help maintain the balance of microorganisms in the gut. In this section, we’ll explore further into the definition of probiotics and their role in digestion.
How Probiotics Work
Probiotics are live microorganisms that live in our gut and provide many health benefits. How they work depends on the unique strains of bacteria in the specific probiotic supplement or food.
| Function | Description |
| Restoring Gut Microbiome Diversity | Probiotics help restore the natural balance of microorganisms in the gut, which might have been affected by factors such as a poor diet, certain medications, or illness. They provide beneficial bacteria, which can crowd out harmful bacteria and help keep the digestive system healthy. |
| Enhancing Gut Barrier Function | Probiotics have been shown to improve the gut’s barrier function. This means that they can help maintain the integrity of the digestive tract lining, which reduces the risk of harmful bacteria and toxins entering the bloodstream. |
| Producing Essential Nutrients and Vitamins | Some probiotic strains produce vitamins, such as B vitamins and vitamin K, which play an important role in overall health. These vitamins are essential for functions such as blood clotting, energy metabolism, and nervous system health. |
| Regulating Immune Function | Probiotics can regulate the immune system and reduce inflammation in the gut. This is important because chronic inflammation is thought to play a role in many diseases, including digestive disorders. |
How probiotics work is still being studied, but the evidence suggests that they can have a significant impact on digestive health. However, it’s important to note that not all probiotics are created equal, so it’s important to choose a high-quality supplement or food source that has been shown to provide health benefits.
While taking probiotics is one way to support digestive health, it’s important to also incorporate other healthy habits such as eating a high-fiber diet, managing stress, and getting regular exercise to achieve optimal digestive wellness.
Why Probiotics are Important for Digestion
Probiotics are essential for maintaining a healthy digestive system. They improve digestion and absorption of food by breaking down nutrients and making them more available for the body to use. They also help to maintain the balance of the gut microbiota, which is important for overall health.
When the gut microbiota is out of balance, it can cause digestive problems like constipation, diarrhea, and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). In addition, a lack of probiotics in the diet can lead to an overgrowth of harmful bacteria in the gut, which can cause inflammation and damage to the gut lining. This can lead to a condition called leaky gut, which allows toxins and other harmful substances to leak into the bloodstream.
Incorporating probiotics into the diet can also help to boost the immune system, as 70-80% of immune cells are located in the gut. Probiotics have been shown to reduce the risk of infections, allergies, and other immune-related diseases.
Probiotics are important for promoting a healthy digestive system and overall health. By consuming probiotic-rich foods, individuals can improve their digestion, boost their immune system, and reduce the risk of digestive problems and related health issues.
Internal link: For those who suffer from digestive problems, there are many ways to aid digestion. You can read our article on food for digestive problems for more information.
Probiotic Food Sources
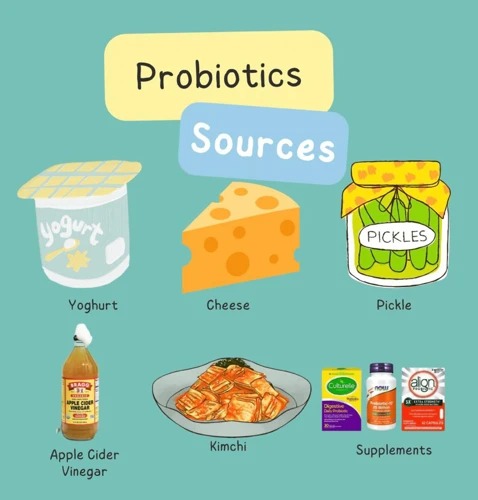
Probiotics are live bacteria and yeasts that are considered good for the body and are essential for maintaining a healthy digestive system. There are many food sources from which one can get good probiotics.
Yogurt: Yogurt is one of the most well-known and easily accessible sources of probiotics. It contains live and active cultures, including Lactobacillus bulgaricus and Streptococcus thermophilus, which help to break down lactose and make it easier for the body to digest.
Kefir: Kefir is a fermented milk drink that is similar to yogurt but with a thinner consistency. It contains a great source of beneficial bacteria and yeast which aid digestion and boost the immune system.
Sauerkraut: Sauerkraut is a traditional German dish made from fermented cabbage. It contains many strains of good bacteria such as Lactobacillus acidophilus and Lactobacillus plantarum. It is also a great source of vitamins C and K.
Kombucha: Kombucha is a fermented tea that contains live bacteria and yeast. It is known for its detoxifying properties and is an excellent source of antioxidants. It can be consumed on its own or mixed with other beverages.
Kimchi: Kimchi is a Korean dish made from fermented vegetables such as cabbage, radish, and scallions. It is a great source of probiotics and vitamins A, B, and C. It has a unique flavor and can be eaten on its own or as a condiment.
Miso: Miso is a Japanese seasoning made from fermented soybeans, often used to make soup. It is rich in probiotics, protein, and vitamins B and K.
Tempeh: Tempeh is a soy-based product that is high in protein and contains many beneficial bacteria. It is often used as meat substitute in vegetarian and vegan diets.
Pickles: Pickles are cucumbers that have been pickled in vinegar and salt. They are a great source of probiotics and are often used as a condiment or snack.
Traditional Buttermilk: Traditional buttermilk is a fermented dairy product that is low in fat and high in probiotics. It is often used as a base for salad dressings and smoothies.
Soft Cheese: Soft cheeses such as cheddar and gouda, are a great source of probiotics. They are often used in sandwiches and salads.
Apple Cider Vinegar: Apple cider vinegar is a fermented vinegar that contains many strains of good bacteria. It is often used in salad dressings, marinades, and as a drink mixed with water.
Incorporating probiotic-rich foods into your diet can be very easy. It can be as simple as adding a few spoonfuls of yogurt or kefir to your breakfast smoothie. Fermented foods such as kimchi and sauerkraut can be used as toppings for salads and sandwiches. Pickles can be enjoyed as a snacking option. Miso soup and tempeh can be incorporated into main dishes. Apple cider vinegar can be used in salad dressings and marinades.
Conclusion: Consuming probiotic-rich foods on a regular basis can greatly benefit your digestive health in a natural and effective way. Incorporating these foods into your diet can be easy and delicious. For more tips about digestion, check out 10 Ways to Aid Digestion After Overeating.
Yogurt
Yogurt is a common food source that contains probiotics, which are live microorganisms that can benefit the digestive system. This dairy product is produced by the bacterial fermentation of milk, which generates lactic acid, making it tart in taste. Yogurt is known to help alleviate symptoms of lactose intolerance and has been associated with improved gut health. It can also enhance the immune system and reduce inflammation. If you are interested in learning more about the link between yoga and digestion or the impact of stress on digestion, check out our articles on yoga and digestion and stress and digestion. Additionally, if you want a creative way to incorporate yogurt into your diet, take a look at our healthy smoothie for digestion recipe.
Kefir
One of the best natural sources of probiotics is kefir. Kefir is a fermented dairy product that has a slightly tangy taste and a texture similar to yogurt. It is made by adding kefir grains, which are a combination of bacteria and yeast, to milk. These grains ferment the milk, producing a drink that is full of beneficial probiotics.
The Benefits of Kefir
Kefir is an excellent source of probiotics, which can help promote healthy digestion. In fact, kefir contains up to 61 different strains of bacteria and yeast, making it one of the most diverse probiotic sources available. Additionally, kefir is also rich in vitamins and minerals, including calcium, magnesium, and vitamin B12.
How to Use Kefir
Kefir can be used in a variety of ways, making it a versatile addition to any diet. Some people prefer to drink it straight, while others like to add it to smoothies or use it as a base for salad dressings. Kefir can also be used in place of milk in recipes, such as pancakes or muffins.
Where to Find Kefir
Kefir can be found in most health food stores and some grocery stores. It is available in both dairy and non-dairy options, such as coconut milk kefir. Additionally, kefir can also be made at home using kefir grains, which can be purchased online or from a friend who makes their own kefir.
Important Considerations
While kefir is generally safe for most people, it is important to note that it is a dairy product and may not be suitable for those with lactose intolerance or dairy allergies. Additionally, some kefir products may contain added sugar, so it is important to read the label carefully before making a purchase.
Kefir is an excellent source of probiotics and can be a great addition to any diet. Whether you prefer to drink it straight or use it in a recipe, kefir can help promote healthy digestion and provide essential vitamins and minerals to support overall health.
Sauerkraut
Sauerkraut is a type of fermented cabbage that originated in Germany. It is a good source of several beneficial probiotic strains, such as Lactobacillus plantarum and Lactobacillus brevis.
These probiotics provide a host of benefits to our digestive system, including aiding in the breakdown of food and the absorption of nutrients. In addition to this, the probiotics in sauerkraut also help to reduce inflammation in the gut and boost our immune system.
One of the best things about sauerkraut is how easy it is to incorporate into your diet. You can add it to salads, sandwiches, or even just eat it on its own as a snack. It is also a great condiment to add to meals, particularly meat dishes.
Here is a table that shows the nutritional breakdown of sauerkraut:
| Nutrient | Amount per 1 cup (142 grams) |
|---|---|
| Calories | 27 |
| Carbohydrates | 6 grams |
| Fiber | 4 grams |
| Protein | 1 gram |
| Fat | 0 grams |
| Vitamin C | 35% of the RDI |
| Vitamin K | 23% of the RDI |
| Sodium | 39% of the RDI |
| Iron | 12% of the RDI |
As you can see, sauerkraut is a low-calorie, high-fiber food that is packed with nutrients. So, add some sauerkraut to your diet and enjoy the delicious taste and digestive benefits it provides.
Kombucha
Kombucha is a fermented tea that has gained popularity in recent years due to its potential health benefits. This tea contains live probiotics that can help promote digestion and support a healthy immune system. Kombucha is also low in calories and sugar, making it a great alternative to sugary drinks.
| Probiotic Strains: | Acetobacter, Gluconacetobacter, Lactobacillus, Zygosaccharomyces |
| Other Nutrients: | Antioxidants, polyphenols, B-vitamins, enzymes |
| Possible Health Benefits: | Improved digestion, immune system support, reduced inflammation |
| How to Incorporate into Your Diet: | Enjoy as a drink or use in marinades or salad dressings |
Kombucha can be found in many health food stores and is often available in a variety of flavors. It can also be made at home using a SCOBY (symbiotic culture of bacteria and yeast) and a few simple ingredients like tea, sugar, and water. Incorporating kombucha into your diet is easy – simply enjoy as a refreshing drink, or use it as a base for dressings and marinades. With its potential health benefits and delicious flavor options, kombucha is a great addition to any probiotic-rich diet.
Kimchi
Kimchi is a traditional Korean dish that has gained immense popularity worldwide due to its unique taste and health benefits. Kimchi is a fermented vegetable dish that is made by combining cabbage, radishes, carrots, onions, garlic, and chili pepper flakes. Once the vegetables are mixed with spices, they are left to ferment for several days. During this process, the beneficial bacteria in the vegetables grow and multiply, leading to the formation of probiotics.
Kimchi is a great source of probiotics and has been shown to improve digestive function, reduce inflammation, and boost the immune system. Kimchi is also low in calories and high in vitamins and minerals such as vitamin C, vitamin K, and potassium.
Below is a table outlining the nutritional properties of kimchi:
| Nutrient | Amount per 100g |
|---|---|
| Calories | 15 |
| Carbohydrates | 3g |
| Fat | 0g |
| Protein | 1g |
| Fiber | 1g |
| Vitamin C | 18.4mg |
| Vitamin K | 21.0mcg |
| Potassium | 135mg |
Kimchi can easily be incorporated into your diet as a side dish or a condiment. It can be added to salads, sandwiches, and stir-fries for added flavor and nutrition. When purchasing kimchi, it is important to choose a brand that uses natural fermentation methods and doesn’t contain added preservatives.
Adding kimchi to your diet is an excellent way to improve your gut health and enjoy a delicious and nutritious dish.
Miso
Miso is a traditional Japanese seasoning made from fermented soybeans, rice or barley. It has a salty and umami flavor that is perfect for soups, marinades, and dressings. Miso contains a variety of beneficial microorganisms, making it a great probiotic food source.
One serving (1 tablespoon) of miso contains approximately:
| Nutrient | Amount |
|---|---|
| Calories | 34 |
| Protein | 2 grams |
| Fat | 1 gram |
| Carbohydrates | 4 grams |
| Fiber | 1 gram |
| Sodium | 573 milligrams |
| Probiotic microorganisms | Lactobacillus, Pediococcus, and Leuconostoc |
These probiotic microorganisms in miso can help improve digestion and boost the immune system. Additionally, miso contains antioxidants and anti-inflammatory compounds.
There are several types of miso available, including white (shiro), yellow (shinshu), red (aka), and brown (genmai). White miso has a milder flavor and is great for dressings and sauces, while red miso has a stronger and saltier flavor that is perfect for soups.
To incorporate miso into your diet, try making miso soup or adding it to salad dressings or marinades. Just be sure not to boil miso, as high heat can kill the beneficial microorganisms. Instead, add miso to hot (but not boiling) liquids or use it as a finishing touch to your dish.
Miso can also be found in the refrigerated section of most health food stores and supermarkets. Look for miso that is unpasteurized, as pasteurization can kill the beneficial bacteria.
Tempeh
Tempeh is a traditional Indonesian soy product that has gained popularity as a plant-based protein source in recent years. It is made by fermenting cooked soybeans with a type of fungus called Rhizopus oligosporus.
Nutritional Value of Tempeh:
Tempeh is a good source of protein, fiber, iron, and calcium. It also contains probiotics that help to promote gut health.
Here is a table that shows the nutritional content of a 3-ounce (85-gram) serving of tempeh:
| Nutrient | Amount per 3 ounces (85 grams) |
|---|---|
| Calories | 162 |
| Protein | 15 grams |
| Fiber | 4 grams |
| Iron | 2.3 mg |
| Calcium | 92 mg |
| Probiotics | Varies based on fermentation process |
Health Benefits of Tempeh:
In addition to being a good source of nutrients, tempeh also has several health benefits. The probiotics found in tempeh can help to improve digestion and boost the immune system. It may also have a positive effect on cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of heart disease.
How to Incorporate Tempeh into Your Diet:
Tempeh has a nutty flavor and firm texture, making it a versatile ingredient that can be used in a variety of dishes. It can be marinated, grilled, stir-fried, or crumbled for use in salads or tacos.
Here are a few recipe ideas for incorporating tempeh into your diet:
– Tempeh stir-fry with vegetables and brown rice
– Tempeh bacon for a plant-based breakfast option
– Tempeh and avocado sandwich on whole grain bread
– Tempeh crumbles for tacos or chili
Caution:
It is important to note that tempeh is a fermented food and should be stored properly to avoid spoilage. It should also be cooked thoroughly before consumption to avoid any potential health risks.
Pickles
Pickles are one of the lesser-known sources of probiotics, but they are a great addition to any diet. Pickles are cucumbers that have been soaked in vinegar or brine, along with various spices and herbs. The fermentation process used to produce pickles creates the ideal environment for good bacteria to grow, making them a great source of probiotics.
Benefits of Pickles as a Probiotic Source
Pickles are rich in probiotics, which can offer several benefits, including improved digestion, boosted immune function, and better nutrient absorption. They are also low in calories and high in fiber, making them an excellent option for those trying to lose weight or maintain a healthy weight. Additionally, pickles are a good source of vitamin K, which is important for bone health.
Types of Pickles
There are several types of pickles available, including dill, sweet, and bread and butter pickles. Dill pickles are the most common and are made with dill and garlic, giving them a tangy taste. Sweet pickles, on the other hand, are made with sugar, giving them a sweeter taste. Bread and butter pickles have a sweet and sour taste and are typically made with onions and celery seed.
How to Incorporate Pickles into Your Diet
Pickles can be eaten as a snack, added to sandwiches or salads, or used as a condiment for burgers and hot dogs. They can also be chopped up and added to relish, hummus or tzatziki sauce for an extra dose of probiotics. It’s important to note that pickles can be high in sodium, so those watching their salt intake should consume them in moderation.
Pickles are an excellent source of probiotics that can offer several health benefits. They are a delicious and easy-to-incorporate addition to any diet and can be enjoyed in a variety of ways.
Traditional Buttermilk
Traditional buttermilk is an excellent source of probiotics that can help improve digestion. This type of buttermilk is different from what is commonly found in grocery stores, which is actually a cultured milk product, rather than a byproduct of butter-making.
How is Traditional Buttermilk Made?
Traditional buttermilk is made by fermenting the liquid that remains after butter is churned from cream. This liquid is rich in lactic acid bacteria, which are probiotics that help break down food in the gut.
Probiotic Content of Traditional Buttermilk
Traditional buttermilk is a rich source of several strains of lactic acid bacteria, including Lactococcus lactis, Lactobacillus casei, and Streptococcus thermophilus. These strains have been shown to have a variety of health benefits, such as improving lactose digestion and boosting the immune system.
To showcase the probiotic content of traditional buttermilk, here is a table comparing the probiotic content of traditional buttermilk to other probiotic-rich foods:
| Food | Probiotic Strains |
|---|---|
| Traditional Buttermilk | Lactococcus lactis, Lactobacillus casei, Streptococcus thermophilus |
| Yogurt | Lactobacillus bulgaricus, Streptococcus thermophilus |
| Sauerkraut | Lactobacillus plantarum, Leuconostoc mesenteroides, Pediococcus pentosaceus |
| Kombucha | Saccharomyces boulardii, Lactobacillus acidophilus, Bifidobacterium bifidum |
Health Benefits of Traditional Buttermilk
Consuming traditional buttermilk may benefit digestion due to the high concentration of probiotics. The probiotic strains found in traditional buttermilk have been shown to improve lactose digestion, reduce inflammation in the gut, and strengthen the immune system. Additionally, traditional buttermilk is a good source of several key nutrients, such as calcium, potassium, and vitamin B12.
Incorporating traditional buttermilk into your diet can be a healthy way to add probiotics and nutrients to your meals. It can be used in place of regular milk in recipes or enjoyed as a refreshing drink.
Soft Cheese
Soft cheese, like brie, camembert, and feta, are also fantastic sources of probiotics. These cheeses are made by a fermentation process, which allows beneficial bacteria to grow and thrive. During this process, lactose in the milk is transformed into lactic acid, creating the tangy flavor characteristic of these cheeses. The fermentation process also creates a perfect environment for probiotics to thrive.
Below is a table with some examples of soft cheeses that are good sources of probiotics:
| Cheese | Probiotic Strains |
|---|---|
| Brie | Lactobacillus plantarum, Lactococcus lactis, Leuconostoc mesenteroides |
| Camembert | Lactobacillus casei, Lactobacillus plantarum, Lactococcus lactis, Penicillium camemberti |
| Feta | Lactobacillus casei, Lactobacillus plantarum, Lactococcus lactis, Streptococcus thermophilus |
When choosing a soft cheese, it is important to select those that are made using traditional methods, as these are more likely to contain live probiotics. Additionally, be sure to check the ingredients list and avoid cheeses that contain added preservatives or stabilizers.
Soft cheeses can be enjoyed on their own or incorporated into a variety of dishes, such as salads, sandwiches, and omelets. Whether eaten as a snack or part of a meal, soft cheeses are a delicious way to add probiotics to your diet.
Apple Cider Vinegar
One of the lesser known sources of probiotics is apple cider vinegar. While it may not be as popular as yogurt or kefir, apple cider vinegar is still worth considering as part of a probiotic-rich diet.
The reason apple cider vinegar is a source of probiotics is that it is made through a fermentation process that involves bacteria and yeast. During this process, acetic acid bacteria are formed, which are a type of probiotic.
In addition to being a source of probiotics, apple cider vinegar is also known for its many health benefits. It has been claimed to help with weight loss, improve heart health, and even reduce the risk of cancer. However, some of these claims are not fully supported by scientific evidence.
When choosing apple cider vinegar, it is important to look for products that contain the “mother” – a cloudy substance that forms naturally during the fermentation process. This is where many of the beneficial bacteria and enzymes are found.
To incorporate apple cider vinegar into your diet, you can use it as a salad dressing, mix it into smoothies, or dilute it in water and drink it as a tonic. However, it is important to note that apple cider vinegar is highly acidic, so it should always be diluted to avoid damaging tooth enamel or causing digestive upset.
While apple cider vinegar may not be the most well-known source of probiotics, it is still a viable option for those looking to add more beneficial bacteria to their diet.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Source of probiotics | Claims of health benefits not fully supported by scientific evidence |
| Contains the “mother” | Highly acidic |
| Versatile – can be used as a salad dressing, added to smoothies, or consumed as a tonic | Should be diluted to avoid damaging tooth enamel or causing digestive upset |
How to Incorporate Probiotics into Your Diet
When it comes to incorporating probiotics into your diet, there are a few different approaches you can take. One option is to take probiotic supplements, which are available in capsule, tablet, and powder forms. However, another option is to get your probiotics from whole foods. Here are some tips for incorporating probiotic-rich foods into your diet:
1. Supplements vs. Whole Foods: While supplements can be a convenient way to get a concentrated dose of probiotics, there are advantages to getting your probiotics from whole foods. Whole foods not only provide a variety of different beneficial bacteria strains, but they also offer other important nutrients such as fiber, vitamins, and minerals. Additionally, the live bacteria in whole foods are able to survive the acidic environment of the stomach better than some strains in supplements.
2. Tips for Adding Probiotic Foods to Your Diet: Here are some suggestions for incorporating probiotic-rich foods into your meals and snacks:
– Start your day with a cup of kefir or yogurt topped with fresh fruit and granola.
– Add sauerkraut or kimchi to a sandwich or wrap for a zesty, probiotic-packed kick.
– Sip on a glass of kombucha instead of soda or juice.
– Use miso to season soups, stews, and dressings.
– Top salads with pickled vegetables or crumble a bit of soft cheese on top.
– Swap traditional buttermilk for sour cream or mayonnaise in dips and dressings.
– Enjoy a slice of tempeh or add it to stir-fries or grain bowls.
3. Probiotic-Rich Recipes: If you’re looking for more ways to incorporate probiotics into your diet, try these recipes:
– Overnight oats with yogurt and berries
– Kimchi fried rice
– Kefir smoothie bowl
– Miso-glazed salmon
– Kombucha vinaigrette
– Sauerkraut and sausage skillet
Incorporating probiotics into your diet can have a positive impact on your digestive health. By choosing a variety of probiotic-rich foods, you can promote the growth of beneficial bacteria in your gut and support a healthy microbiome.
Supplements vs. Whole Foods
As you begin to explore the world of probiotics, you may come across many different options, including supplements and whole foods. While both options can provide benefits for digestive health, many people wonder which one is best. Supplements offer a convenient and concentrated form of beneficial bacteria, while whole foods offer a natural and diverse selection of probiotic strains. However, it’s important to understand the potential advantages and limitations of both supplements and whole foods before making a choice.
Tips for Adding Probiotic Foods to Your Diet
Incorporating probiotic foods into your diet can be a great way to improve digestion and overall gut health. Here are some tips for adding probiotic foods to your daily routine:
- Start slow: If you’re new to probiotic foods, it’s best to start slowly and gradually build up your intake. Begin with one serving per day and gradually increase as your body adjusts.
- Experiment with different foods: There are many different types of probiotic foods to choose from, so don’t be afraid to try something new. Experiment with different flavors and textures to find what you enjoy the most.
- Buy high-quality products: When purchasing probiotic foods, look for high-quality options that contain live, active cultures. Choose products that have been stored properly and are not past their expiration date.
- Make your own: Another great way to incorporate probiotic foods into your diet is by making your own. This can be a fun and rewarding process, and you’ll have control over the ingredients and fermentation process.
- Pair with prebiotic foods: Prebiotic foods help feed the good bacteria in your gut, making it easier for probiotics to thrive. Add prebiotic-rich foods like onions, garlic, and asparagus to your meals to maximize the benefits of probiotic foods.
- Be consistent: Incorporating probiotic foods into your diet is most effective when done consistently over time. Make it a part of your daily routine to ensure you’re getting the most out of these beneficial foods.
By following these tips, you can easily add more probiotic-rich foods into your diet and improve your digestive health.
Probiotic-Rich Recipes
Incorporating probiotic-rich recipes into your diet can be a delicious way to improve your gut health. Here are some easy and tasty recipes to try:
- Greek Yogurt Parfait: Layer Greek yogurt with fresh berries, nuts, and a drizzle of honey for a tasty and probiotic-packed breakfast or snack.
- Kefir Smoothie: Blend kefir with your favorite fruits and spinach for a refreshing and nutrient-dense smoothie.
- Sauerkraut Salad: Mix sauerkraut with cucumbers, avocado, and a vinaigrette dressing for a crunchy and probiotic-rich salad.
- Kombucha Spritzer: Mix kombucha with sparkling water and a splash of fruit juice for a refreshing and gut-healthy drink.
- Kimchi Fried Rice: Sauté cooked rice with kimchi, vegetables, and scrambled eggs for a flavorful and probiotic-packed meal.
- Miso Soup: Simmer miso paste with vegetables and tofu for a warm and comforting soup that’s also high in probiotics.
By incorporating these easy and delicious probiotic-rich recipes into your diet, you can improve your gut health and feel your best. It’s important to remember that while supplements can be beneficial, consuming probiotics through whole food sources is generally the most effective way to reap the benefits.
Conclusion
In conclusion, it is clear that probiotics play a crucial role in maintaining a healthy digestive system. The beneficial bacteria found in probiotics help to balance the gut microbiome, support immune function, and aid in digestion. It is important to note that a healthy diet consisting of probiotic-rich foods is essential for optimal gut health.
While supplements may be beneficial in certain circumstances, it is always best to obtain nutrients from whole food sources whenever possible. Incorporating probiotic-rich foods such as yogurt, kefir, and sauerkraut into your diet is relatively simple and can have a significant impact on your overall health.
It is important to keep in mind that not all probiotics are created equal. When selecting probiotic supplements or foods, be sure to choose products that contain live, active cultures and are free from added sugars and artificial ingredients.
Incorporating probiotics into your diet can be as simple as adding a serving of yogurt to your breakfast or incorporating fermented vegetables into your daily meals. With a little creativity and experimentation, anyone can reap the benefits of probiotics and support a healthy gut.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the benefits of probiotics?
Probiotics can improve digestive health, boost the immune system, aid in weight loss, reduce the risk of certain diseases, and improve mental health.
Who can benefit from probiotics?
Anyone can benefit from probiotics, particularly those experiencing digestive issues or looking to improve their overall health.
Are there any risks to taking probiotics?
In general, probiotics are safe for most people. However, those with compromised immune systems or serious health conditions should speak with a doctor before taking probiotics. Additionally, some people may experience mild digestive side effects such as gas and bloating when first incorporating probiotics into their diet.
Are all probiotics created equal?
No, not all probiotics are created equal. Different strains of probiotics have different benefits, and it’s important to choose a supplement or food source that contains the specific strains that are best suited for your individual needs.
Can I get enough probiotics from food sources alone?
Yes, it is possible to get enough probiotics from food sources alone, although it may be more difficult than taking a supplement. It’s important to eat a variety of probiotic-rich foods to ensure you’re getting a range of beneficial strains.
How should I store probiotic supplements?
Probiotic supplements should be stored in a dry, cool place, away from direct sunlight. It’s also important to check the expiration date and make sure the product is not expired before taking.
Can probiotics help with skin issues?
There is some evidence to suggest that certain strains of probiotics can help improve skin conditions such as acne and eczema. However, more research is needed in this area.
Can probiotics help with anxiety or depression?
There is some research to suggest that probiotics may have a positive impact on mental health, although more studies are needed. Some studies have found that certain strains of probiotics can help reduce symptoms of anxiety and depression.
Are there any dietary restrictions when taking probiotics?
There are usually no dietary restrictions when taking probiotics, although it’s important to check the label to make sure the product doesn’t contain any ingredients that you’re allergic to or intolerant of.
Can probiotics be harmful if taken in excess?
While probiotics are generally safe, taking excessive amounts can lead to digestive side effects such as gas and bloating. It’s important to follow the recommended dosage on the supplement label and not to exceed it without consulting a healthcare professional.