The human body is a complex system, with a multitude of factors that affect its overall health and functioning. One such factor is the presence of probiotics – a group of beneficial bacteria that reside in the gut and have a range of health benefits. But what exactly are probiotics, and how do they work? In this article, we’ll delve deeper into the world of probiotics, exploring their various types, benefits, and sources, as well as some precautions to keep in mind when incorporating them into your diet. So, let’s take a closer look at how these tiny superheroes can boost your immune system and improve your overall health.
What Are Probiotics?

Probiotics have gained immense popularity in recent years for their potential health benefits, but what exactly are they? Probiotics are live microorganisms that are considered as “good” or “friendly” bacteria, similar to the ones already present in our body. These bacteria are essential for maintaining a healthy gut and immune system. But, how do probiotics work? Let’s explore further. Probiotics are not a magical cure, but rather a supplement to a healthy lifestyle including diet and exercise. To learn more about healthy foods and diets to boost your immune system naturally, check out foods that boost immunity naturally or balanced diets for a healthy immune system.
How Do Probiotics Work?
Probiotics are live microorganisms that provide a wide range of health benefits to the human body. Once consumed, these microorganisms travel down to the gut microbiome where they colonize and reproduce. But, how do probiotics work? Let’s take a closer look.
The Role of Probiotics in the Gut Microbiome
The gut microbiome is a complex ecosystem where trillions of microorganisms live, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and more. This environment plays a crucial role in nutrient absorption, metabolism, and immune function.
When the gut microbiome is out of balance, it can lead to a range of health issues including digestive disorders, inflammation, and weakened immune function. This is where probiotics come in.
Probiotics work by adding beneficial bacteria to the gut microbiome, which can help to restore balance and improve overall health. They also help to reduce harmful bacteria and prevent them from colonizing in the gut.
Stimulate the Immune System
Probiotics stimulate the production of immune cells which can help to fight off infections and diseases. They also reduce inflammation in the gut, which is a common cause of weakened immune function.
Enhance Nutrient Absorption and Digestion
Probiotics can break down food in the gut and release essential nutrients which are then absorbed by the body. This can improve overall nutrient absorption and digestion.
Types of Probiotics
Probiotics come in many different strains, each with a unique set of benefits. Some of the most common strains include Lactobacillus acidophilus, Bifidobacterium bifidum, and Streptococcus thermophilus.
To get the most out of your probiotics, it’s important to choose a supplement or food source that contains a variety of strains.
By understanding how probiotics work and the benefits they provide, you can start to incorporate them into your diet for a healthier gut microbiome and improved overall health.
If you want to learn more about nutrition and the immune system, check out our related articles on stress and the immune system, antioxidants and immune strength, immune system boosting vitamin C foods, and immune boosting soups for winter.
Types of Probiotics
When it comes to probiotics, there are various types that offer different benefits. Here are some of the most common types of probiotics and their important characteristics:
| Probiotic Strain | Benefits | Food Sources |
|---|---|---|
| Lactobacillus acidophilus | May help alleviate lactose intolerance and support digestive health | Yogurt, kefir, miso, kimchi, sauerkraut |
| Bifidobacterium lactis | May improve gut health and potentially reduce inflammation | Yogurt, kefir, tempeh |
| Streptococcus thermophilus | May aid in lactose digestion and support immune function | Yogurt, kefir, cheese |
| Lactobacillus plantarum | May help reduce inflammation and improve digestive health | Miso, sauerkraut, pickles, kimchi |
| Bifidobacterium bifidum | May support immune function and potentially improve gut health | Yogurt, kefir, miso |
| Lactobacillus rhamnosus | May help reduce symptoms of diarrhea and improve gut health | Yogurt, kefir, cheese |
| Saccharomyces boulardii | May help alleviate symptoms of diarrhea and support gut health | Supplements |
It’s important to note that different probiotic strains offer different benefits, so it’s best to consume a variety of probiotics from different food sources. Additionally, it’s important to check the labels of probiotic supplements to ensure that they contain specific strains that have been shown to be effective in research studies. It’s also important to talk to your doctor before taking any new supplements, especially if you have any underlying health conditions or are pregnant or breastfeeding.
Benefits of Probiotics
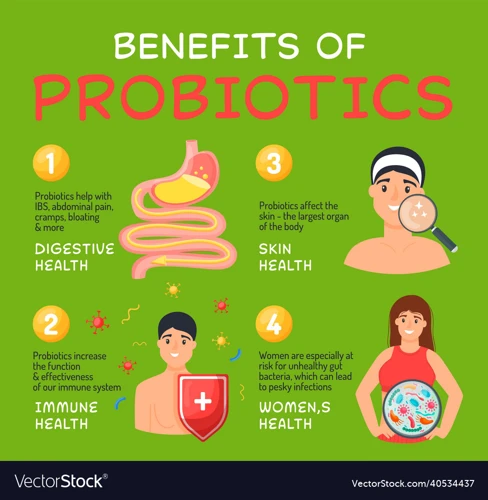
When it comes to leading a healthy lifestyle, maintaining a healthy gut is of vital importance. With the rise in popularity of probiotics, many have started incorporating these “good” bacteria into their diets. Probiotics are known for their numerous health benefits, from improving digestive health to reducing inflammation. In this section, we will dive deeper into the many advantages of including probiotics in your daily routine. So, let’s explore the impact they can have on your health!
Boosting the Immune System
Probiotics are known for their ability to boost the immune system. They do this by promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria in the gut, which in turn helps to fight off harmful infections and bacteria.
Probiotics Boost the Immune System
When you consume probiotics, they help to regulate the immune system by increasing the production of antibodies and immune cells. This can help to strengthen and enhance the immune system, increasing the body’s overall ability to fight off infections and diseases.
A study published in the Journal of Food Science and Technology found that probiotics can improve the immune response in humans by increasing the production of natural killer cells, which are responsible for fighting off infections and tumors.
Probiotics Prevent and Treat Infections
Probiotics can also help to prevent and treat infections. They are particularly useful in treating vaginal and urinary tract infections, as well as diarrhea caused by infections such as Clostridium difficile.
In a study published in the International Journal of Women’s Health, probiotics were found to be an effective treatment for bacterial vaginosis, a common bacterial infection that can cause vaginal odor and discharge.
Similarly, a study published in the Journal of Clinical Gastroenterology found that probiotics can be effective in preventing and treating diarrhea caused by Clostridium difficile.
Probiotics Reduce Inflammation in the Body
In addition to boosting the immune system, probiotics can also help to reduce inflammation in the body. Chronic inflammation is associated with a wide range of health problems, including heart disease, arthritis, and even cancer.
By promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria in the gut, probiotics can help to reduce inflammation in the body, which in turn can have a positive impact on overall health.
A study published in the British Journal of Nutrition found that probiotics can reduce inflammation in the body and improve markers of immune function.
Incorporating probiotic-rich foods into your diet can provide a wide range of health benefits, including boosting the immune system, improving digestive health, and reducing inflammation in the body.
Improving Digestive Health
Probiotics are known to have a positive impact on digestive health, specifically by improving gastrointestinal function and alleviating several digestive issues. Below are a few ways probiotics can improve digestive health:
- Reducing diarrhea – Probiotics, particularly the strains of Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium, can reduce the severity and duration of diarrhea caused by various triggers such as infections or antibiotic use. They do this by preventing harmful bacteria from taking over the gut and by producing lactic acid and other substances that inhibit the growth of harmful organisms.
- Treating irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) – Studies have shown that probiotics can alleviate symptoms of IBS, such as bloating, gas, and constipation, by improving intestinal transit time, reducing inflammation, and restoring the gut microbiome balance. Certain strains like Bifidobacterium infantis have been found to be particularly effective for IBS-D (IBS with diarrhea).
- Relieving inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) – Probiotics have shown potential in reducing inflammation and promoting healing in individuals with Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, the two major forms of IBD. The strains such as Lactobacillus plantarum and Bifidobacterium longum have been found to be beneficial in reducing gut inflammation and protecting the intestinal barrier.
- Enhancing nutrient absorption – Healthy gut bacteria help break down and absorb nutrients from food, particularly fiber, vitamins, and minerals. Probiotics can enhance nutrient absorption by increasing gut surface area, stimulating enzyme production, and improving gut motility.
Improving digestive health with probiotics can take time and patience, but including a variety of probiotic-rich foods in your diet can help ensure you are getting the right types of beneficial bacteria. Additionally, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new probiotic regimen, especially if you have a pre-existing medical condition or are taking medications.
Reducing Inflammation
Studies have shown that probiotics can help reduce inflammation in the body. Inflammation is the body’s natural response to infection, injury or irritation, but chronic inflammation can lead to serious health problems such as heart disease, diabetes, and cancer. Some types of probiotics, such as Bifidobacteria and Lactobacilli, may even help reduce markers of inflammation in the body.
| Probiotic Strain | Effect on Inflammation |
|---|---|
| Bifidobacteria bifidum | Reduces inflammation in the gut and may improve symptoms of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) |
| Lactobacillus acidophilus | May help reduce inflammation in people with rheumatoid arthritis |
| Bifidobacterium lactis | May help improve symptoms of eczema, a chronic inflammatory skin condition |
| Lactobacillus plantarum | May help reduce inflammation in the gut and improve symptoms of IBD |
While more research is needed to fully understand the role of probiotics in reducing inflammation, incorporating probiotic-rich foods into your diet may be a helpful addition to an anti-inflammatory lifestyle. Some probiotics may also improve the production of short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) in the gut, which can also help reduce inflammation.
Other Health Benefits
Probiotics not only boost the immune system and improve digestive health, but also offer a host of other health benefits1. Below are some of the lesser-known benefits of adding probiotics to your diet.
| Benefit | Description |
| Reducing depression and anxiety | Probiotics may improve mental health by reducing symptoms of depression and anxiety2. |
| Lowering blood pressure | Several studies have found that consuming probiotics may help lower blood pressure3. |
| Improved skin health | Some research suggests that probiotics may improve the health of the skin by reducing skin inflammation and acne4. |
| Reducing allergy symptoms | Studies have shown that probiotics may help reduce symptoms of allergies and eczema5. |
| Managing symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) | Probiotics may improve symptoms of IBS, such as bloating and abdominal pain6. |
| Reducing the risk of certain cancers | Research suggests that consuming certain strains of probiotics may reduce the risk of certain types of cancer, such as colon cancer7. |
While probiotics may not be a miracle cure for these health issues, they offer a potential complementary approach to conventional treatment options. As always, it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider before making any significant changes to your diet or health regimen.
Probiotic-Rich Foods

When it comes to maintaining a healthy immune system and digestive tract, probiotics can be a powerful ally. These beneficial bacteria help to keep harmful pathogens at bay and provide essential support for our overall health. But where can we find these superheroes in our diets? Fortunately, a variety of probiotic-rich foods are available, each offering unique and delicious ways to support our gut health. Let’s explore some of the best options for getting your daily dose of probiotics.
Yogurt
One of the most popular and accessible sources of probiotics is yogurt. Made by fermenting milk with live bacterial cultures, yogurt is packed with beneficial microorganisms that help support a healthy gut.
Here is a table of some of the probiotic strains commonly found in yogurt:
| Probiotic Strain | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Lactobacillus acidophilus | May help reduce symptoms of lactose intolerance and vaginal infections, as well as improve digestion and boost the immune system |
| Bifidobacterium lactis | May improve digestive health, boost the immune system, and help reduce symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome and diarrhea |
| Streptococcus thermophilus | May boost the immune system, improve digestion, and increase lactose digestion in those with lactose intolerance |
When choosing a yogurt, it’s important to look for one that contains live and active cultures. Some yogurts on the market are pasteurized or processed in a way that kills off the beneficial bacteria, so be sure to read the label carefully.
Additionally, be aware that some yogurts may contain added sugars or artificial flavors, which can counteract the health benefits of the probiotics. Look for plain or Greek yogurt, and consider adding your own natural sweeteners, such as fruits or honey, if desired.
Kefir
Kefir is a sour, yogurt-like drink that originated from the Caucasus Mountains in Eastern Europe. It is made by fermenting kefir grains, which are clusters of yeast and bacteria, in milk. This process leads to the formation of a drink that is rich in probiotics and other nutrients.
| Nutrient | Amount per Serving |
| Probiotics | Varies, but can contain up to 61 different strains of bacteria and yeast |
| Calcium | 10% of the Daily Value (DV) |
| Vitamin K2 | 30% of the DV |
| Phosphorus | 5% of the DV |
| Protein | 6 grams |
Kefir is a good source of probiotics, and it can contain up to 61 different strains of bacteria and yeast. This variety is a significant advantage over other probiotic sources, as it helps promote a diverse gut microbiome. Additionally, kefir is rich in calcium, which is crucial for maintaining healthy bones and teeth. It also contains vitamin K2, which plays a role in calcium metabolism, and phosphorus, which is important for energy production and healthy bones.
Kefir is a versatile ingredient that can be used in a wide range of recipes. It can be enjoyed as a refreshing drink on its own or used as a base for smoothies. It can also be added to dips, sauces, and dressings, or even used as a marinade for meat. Those who are lactose-intolerant can try making kefir with non-dairy milk alternatives, such as coconut milk or almond milk.
Kefir is an excellent addition to a healthy diet. Its probiotic content and nutrient density make it a ‘superhero food’ for promoting good gut health and supporting overall wellbeing.
Sauerkraut
Sauerkraut is a type of fermented cabbage that originated in Germany. It is a traditional food that has been enjoyed for centuries, and is rich in probiotics that can benefit the immune and digestive systems.
Health Benefits
Sauerkraut is a great source of probiotics, which are beneficial bacteria that can promote gut health and boost the immune system. The fermentation process involved in making sauerkraut naturally creates lactobacillus bacteria, which promote the growth of other beneficial bacteria in the gut. This can improve digestion, reduce inflammation, and even improve mental health.
In addition to being a good source of probiotics, sauerkraut is also high in vitamins C and K, as well as fiber. These nutrients can support overall health and wellbeing.
How to Incorporate Sauerkraut into Your Diet
Sauerkraut is a versatile food that can be added to a variety of dishes. Here are a few ideas:
| Food | Ideas for Adding Sauerkraut |
|---|---|
| Sandwiches | Add sauerkraut to a Reuben or other deli-style sandwich for a tangy crunch. |
| Salads | Add sauerkraut to a green salad for extra flavor and a probiotic boost. |
| Sides | Top roasted potatoes with sauerkraut and a dollop of sour cream for a tasty side dish. |
| Entrees | Use sauerkraut as a topping for hot dogs or sausages, or mix it into a casserole for added flavor and nutrition. |
Precautions When Eating Sauerkraut
While sauerkraut is generally safe to eat, it is high in sodium, so people on a low-sodium diet should consume it in moderation. It is also important to choose unpasteurized sauerkraut, as pasteurization can destroy the beneficial bacteria. Additionally, some people may experience gas or bloating when first introducing probiotics into their diet, so it is important to start slowly and gradually increase intake.
Kombucha
Kombucha is a fermented drink made from tea, yeast, and bacteria. It has gained popularity in recent years as a tasty way to incorporate probiotics into your diet. Kombucha contains several strains of beneficial bacteria and yeast, including Acetobacter, Gluconacetobacter, Lactobacillus, and Zygosaccharomyces.
Benefits of Kombucha
Kombucha has been touted for its numerous health benefits, including improving digestion, boosting immunity, and reducing inflammation. It also contains antioxidants and may have antibacterial properties.
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Improves Digestion | The probiotics in kombucha can help promote healthy gut bacteria and improve digestion. It may also aid in the breakdown of food, easing the burden on the digestive system. |
| Boosts Immunity | Kombucha’s probiotics may help stimulate the immune system, protecting against harmful bacteria and viruses. |
| Reduces Inflammation | Kombucha contains antioxidants that can help reduce inflammation in the body, potentially easing symptoms of conditions such as arthritis and allergies. |
| Antibacterial Properties | Some studies suggest that kombucha may have antibacterial properties, helping to fight off harmful bacteria in the body. |
How to Incorporate Kombucha into Your Diet
Kombucha can be found at most health food stores and some supermarkets. It is also easy to make at home using a Kombucha kit. However, it is important to be cautious when brewing kombucha at home, as improper fermentation can lead to contamination.
When choosing a kombucha, look for one with minimal added sugars and a high number of live probiotic cultures. Kombucha can be enjoyed on its own or used as a mixer in cocktails and other beverages.
As with all probiotic-rich foods, it is important to incorporate them regularly into your diet to experience the benefits. Start with small servings and gradually increase to avoid any digestive discomfort.
Precautions When Taking Kombucha
While kombucha is generally considered safe, there are some precautions to take. It is important to avoid consuming too much kombucha, as it can lead to excess sugar and calorie intake. It is also important to be cautious when brewing kombucha at home, as improper fermentation can lead to contamination.
As with all dietary changes, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional before incorporating kombucha into your diet, especially if you are pregnant, nursing, or have any underlying health conditions.
Kimchi
Kimchi is a traditional Korean dish that is made from fermented vegetables, particularly Napa cabbage. It is typically spicy, tangy, and has a slightly sour taste that many people find addictive. Kimchi is a probiotic-rich food that can be beneficial to your gut health and immune system.
Here are some of the benefits of adding kimchi to your diet:
- Improved digestion: Kimchi is loaded with beneficial bacteria that help to break down food, making it easier to digest. This can help to reduce the risk of digestive issues such as bloating, constipation, and diarrhea.
- Boosted immunity: The probiotics in kimchi can also help to boost your immune system by increasing the production of antibodies and enhancing the activity of immune cells.
- Reduced inflammation: Studies have shown that consuming probiotic-rich foods like kimchi can help to reduce inflammation in the body, which is a contributing factor to many chronic diseases.
- Improved heart health: Kimchi contains garlic and ginger, both of which have been shown to have heart-protective effects. The probiotics in kimchi may also help to reduce cholesterol levels in the blood.
How to incorporate kimchi into your diet:
Kimchi is a versatile food that can be added to a variety of dishes, or eaten on its own as a snack. Here are some ideas for incorporating kimchi into your diet:
- Top your rice bowl with a few spoonfuls of kimchi for added flavor and nutrition.
- Use kimchi as a topping for tacos, quesadillas, or other Mexican-inspired dishes.
- Add kimchi to your scrambled eggs or omelet for a spicy and flavorful breakfast.
- Serve kimchi as a side dish to grilled meats or fish.
- Eat kimchi straight out of the jar as a healthy and satisfying snack.
Precautions when consuming kimchi:
While kimchi is generally considered safe and nutritious, there are a few precautions to keep in mind:
- Kimchi is high in sodium, so people on a low-sodium diet should consume it in moderation.
- Some people may have an allergic reaction to the spices or other ingredients in kimchi.
- Because kimchi is a fermented food, it may contain trace amounts of alcohol. People who are abstaining from alcohol should be aware of this.
Kimchi is a delicious and healthy food that can be a great addition to a balanced diet.
Miso
One probiotic-rich food that is popular in Japanese cuisine is miso. This paste is made by fermenting soybeans with a fungus called koji, along with rice or other grains. The result is a savory, umami flavor that can add depth to soups, marinades, and dressings.
Miso is also rich in a type of probiotic called lactobacillus, which has been shown to promote digestive health and boost the immune system. In fact, miso soup is often recommended as a natural remedy for colds and flu due to its immune-boosting properties.
One tablespoon of miso contains approximately 2 billion CFUs (colony forming units) of probiotics. It also contains other beneficial compounds such as antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals.
Here is a table outlining the nutritional content of one tablespoon of miso:
| Nutrient | Amount per tablespoon |
|---|---|
| Calories | 35 |
| Protein | 2.2 grams |
| Fat | 1.4 grams |
| Carbohydrates | 4.4 grams |
| Sodium | 711 milligrams |
| Lactobacillus bacteria | 2 billion CFUs |
When using miso, it’s important to note that it is often high in sodium, so it’s best to consume it in moderation. Look for organic miso paste that has been naturally fermented, as some commercial brands may contain additives, preservatives, or non-organic soybeans.
Miso can be a delicious and nutritious way to incorporate probiotics into your diet. Try adding it to soups, stir-fries, and salad dressings for a boost of flavor and gut-friendly bacteria.
Pickles
Pickles are a popular and tasty way to add probiotics to your diet. Made from cucumbers that have been soaked in a brine of water, vinegar, and salt, pickles are a great source of beneficial bacteria.
Here are some benefits of eating pickles:
- Pickles are low in calories and high in fiber, making them a great snack for weight loss and digestive health.
- They contain vitamins and minerals like vitamin C, potassium, and iron.
- Pickles are a good source of antioxidants, which can help protect your cells from damage caused by free radicals.
- They may help regulate blood sugar levels and lower the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
- Pickles are also a natural diuretic, helping to flush out excess fluids and toxins from your body.
When choosing pickles, look for:
- Unpasteurized options, which will contain more live bacteria.
- Low sodium options, as too much salt can be detrimental to your health.
- Avoid pickles that have been made with vinegar that contains added sugars, as this can counteract the beneficial effects of the probiotics.
How to incorporate pickles into your diet:
- Enjoy pickles as a snack on their own or add them to your sandwiches and salads.
- Try making your own pickles at home using cucumbers and a probiotic-rich brine of water, vinegar, and salt.
- Use pickle juice as a natural marinade for meats, vegetables, and tofu.
- Add chopped pickles to dips and spreads like hummus or tzatziki for an extra boost of flavor and nutrition.
Pickles may not be the first food that comes to mind when you think of probiotics, but they are a delicious and easy way to boost your gut health. Just make sure to choose the right kind and enjoy them in moderation as part of a balanced diet.
Tempeh
Tempeh is a lesser-known but powerful probiotic food that is made from fermented soybeans. It has been a staple in Indonesian cuisine for centuries, and is becoming more popular in Western countries due to its health benefits. Here are some reasons why you should consider adding tempeh to your diet:
– Probiotic Powerhouse: Tempeh contains a wide variety of probiotic strains, including Bifidobacterium bifidum, Lactobacillus acidophilus, and Streptococcus thermophilus. These probiotics help to promote a healthy balance of bacteria in the gut, which can improve digestive health and boost the immune system.
– Source of Plant-Based Protein: Tempeh is a great source of plant-based protein, which is important for building and repairing tissues in the body. A 100-gram serving of tempeh contains about 18 grams of protein, which is more than tofu or other vegetarian protein sources.
– Rich in Nutrients: Tempeh is also a good source of many important vitamins and minerals, including iron, calcium, and vitamin B12. These nutrients are important for maintaining healthy bones, supporting nerve function, and producing red blood cells.
– Versatile in the Kitchen: Because of its nutty flavor and firm texture, tempeh can be used in a variety of dishes, including stir-fries, sandwiches, and salads. It can be sliced, diced, or crumbled to add protein and flavor to any meal.
If you are new to tempeh, try incorporating it into your diet by marinating it in your favorite sauce or seasoning before cooking it. You can also crumble tempeh and use it as a plant-based substitute for ground meat in your favorite recipes. And as with any new food, start with small amounts to avoid any digestive discomfort.
Other Foods to Try
Aside from the main probiotic-rich foods already mentioned, there are several other options to try. Here are some additional foods to consider adding to your diet:
- Apple cider vinegar: contains both probiotics and prebiotics, making it a double-whammy for gut health. Use it to dress salads or drink diluted in water.
- Natto: a traditional Japanese food made from fermented soybeans. It is a great source of the probiotic Bacillus subtilis.
- Raw cheese: cheese made from raw, unpasteurized milk can contain high levels of probiotics, but be careful to choose a reputable source to avoid the risk of foodborne illness.
- Sourdough bread: made with a fermented dough starter, sourdough bread can contain lactobacillus, a common probiotic strain.
- Dark chocolate: contains polyphenols which can act as food for probiotic bacteria in the gut.
Keep in mind that while these foods may contain probiotics, they may not have the same amount or variety as the main probiotic-rich foods. It’s also important to listen to your body and take note of any digestive reactions when introducing new foods into your diet.
How to Incorporate Probiotics into Your Diet
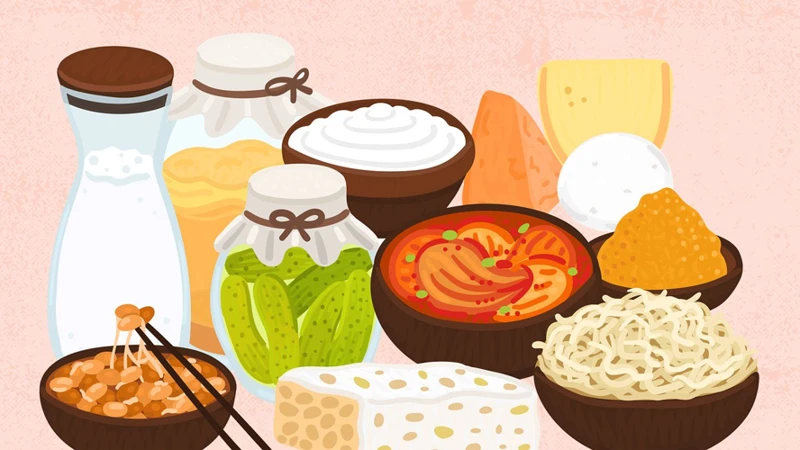

Now that you understand the many benefits of probiotics, you may be wondering how to incorporate them into your daily diet. Fortunately, adding probiotics to your meals can be relatively easy and delicious. From yogurt to tempeh, there are many probiotic-rich foods to choose from, and you can also consider taking supplements. However, it’s important to keep a few things in mind when incorporating probiotics into your diet, such as pairing them with prebiotics and avoiding certain foods that can harm healthy bacteria. In this section, we will guide you on how to add these superhero foods to your meals for optimal health.
Choose the Right Probiotic Foods and Supplements
When it comes to choosing the right probiotic foods and supplements, there are a few things to keep in mind. Here are some tips to help guide your choices:
- Look for specific strains: Different strains of probiotics have different health benefits, so it’s important to choose a product that contains strains that have been shown to be effective for your particular health concern. For example, if you’re looking to boost your immune system, you might want to look for a supplement that contains Lactobacillus rhamnosus or Bifidobacterium lactis.
- Choose products with high CFU counts: CFUs, or colony-forming units, are a measure of the number of viable bacteria in a product. To get the most benefit from your probiotic supplement or food, look for products with high CFU counts. A minimum of 10 billion CFUs per serving is a good starting point.
- Consider the delivery method: Some probiotic supplements are shelf-stable, while others need to be refrigerated to maintain their potency. Decide which delivery method is most convenient for you, and choose a product that fits the bill.
- Check the expiration date: Probiotic supplements and foods have a limited shelf life, and their effectiveness can diminish over time. Be sure to check the expiration date on any product you’re considering to ensure that it’s still active.
- Choose whole foods: When it comes to getting probiotics from your diet, it’s best to choose whole, nutritious foods that naturally contain probiotics. This includes fermented foods like yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and kimchi.
By choosing the right probiotic foods and supplements, you can ensure that you’re getting the right strains in the right amounts to help support your immune system and overall health.
Combine Probiotic Foods with Prebiotic Foods
Incorporating prebiotic foods is essential when consuming probiotics. Prebiotics are indigestible fibers that nourish the good bacteria in your gut. By consuming both probiotic and prebiotic foods together, you can ensure that the beneficial bacteria in your gut have the proper nutrition to thrive.
Examples of prebiotic foods include:
- Asparagus
- Garlic
- Onions
- Bananas
- Apples
- Legumes
Including these foods in your diet along with probiotic-rich foods can help boost the number of good bacteria in your gut and promote better overall digestive health.
Another benefit of combining probiotic and prebiotic foods is improved absorption of nutrients. The good bacteria in your gut play an important role in breaking down and absorbing nutrients from the foods you eat. By optimizing the number of good bacteria with a combination of probiotics and prebiotics, you can improve your body’s ability to absorb essential vitamins and minerals from your diet.
However, it is important to note that some people may experience digestive discomfort when consuming large amounts of prebiotic foods. In this case, it is recommended to gradually increase intake and also speak with a healthcare provider.
Incorporating prebiotic foods with probiotic-rich foods can assist in promoting healthy gut bacteria, digestive health, and nutrient absorption.
Eat Probiotic Foods Regularly
It is important to incorporate probiotic-rich foods regularly into your diet in order to experience the full benefits that they offer for your immune system and digestive health. Here are some examples of probiotic-rich foods and how often you should aim to consume them:
| Probiotic Food | Recommended Frequency of Consumption |
|---|---|
| Yogurt (with live and active cultures) | Eat at least 1 serving per day |
| Kefir | Eat at least 1 serving per day |
| Sauerkraut | Eat at least 1-2 tablespoons per day |
| Kombucha | Drink one 8-ounce serving 1-3 times per day |
| Kimchi | Eat at least 1-2 tablespoons per day |
| Miso | Eat at least 1-2 teaspoons per day |
| Pickles | Eat at least 1-2 small pickles per day |
| Tempeh | Eat at least 1 serving per day |
As you can see, there are many options for probiotic-rich foods to choose from. It is important to note that consuming a variety of these foods will provide a diverse range of probiotic strains to support overall gut health. Additionally, you may want to consider taking a probiotic supplement to ensure you are getting enough beneficial bacteria. However, it is important to consult with your healthcare provider before starting any new supplements.
Avoid Foods That Kill Good Bacteria
It is important to avoid certain foods that can kill the good bacteria in your gut and undo the benefits of probiotics. Some of these foods include:
| Food | Reason |
|---|---|
| Processed foods | They are typically high in sugar, preservatives, and artificial ingredients, which can disrupt the balance of bacteria in your gut. |
| Antibiotics | While antibiotics are sometimes necessary to treat infections, they can also kill good bacteria along with the harmful bacteria. |
| Sugar | Excess sugar can feed harmful bacteria in your gut and lead to an overgrowth of bad bacteria. |
| Artificial sweeteners | Studies have shown that artificial sweeteners can disrupt the balance of bacteria in your gut and even cause glucose intolerance. |
| Alcohol | Excessive alcohol consumption can damage the lining of your gut and negatively impact the balance of bacteria. |
| Non-organic meat | Conventionally-raised animals are often given antibiotics and hormones that can kill good bacteria in your gut when you consume their meat. |
It is important to be mindful of these foods and limit your consumption of them in order to support the growth of probiotics in your gut and maintain a healthy microbiome.
Precautions When Taking Probiotics
Before incorporating any new food or supplement into your diet, it’s important to consider any potential risks and precautions. Probiotics may have numerous health benefits, but it’s important to proceed with caution. In this section, we’ll explore some of the precautions to keep in mind when taking probiotics, including potential side effects and risks, the importance of consulting your doctor, and the necessity of doing your research before trying any new product or supplement. By being informed and cautious, you can make sure that probiotics are a superhero addition to your diet without any negative consequences.
Side Effects and Risks
Probiotics have gained a lot of attention in recent years for their potential health benefits, but like any supplement or food, they do come with some potential side effects and risks. It’s important to be aware of these risks before adding probiotics to your diet, and to consult with a healthcare provider if you have any concerns.
One of the most common side effects of probiotics is digestive upset, such as bloating, gas, or diarrhea. This is often due to the introduction of new bacteria into the digestive system, which can cause a temporary disruption in the balance of gut flora. However, these symptoms usually subside within a few days to a week.
In rare cases, probiotics can cause serious infections, particularly in people with weakened immune systems. This is more likely to occur in people who have had recent surgery, are critically ill, or have other medical conditions that compromise their immune function.
Probiotics can also interact with certain medications, such as antibiotics and immunosuppressants. In some cases, this can reduce the effectiveness of the medication or cause unwanted side effects. It’s important to talk to a healthcare provider before taking probiotics if you are currently taking any medications.
Some probiotics may also trigger allergies in certain people, particularly those with a history of food allergies. Symptoms can include hives, swelling, and difficulty breathing. If you have a known allergy to a specific type of food, be sure to check the ingredients of any probiotic supplements or foods you are considering.
The risks associated with probiotics are relatively low, and most people can safely incorporate them into their diet. However, it’s always a good idea to be informed and cautious when trying any new supplement or food, and to consult with a healthcare provider if you have any concerns.
Consult Your Doctor
Before incorporating probiotics into your diet, it is important to consult with your doctor, especially if you have any underlying health conditions or if you are pregnant or breastfeeding. Consultation with a healthcare professional is crucial, as they can advise you on the best course of action based on your medical history and any medications you may be taking.
Your doctor can also help you choose the most appropriate probiotics supplement or food sources, depending on your health needs. It is essential to be aware of the potential side effects or risks associated with probiotics, such as abdominal discomfort or bloating.
Do not start taking probiotics without first consulting your doctor. They can also help you determine the appropriate dosage and duration of use, as well as identify any possible interactions between probiotics and other medications.
Additionally, if you experience any adverse symptoms after starting probiotics, such as persistent abdominal discomfort or fever, contact your doctor immediately. It may be necessary to discontinue the use of probiotics, depending on the severity of your symptoms.
Always talk to your doctor before starting any new supplements or making significant changes to your diet. This way, you can reap the full benefits of probiotics while ensuring your overall health and well-being.
Do Your Research
When it comes to taking probiotics, it’s important to always stay informed and do your own research before making any decisions.
Here are some key steps to take when conducting your own research on probiotics:
- Read up on different strains: There are many different strains of probiotics, each with its own unique benefits. Research the specific strains that you’re interested in to learn more about their potential benefits and any potential risks or side effects.
- Look for reputable sources: Make sure that you’re getting your information from reputable sources, such as scientific journals or well-respected health websites. Be wary of sensational or exaggerated claims, and always double-check any information that you find.
- Consider the quality of the probiotics: Quality can vary widely when it comes to probiotic supplements and foods. Look for products that have been independently tested and verified to contain the strains and amounts of probiotics that they claim to have.
- Check for potential interactions: Probiotics may interact with certain medications or medical conditions. Research any potential interactions beforehand, and talk to your doctor if you have any questions or concerns.
- Learn about dosage and duration: The optimal dosage and duration of probiotic use can vary depending on the type and strain of probiotic you’re using, as well as your individual health needs. Research recommended dosages and duration of use, and consider consulting with a healthcare professional if you’re unsure.
By taking the time to do your own research and staying informed about probiotics, you’ll be better equipped to make informed decisions about incorporating probiotics into your diet and taking care of your overall health.
Conclusion
In conclusion, probiotics are a superfood group that can work wonders for your immune system and digestive health. These beneficial bacteria can even have an impact on reducing inflammation and providing other health benefits. Incorporating probiotic-rich foods like yogurt, kefir, and sauerkraut into your diet may be easier than you think. However, it’s important to choose the right type of probiotic and combine them with prebiotic foods for maximum effectiveness.
While there are some precautions to take when it comes to probiotics, such as being aware of potential side effects and consulting with a doctor, the benefits are clear. As a superhero food group, probiotics can improve and protect your immune system, leading to a healthier and happier life. So why not give these bacteria a try and see how they can benefit your health today?
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the best probiotics for a healthy gut?
The best probiotics for a healthy gut are those that contain a variety of strains, such as lactobacilli, bifidobacteria, and saccharomyces boulardii.
Are there any vegan sources of probiotics?
Yes, some vegan sources of probiotics include fermented foods like sauerkraut, kimchi, and tempeh.
Can probiotics help with weight loss?
While probiotics alone are not a weight-loss solution, some evidence suggests that they may aid in weight loss when combined with a healthy diet and exercise.
What is the difference between probiotics and prebiotics?
Probiotics are live bacteria that are beneficial for gut health, while prebiotics are non-digestible fibers that promote the growth of good bacteria in the gut.
Can probiotics help with lactose intolerance?
Yes, certain strains of probiotics can help improve digestion of lactose in individuals with lactose intolerance.
Are there any safety concerns when taking probiotics?
While probiotics are generally considered safe, individuals with weakened immune systems or serious underlying health conditions should consult with their doctor before taking probiotics.
How long does it take for probiotics to start working?
The timeline for when probiotics start to work varies depending on the individual and the specific probiotic strain. Some may notice improvements within a few days, while it may take others weeks or even months.
Can probiotics be harmful?
In some cases, probiotics can cause mild digestive discomfort or allergic reactions in sensitive individuals. However, serious negative effects are rare.
What is the recommended daily dosage of probiotics?
There is currently no established recommended daily dosage for probiotics, as the optimal intake may vary depending on the individual and specific probiotic strain.
Can probiotics help with anxiety and depression?
While more research is needed, some studies suggest that certain strains of probiotics may have a positive effect on anxiety and depression symptoms, likely due to the gut-brain connection.







