The Link Between Stress and Eating Habits

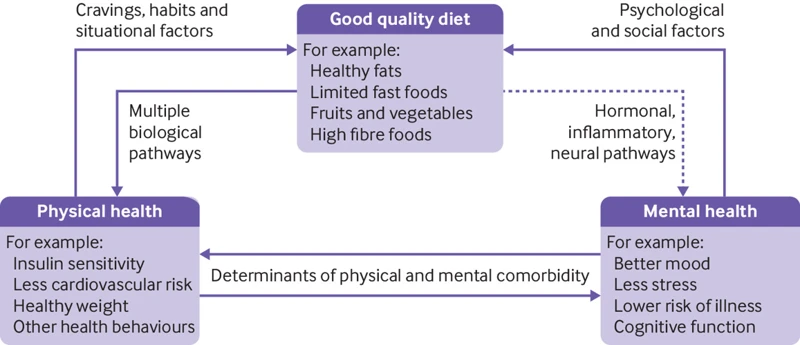
Stress and eating habits are closely interconnected, and they can have a significant impact on each other. Stressful situations, whether related to work, relationships, or health, often lead to changes in eating behavior. This is because stress triggers the release of hormones such as cortisol and adrenaline, which can affect appetite and the body’s response to food.
When we experience stress, our bodies go into a “fight or flight” response, preparing us to either fight the stressor or run away from it. This response involves the release of adrenaline, which can suppress appetite in the short term. However, once the adrenaline wears off, cortisol, a stress hormone produced by the adrenal glands, takes over. Cortisol can increase appetite, particularly for high-calorie and high-fat foods, and can cause the body to store fat around the midsection.
Emotional eating is a type of stress-eating that involves using food as a way to cope with difficult emotions rather than to satisfy physical hunger. Emotional eating can develop over time due to a variety of reasons, including chronic stress, trauma, depression, or anxiety. Overeating or eating comfort foods may offer a temporary sense of relief, but it ultimately leads to a deeper sense of guilt and shame, exacerbating the emotional distress.
Comfort foods are typically high in fat, sugar, and salt, which can activate the brain’s reward center and provide a temporary sense of pleasure and satisfaction. The combination of stress-induced cortisol release and the pleasurable effects of comfort food can make it challenging to resist cravings, even when one is not physically hungry. However, giving in to these cravings can lead to a vicious cycle of stress-eating, guilt, and shame, which can be difficult to break.
Understanding the link between stress and eating habits is crucial for developing healthy coping mechanisms and breaking unhealthy patterns. While it is natural to turn to food to soothe stress and anxiety, adopting a balanced and nutrient-dense diet, practicing mindful eating, getting enough sleep and exercise, and seeking professional help when necessary can all contribute to managing stress and reducing its impact on our eating habits. Additionally, certain herbs such as chamomile, lavender, and passionflower, as well as omega-3-rich foods, such as fatty fish, and gut-healthy foods, such as fermented vegetables, can all have stress-reducing effects, and incorporating them in one’s diet might also be helpful.
The Physiology of Stress-Eating
When you experience stress, your body releases various hormones, such as cortisol and adrenaline, which trigger a range of physiological responses. These responses include increased heart rate, elevated blood pressure, and rapid breathing, which are all part of your body’s natural “fight or flight” response. However, the effects of stress on your body extend beyond these immediate physical responses. Stress can also affect your eating habits and food choices, leading to what is often called “stress-eating”. This is when you have an increased appetite or cravings for certain types of food, particularly those high in sugar, fat, and calories. In this section, we will dive into the physiological processes that underlie stress-eating and explore some coping strategies to overcome it. If you want to learn more about foods that can help reduce stress and anxiety, check out our article on stress-reducing foods.
How Emotional Eating Develops
Emotional eating develops as a coping mechanism for dealing with difficult emotions such as stress, anxiety, depression, and even boredom. It involves using food as a way to distract oneself from unpleasant feelings, numb emotional pain, or seek pleasure and comfort. Emotional eaters often crave sugary, salty, and fatty foods that activate the brain’s reward centers and provide a temporary mood boost. However, this pleasure is short-lived and often followed by guilt, shame, and worsening of the original negative emotions.
To make matters worse, emotional eating can become a habit that is triggered automatically by specific situations or emotions, without conscious awareness or control. For example, someone who associates watching TV with snacking may reach for chips and cookies every time they turn on the TV, regardless of whether they are hungry or not. Similarly, someone who feels anxious before a big deadline may seek relief from their stress by raiding the office vending machine. These habits can be hard to break because they are reinforced by both the food’s immediate gratification and the relief from unpleasant emotions.
To break the cycle of emotional eating, it’s important to identify the underlying triggers and find alternative coping mechanisms that are healthier and more effective in the long run. This may involve seeking therapy or counseling to address the root causes of stress or emotional distress, practicing mindfulness and self-compassion, engaging in stress-reducing activities such as exercise or meditation, and creating a supportive environment that encourages healthy habits. Learning to recognize and respond to hunger and fullness cues through mindful eating can also help reduce emotional eating and its negative consequences.
Why Stress Causes Cravings for Comfort Food
Why do people crave comfort foods when they are stressed?
Stress can trigger the release of the hormone cortisol, which can increase our appetite for high-calorie and high-carbohydrate foods. This is because cortisol stimulates the production of glucose in the liver, which provides us with a burst of energy to deal with a perceived threat or danger. While this response may have been helpful for our ancestors who needed to flee from predators or hunt for food, it is less useful in our modern, sedentary lifestyle.
When we are stressed, our body also experiences a decrease in the neurotransmitter serotonin, which regulates mood, anxiety, and appetite. Low levels of serotonin can lead to feelings of depression and anxiety, which we may try to counteract by eating foods that boost our mood and give us a sense of comfort and satisfaction.
Additionally, we may have learned to associate certain foods with positive emotions and experiences from our childhood, such as memories of our favorite meals cooked by our parents or treats that we were given when we did something good. As adults, we may turn to these same foods as a way to cope with negative emotions or situations.
The combination of hormonal and psychological factors can create a powerful urge to indulge in comfort foods when we are stressed. However, it is important to find healthier ways to manage stress and satisfy our cravings without sacrificing our well-being.
Some effective strategies for reducing stress and resisting the temptation of comfort food cravings include practicing mindful eating, adopting a balanced diet, getting regular physical exercise, improving sleep hygiene, drinking herbal teas with relaxing properties, taking omega-3 supplements to support mental health, practicing meditation and mindfulness, and improving gut health through probiotics and fiber-rich foods. By taking a proactive approach to stress management, we can break the cycle of stress-eating and improve our physical and mental health.
How Stress Affects Your Food Choices

Stress can have a significant impact on your food choices. Many people turn to food as a coping mechanism when they are feeling stressed out. Unfortunately, the foods that people tend to crave when they are under stress are not always the healthiest options.
The Role of Stress in Overeating and Binge Eating
One of the most common ways that stress affects food choices is by leading to overeating and binge eating. When people are stressed out, they often turn to food as a way to comfort themselves. They may snack on high-calorie, high-fat comfort foods like chips, cookies, or ice cream to help alleviate their stress.
The problem with this type of eating is that it can quickly spiral out of control. Eating in this way can cause people to consume more calories than they need, which can lead to weight gain and other health problems.
How Stress Affects Healthy Eating Patterns
Stress can also have a negative impact on healthy eating patterns. When people are feeling the pressure of stress, they may be more likely to grab convenience foods or fast food meals instead of cooking a healthy meal at home. Busy schedules and tight deadlines can make it difficult for people to find the time or energy to prepare healthy meals.
This can lead to a lack of important nutrients that the body needs to function properly. Additionally, eating unhealthy foods can cause blood sugar levels to spike and then crash, which can lead to feelings of fatigue and mood swings.
What Happens When You Ignore Hunger or Fullness Cues Due to Stress
Stress can also cause people to ignore their body’s natural hunger and fullness cues. When people are under stress, they may be so preoccupied with other things that they don’t pay attention to their body’s signals. This can cause them to either overeat or undereat, depending on the person and the situation.
Ignoring hunger and fullness cues can lead to disordered eating patterns and may contribute to the development of eating disorders. It’s important to listen to your body and pay attention to its natural signals, even when you’re feeling stressed out.
If you’re struggling with stress-related eating habits, there are things you can do to break the cycle. Consider adopting a balanced and nutrient-dense diet that supports your physical and emotional well-being. You can also try practicing mindful eating, which involves paying attention to the taste, texture, and smell of your food, as well as your body’s hunger and fullness cues. Another strategy is to seek support from loved ones or professionals, such as a therapist or registered dietitian.
To reduce stress in general, you can try incorporating practices like exercise, meditation, and sleep hygiene into your routine. Additionally, there are herbal teas that are known for their relaxing properties and can be a great alternative to comfort foods when dealing with stress.
Read more: Balanced Diet for Stress Management
The Role of Stress in Overeating and Binge Eating
The effects of stress on eating habits can range from minor changes in food choices to more severe patterns of overeating and binge eating. When people experience stress, their bodies release hormones that can trigger hunger and cravings for foods that provide comfort and pleasure. Unfortunately, these foods are often high in calories, sugar, and fat, which can lead to weight gain and other health problems. Stress-related eating habits can create a cycle of emotional eating and guilt, which can worsen both physical and mental health. To learn more about the role of stress in overeating and binge eating, continue reading. And if you want to know how to reduce stress, you can read our article on the benefits of meditation for stress.
How Stress Affects Healthy Eating Patterns
Stress can have a significant impact on healthy eating patterns. When we are under stress, we tend to make poor dietary choices and consume high-calorie, high-fat foods that provide a temporary sense of comfort but ultimately lead to negative health consequences.
One way that stress affects healthy eating patterns is by disrupting our hormonal balance. Chronic stress can lead to an overproduction of the hormone cortisol, which can increase appetite and cause us to crave sweet, salty, and fatty foods. These types of foods provide immediate pleasure and satisfaction, which can help us temporarily forget our stressors. However, overconsumption of such foods is linked to numerous negative health outcomes, including weight gain and obesity.
Stress can also interfere with the digestion process. When we are under stress, our body goes into fight or flight mode, redirecting blood flow away from our digestive organs towards our muscles. This can cause digestive problems like bloating, constipation, and abdominal cramps, making it difficult to maintain a healthy diet.
Another way that stress affects healthy eating patterns is by reducing our motivation to engage in healthy behaviors. When we are stressed, we tend to feel overwhelmed and demotivated, which can make it harder to prioritize healthy eating and exercise habits.
How can we overcome these negative effects of stress on eating habits?
To combat stress-related unhealthy eating patterns, we need to adopt strategies that focus on stress reduction. Practicing mindfulness, incorporating regular physical activity into our routine, and getting adequate sleep are all important ways to reduce stress levels. Additionally, we can modify our diet to include more nutrient-dense foods that support our emotional and physical well-being. This includes increasing our intake of fresh fruits and vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
Certain foods and beverages have been found to have relaxing properties that can reduce stress levels. For example, omega-3 rich foods like salmon, chia seeds, and flaxseeds have been associated with reduced symptoms of anxiety and depression, while herbal teas like chamomile or lavender can calm our nerves and improve our ability to cope with stress.
By adopting a holistic approach to stress management, we can break the cycle of stress-induced unhealthy eating patterns and promote overall well-being.
What Happens When You Ignore Hunger or Fullness Cues Due to Stress
When we’re under stress, it’s not uncommon to either lose our appetite or reach for the nearest comfort food. Sometimes, however, we may ignore our body’s hunger and fullness cues altogether, leading to a host of negative consequences.
Ignoring Hunger Cues
When we ignore our natural hunger cues, we’re essentially telling our body to enter a state of famine. This can lead to:
| Physical Effects | Psychological Effects |
| – Slower metabolism | – Difficulty focusing |
| – Decreased energy levels | – Irritability |
| – Lowered immune function | – Poor decision-making |
| – Reduced ability to perform physical tasks | – Increased anxiety |
Ignoring Fullness Cues
Ignoring fullness cues can also be detrimental to our health. When we eat beyond our fullness point, we may experience:
| Physical Effects | Psychological Effects |
| – Stomach discomfort, such as bloating and gas | – Guilt and shame |
| – Digestive issues, such as acid reflux | – Negative self-talk |
| – Increased risk of weight gain and obesity | – Loss of confidence and self-esteem |
| – Disrupted sleep patterns (especially if eating close to bedtime) | – Increased stress levels |
It’s important to listen to our bodies and honor its hunger and fullness signals, even during times of stress. If you find it difficult to do so, there are several strategies that can help, such as practicing mindful eating, incorporating relaxing herbal teas into your routine, getting regular exercise, and maintaining good sleep hygiene. Additionally, incorporating stress-reducing practices such as taking omega-3 supplements or meditation can also help improve the mind-body connection and reduce stress levels, which can in turn benefit our eating habits. And, as always, if you feel that your stress-related eating habits are causing significant disturbances in your physical or mental health, seeking guidance from a healthcare professional may be beneficial.
Ignoring hunger and fullness cues can have negative effects on our physical and emotional well-being. By being mindful and listening to our bodies, we can support our health and reduce the negative impact that stress can have on our eating habits.
Consequences of Stress-Related Eating Habits

Stress-related eating habits can have numerous negative consequences on an individual’s physical and mental health. Firstly, chronic stress-related eating habits can lead to weight gain and obesity. Research has shown that stress can increase levels of the hormone cortisol, which in turn increases insulin levels and causes blood sugar levels to drop. This can result in cravings for high-calorie and high-sugar comfort foods.
Stress can also affect digestion and metabolism. When a person is under stress, their body goes into “fight or flight” mode, which slows down digestion and can cause stomach discomfort, bloating, and constipation. Chronic stress may also affect the gut microbiome, which can lead to imbalances and issues such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS).
Additionally, emotional eating can impact mental health and self-esteem. Individuals who engage in emotional eating may feel shame or guilt about their behavior, leading to a negative cycle of stress and unhealthy eating patterns. The excessive consumption of unhealthy foods and neglecting important nutrients can lead to nutrient deficiencies and related health problems.
To prevent or mitigate these negative consequences, it is crucial for individuals to manage their stress levels effectively and adopt healthy coping mechanisms. In addition to practicing mindful eating and listening to hunger and fullness cues, individuals should also focus on adopting a balanced and nutrient-dense diet to support their physical and emotional well-being. Getting enough sleep, exercise, and social support can also help reduce stress levels.
It is important for those struggling with stress-related eating habits and related health problems to seek professional help and guidance. Working with a qualified healthcare professional or nutritionist can provide valuable resources and support to develop healthy eating plans and stress management techniques. One example of a resource for gut health and stress management is /gut-health-stress-reduction/.
How Stress-Related Eating Habits Can Lead to Weight Gain and Obesity
Strong evidence suggests that chronic stress can disrupt the normal regulation of appetite and satiety, leading to overeating, binge eating, and weight gain. When we experience stress, the body releases hormones such as cortisol and ghrelin, which stimulate appetite and promote the storage of fat. As a result, we may find ourselves craving calorie-dense and high-fat foods to comfort ourselves and alleviate negative emotions. However, consuming these foods in excess can lead to obesity, which is a significant risk factor for numerous health conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, and cancer. It is crucial to understand the complex relationship between stress and eating habits to prevent the negative consequences of stress-related weight gain.
How Chronic Stress Affects Digestion, Metabolism, and Overall Health
Chronic stress can take a toll on your body, affecting various systems and processes. Here are some ways in which chronic stress can impact your digestion, metabolism, and overall health:
- Slow digestion: When you’re stressed, your body goes into “fight or flight” mode, diverting resources away from non-essential functions like digestion. This can lead to a slower digestion process, causing problems like constipation, bloating, and indigestion.
- Inflammation: Chronic stress can cause low-grade inflammation in the body, which can contribute to various health problems like heart disease, diabetes, and autoimmune disorders. Inflammation can also affect your gut health, leading to issues like leaky gut and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS).
- Imbalanced gut bacteria: Stress can alter the balance of bacteria in your gut, leading to an overgrowth of harmful bacteria and a depletion of beneficial ones. This imbalance can further exacerbate problems like inflammation and digestive issues.
- Insulin resistance: Chronic stress has been linked to insulin resistance, a condition in which your body’s cells become resistant to the hormone insulin, leading to high blood sugar. This can increase your risk of developing type 2 diabetes and other metabolic disorders.
- Slowed metabolism: Stress can cause your body to produce more cortisol, a hormone that can slow down your metabolism and lead to weight gain. Additionally, stress can disrupt your sleep, which can further contribute to metabolic issues.
- Lowered immunity: Chronic stress can weaken your immune system, making you more susceptible to infections and illnesses. This can also have a negative impact on your overall health and well-being.
It’s important to address chronic stress and its impact on your body in order to maintain good health. This can include lifestyle changes like reducing sources of stress, practicing relaxation techniques, and seeking professional help if necessary. Additionally, a balanced and nutrient-dense diet can help support your body’s functions and mitigate the negative effects of stress.
How Emotional Eating Can Impact Mental Health and Self-Esteem
Emotional eating can have a significant impact on a person’s mental health and self-esteem. People who emotionally eat are more likely to experience symptoms of depression, anxiety, and low self-esteem. They may also feel guilty or ashamed after bingeing on comfort foods, which can further exacerbate their negative emotions. This can lead to a vicious cycle, where negative emotions trigger emotional eating, which in turn leads to more negative emotions.
Emotional eating can contribute to feelings of lack of control and powerlessness. When individuals turn to food to cope with emotional distress, they give up the ability to address their problems directly. This can lead to a sense of helplessness and dissatisfaction with life. Over time, emotional eating habits can become deeply entrenched and difficult to break.
Additionally, emotional eating can lead to weight gain and obesity, which can further negatively impact a person’s self-esteem and mental health. Body dissatisfaction and negative body image can be a direct result of frequent emotional eating. This can lead to feelings of shame, embarrassment, and isolation, which can further perpetuate the cycle of emotional eating.
It’s important to address emotional eating and develop healthy coping mechanisms to manage stress and negative emotions. Building a positive self-image and developing healthy habits can improve mental health and well-being.
How to Break the Cycle of Stress-Eating
With stress eating being a common issue for many individuals, breaking the cycle can feel overwhelming. However, it is important to remember that it is possible to develop healthy eating habits and coping mechanisms to manage stress. Here are some strategies to break the cycle of stress-eating:
Identify Your Stress Triggers: Keeping a food and mood diary can help identify triggers that contribute to stress eating. Note down the times when stress eating occurs, the emotions experienced, and the foods consumed. Once identified, it becomes easier to avoid these stress triggers.
Find Healthy Coping Mechanisms: Instead of reaching for food during times of stress, try finding other healthy coping mechanisms such as meditation, deep breathing, yoga, or spending time in nature. These activities are effective in reducing stress levels and promoting emotional well-being.
Practice Mindful Eating: One of the biggest reasons why stress eating causes overeating is because the individual is not paying attention to how much they are consuming. Mindful eating is the opposite of this as it encourages individuals to be fully present in the moment and enjoy the food being consumed. Paying attention to hunger and fullness cues can help avoid overeating.
Adopt a Balanced and Nutrient-Dense Diet: Eating a balanced and nutrient-dense diet can help manage stress levels and prevent cravings for unhealthy comfort foods. Focus on consuming whole foods such as fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
Get Enough Sleep, Exercise, and Social Support: Lack of sleep, physical inactivity, and social isolation can all contribute to stress eating. Ensuring adequate sleep, exercise, and social support can help reduce stress levels and promote overall well-being.
Seek Professional Help and Guidance: If stress eating persists despite trying the above strategies, it may be necessary to seek professional help from a therapist or registered dietitian. They can provide personalized support and guidance towards developing healthy coping mechanisms and eating habits.
By implementing these strategies, it is possible to break the cycle of stress-eating and manage stress levels in a healthy and sustainable way.
Identify Your Stress Triggers and Find Healthy Coping Mechanisms
If you want to break the cycle of stress-eating, the first step is to identify your stress triggers and learn to manage them in a healthy way. Everyone has different stressors, whether it’s work deadlines, relationship conflicts, financial worries, or health problems. It’s important to take the time to reflect on your own life and pinpoint what specific things tend to cause stress for you. Once you know your triggers, you can start to develop healthy coping mechanisms that will help you deal with stress in a positive and effective way. Without this crucial step, it can be difficult to make lasting changes to your eating habits and overall well-being.
Practice Mindful Eating and Listen to Your Body’s Hunger and Fullness Signals
One way to break the cycle of stress-eating is to practice mindful eating and listen to your body’s hunger and fullness signals. Mindful eating involves paying attention to the experience of eating, without judgment or distraction, to cultivate a greater awareness of your body’s needs and preferences.
To practice mindful eating, try using the following tips:
| Tip | Description |
|---|---|
| Avoid Eating on Autopilot | Many of us eat while working, watching TV or scrolling through social media, which can distract us from our body’s signals that we are full or satisfied. |
| Eat Slowly | Chew your food thoroughly, take your time and enjoy the taste and texture of your meal. This will help you be more present during your meal and notice any signals from your body. |
| Observe Your Hunger and Fullness Cues | Check in with yourself before and after you eat. Are you really hungry, or are you eating for emotional reasons? Are you comfortably full, or are you overeating? Paying attention to these cues can help you make more intentional choices about what and when you eat. |
| Eliminate Distractions | Eating in front of the TV or computer can lead to mindless eating. Try turning off electronic devices and sitting down at a table to eat without distractions so you can pay more attention to your food and signals from your body. |
| Practice Gratitude | Take a moment before your meal to appreciate the effort that went into producing your food, and to think about how it will nourish your body. This can help bring more mindfulness to your eating experience. |
| Listen to Your Body | If you feel satisfied before finishing your plate, stop eating. If you’re still hungry, have a little more. Trust your body’s own signals of hunger and fullness to guide your food choices. |
By practicing mindful eating and listening to your body’s hunger and fullness signals, you can tune into your physical needs and avoid overeating due to stress or emotional cues. This can lead to a healthier relationship with food and a more balanced approach to eating.
Adopt a Balanced and Nutrient-Dense Diet to Support Your Physical and Emotional Well-Being
One of the best ways to combat stress-related eating habits is to adopt a balanced and nutrient-dense diet. This means incorporating a variety of whole foods that provide your body with the nutrients it needs to function properly and support your physical and emotional well-being.
One way to ensure that you are getting enough nutrients is to create a meal plan or schedule that includes a diverse selection of fruits and vegetables. These foods are packed with vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that help support your immune system and reduce inflammation in the body, which can be exacerbated by stress. Additionally, incorporating healthy sources of protein, like lean meats, fish, nuts, and beans, can help keep you feeling full and satisfied throughout the day.
Whole grains are another important component of a balanced and nutrient-dense diet. These foods are rich in fiber, which helps regulate digestion and keep you feeling full between meals. Examples of whole grains include quinoa, brown rice, whole wheat bread, and oatmeal.
It’s important to avoid highly processed and sugary foods, like candy, soda, and pastries. While these foods may provide temporary relief from stress, they can also contribute to inflammation and blood sugar imbalances, which can exacerbate stress and anxiety symptoms.
By focusing on a balanced and nutrient-dense diet, you can provide your body with the nutrients it needs to function properly and reduce the negative effects of stress on your physical and emotional health.
Get Enough Sleep, Exercise, and Social Support to Reduce Stress
One of the most effective ways to reduce stress-related eating habits is by taking care of your physical and emotional well-being. This includes getting enough sleep, engaging in regular exercise, and seeking out social support.
Getting enough sleep is crucial for managing stress levels and preventing overeating. When we don’t get enough sleep, our bodies produce more of the hormone ghrelin, which stimulates hunger, and less of the hormone leptin, which signals feelings of fullness. This can lead to overeating and weight gain. Aim for at least 7-8 hours of sleep per night to support your overall health and well-being.
Regular exercise is also beneficial for reducing stress and promoting healthy eating habits. Physical activity releases feel-good endorphins that can improve your mood and reduce stress levels. Additionally, exercise can help regulate appetite and improve sleep quality. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week, such as brisk walking, jogging, or cycling.
Another important aspect of managing stress is seeking out social support. This could mean talking to a friend or family member about what’s been bothering you, joining a support group, or seeking out counseling services. Having a strong support system can help reduce feelings of stress and anxiety, and also provide motivation and accountability for making positive changes in your life.
Taking care of your physical and emotional well-being through adequate sleep, regular exercise, and social support can be powerful tools for reducing stress-related eating habits. Incorporating these habits into your daily routine can help you feel better both physically and mentally, and ultimately lead to a healthier and happier life.
Seek Professional Help and Guidance If Necessary
When it comes to managing stress-related eating habits, seeking professional help and guidance may be necessary for some individuals. It is important to recognize when these habits have become a significant issue that may require additional support. Mental health professionals such as therapists or counselors can help individuals explore the root causes of their stress and emotional eating, and develop personalized coping strategies.
If stress-related eating habits have led to significant weight gain or other health problems, a registered dietitian may be able to provide guidance and support in developing a healthy, balanced eating plan that meets an individual’s nutrient needs and supports overall well-being. A dietitian can also help individuals recognize and address any underlying issues related to their relationship with food, such as binge eating disorder or disordered eating patterns.
In some cases, medication may be necessary to help manage chronic or severe stress and related mental health conditions. A psychiatrist or primary care physician can help individuals determine if medication is an appropriate option for them and provide ongoing support and monitoring.
It is important to remember that seeking professional help is not a sign of weakness, but rather a proactive step towards improving one’s health and well-being. With the right support and resources, individuals can overcome stress-related eating habits and live a happier, healthier life.
Conclusion
In conclusion, it is clear that stress has a significant impact on our eating habits and can lead to a variety of negative consequences. When we are stressed, our bodies release hormones that can trigger cravings for comfort foods high in sugar, fat, and salt. This can lead to overeating and binge eating, which can contribute to weight gain and obesity.
In addition to weight gain, chronic stress can also affect digestion, metabolism, and overall health. Emotional eating can also impact our mental health and self-esteem, leading to a cycle of negative emotions and unhealthy eating habits.
Fortunately, there are steps we can take to break the cycle of stress-eating. By identifying our stress triggers and finding healthy coping mechanisms, we can better manage our response to stress. Practicing mindful eating and following a balanced, nutrient-dense diet can also support our physical and emotional well-being.
To further reduce stress in our lives, we should prioritize getting enough sleep, exercise, and social support. And if necessary, seeking professional help and guidance can be a valuable resource in managing stress-related eating habits.
Overall, the key to breaking the cycle of stress-eating is to be mindful of our habits and prioritize our physical and emotional well-being. By doing so, we can establish a healthier relationship with food and manage stress in a more positive and effective way.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is stress eating and how is it different from emotional eating?
Stress eating refers to the act of consuming food as a physiological response to stress, while emotional eating is prompted by emotional cues such as sadness, anxiety, or boredom.
Why do we crave unhealthy foods during times of stress?
When we’re stressed, our brain releases hormones that increase our appetite and cravings for high-fat and high-sugar foods, as they provide a quick burst of energy and pleasure.
Can stress eating lead to weight gain?
Yes, chronic stress can contribute to weight gain, especially when accompanied by a lack of physical activity and poor food choices.
What are some common stress triggers that lead to overeating?
Some common stress triggers include work-related stress, financial stress, relationship stress, and major life changes like moving or starting a new job.
How can mindfulness help reduce stress eating?
Mindfulness can help us become more aware of our thoughts, emotions, and physical sensations, enabling us to recognize stress triggers and make more conscious food choices.
What is the link between stress eating and mental health?
Stress eating can exacerbate symptoms of anxiety and depression, and lead to a negative cycle of poor eating habits and low self-esteem.
How can sleep deprivation contribute to stress eating?
Lack of sleep can disrupt hunger and satiety signals, triggering cravings for high-fat and high-sugar foods, and influencing our food choices throughout the day.
Can exercise help reduce stress eating?
Yes, regular exercise can help reduce stress levels and improve our mood, which in turn can reduce our likelihood of engaging in stress eating.
What is the role of social support in managing stress eating?
Having a strong support system can provide emotional comfort and help us cope with stress, reducing our reliance on food as a coping mechanism.
When is it time to seek professional help for stress eating?
If stress eating is interfering with your daily life, causing significant weight gain or loss, or contributing to mental health issues, it may be helpful to seek the guidance of a healthcare professional or registered dietitian.