For years, dietitians and medical professionals have been advising people to avoid trans fats in their diet, but what exactly are trans fats, and why are they so harmful? Trans fats have been a source of confusion for many people, and it can be difficult to know where to start when it comes to understanding their role in our diet. In this article, we will break down the science behind trans fats, explore why they are harmful, and provide tips for avoiding them in your diet. So, pull up a seat and get ready to learn about the hidden dangers of trans fats.
What are Trans Fats?

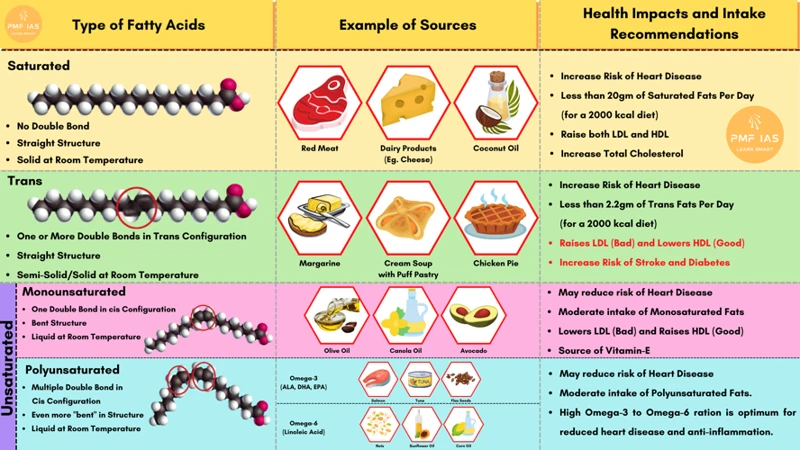
Trans fats are a type of unsaturated fat that have been manipulated through a process called hydrogenation, which turns them into a more solid form. These fats have become increasingly controversial because of their negative impact on our health, leading many countries to ban or limit their use in food production. Let’s delve deeper into what makes trans fats so harmful and how you can avoid them in your diet. To understand trans fats, it is helpful to first understand the different types of fats and their role in our health. For more information on healthy fats, check out saturated fats health truth, healthy monounsaturated fats, omega-3 fatty acids, and polyunsaturated fats diet importance.
Types of Trans Fats
Trans fats are a type of unsaturated fat that can be harmful to the body. They’re commonly found in processed foods, baked goods, and fried foods. There are two types of trans fats: artificial trans fats and naturally occurring trans fats.
Artificial trans fats are created when liquid oils are turned into solid fats through a process called hydrogenation. This process increases the shelf life and flavor stability of foods, making them a popular ingredient in processed foods. However, artificial trans fats are highly unhealthy and have been linked to numerous health problems, including heart disease, inflammation, and cancer.
Naturally occurring trans fats, on the other hand, are found naturally in some animal products, such as meat and dairy. While these trans fats are not as harmful as their artificial counterparts, they still should be consumed in moderation.
Consuming a high amount of trans fats can increase your risk of developing health problems, such as heart disease and diabetes. It’s important to limit your intake of trans fats and choose healthier fat alternatives.
Functions of Trans Fats in Food
Trans fats, while hazardous to human health, also have important functions in the food industry. They can be found in many processed foods and are used for a variety of reasons. Below is a table that outlines some of the primary functions of trans fats in food:
| Function | Description |
| Texture agent | Trans fats provide a desirable texture in baked goods and fried foods. They can help create a crispy and flaky texture in products like pie crust or fried chicken. |
| Flavor enhancement | Trans fats can enhance flavor in foods by making them taste richer and more savory. They are often added to processed foods to make them more palatable. |
| Extended shelf life | Trans fats have a longer shelf life than other fats and oils, making them a popular choice in processed foods. They can help products stay fresh for longer periods of time. |
| Stability during frying | Trans fats are stable at high temperatures, making them ideal for frying. They can be reused multiple times without breaking down, which helps save costs for restaurant owners and food manufacturers. |
Despite their usefulness in the food industry, it’s important to remember that trans fats should be avoided as much as possible in one’s diet to maintain good health. Instead, people should aim to consume healthy fats like those found in nuts, avocados, and olive oil. By making informed choices about the foods we eat, we can work to improve our overall health and wellbeing.
Why Trans Fats are Harmful
Trans fats have gained much attention in recent years as researchers have found that they pose many health risks. Many people may not be aware of the dangers of trans fats and why they should limit their consumption. In this section, we will discuss the harmful effects of trans fats. From increasing the risk of heart disease to contributing to cancer, trans fats have been linked to many health problems. It is important to understand why trans fats are harmful so that you can make informed decisions about your diet. To learn more about how much fat to eat per day, check out our article “How Much Fat Should You Eat Per Day?” However, there are healthy fat alternatives to consider as well, and you can read more about them in our article “Healthy Fat Alternatives to Butter and Margarine.”
Cholesterol and Heart Disease
Trans fats have been linked to an increased risk of heart disease, particularly in their effect on cholesterol levels. Consumption of trans fats raises levels of LDL or “bad” cholesterol while also lowering levels of HDL or “good” cholesterol. LDL cholesterol can form plaques in arteries that can lead to heart disease and stroke.
According to the American Heart Association:
- Trans fats can have a worse effect on cholesterol and heart health than saturated fats.
- Consuming as little as 2% trans fats daily can increase the risk of heart disease by 23%.
- In 2018, the World Health Organization (WHO) launched an initiative aimed at eliminating trans fats from the global food supply by 2023.
To maintain a healthy heart, it’s important to limit the consumption of trans fats. Instead, focus on incorporating healthy fats into your diet such as those found in avocados, nuts, and fish.
A diet rich in healthy fats has been shown to have a positive effect on heart health. For example, the Mediterranean diet is known for its emphasis on healthy fats such as those found in olive oil, nuts, and fish. This type of diet has been shown to lower levels of LDL cholesterol and reduce the risk of heart disease.
Additionally, maintaining a diet low in processed foods and high in whole, unprocessed foods can also improve heart health. Processed and pre-packaged foods are often high in trans fats and other unhealthy ingredients that can increase the risk of heart disease. By choosing to eat a diet full of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, you will reduce your intake of harmful fats and instead consume more nutrient-dense foods that promote heart health.
Consuming trans fats contributes to an increased risk of heart disease by raising LDL cholesterol levels and reducing levels of HDL cholesterol. Limiting the consumption of processed foods and incorporating healthy fats into your diet is important for maintaining a healthy heart. Following a Mediterranean-style diet or a diet high in healthy fats can improve heart health and reduce the risk of heart disease.
Inflammation and Diabetes
Trans fats consumption has also been linked to increased inflammation and a higher risk of diabetes. Studies have shown that a diet high in trans fats can cause an increase in the production of inflammatory markers in the body, such as C-reactive protein (CRP) and interleukin-6 (IL-6).
Inflammation is the body’s natural response to injury or infection. However, chronic inflammation can lead to a variety of health problems, including diabetes. Inflammation can cause insulin resistance, meaning the body is less able to use the hormone insulin to regulate blood sugar levels. This can lead to a buildup of glucose in the blood, which can cause damage to organs and tissues over time.
According to a study published in the Journal of Nutrition, a higher intake of trans fats was associated with an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes. The study found that individuals with the highest trans fat intake had a 40% greater risk of developing diabetes than those with the lowest intake.
It is important to note that not all fats are bad for diabetes. In fact, some fats, such as monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, can have a positive effect on blood sugar control and overall health. The Mediterranean diet, which is rich in healthy fats like olive oil, nuts, and fish, has been shown to improve blood sugar control and reduce the risk of diabetes.
In order to reduce the negative effects of trans fats on inflammation and diabetes risk, it is recommended to limit their consumption. Choosing healthier fats, such as those found in nuts, seeds, avocados, and fatty fish, can provide numerous health benefits without the negative effects of trans fats.
Here is a table listing some healthy fats:
| Fats | Sources |
|---|---|
| Monounsaturated | Olive oil, avocado, nuts, seeds |
| Polyunsaturated | Fatty fish, flaxseed, chia seeds, walnuts |
| Saturated | Coconut oil, grass-fed beef, butter |
Switching to a diet high in healthy fats can be beneficial not only for diabetes prevention, but also for overall health and well-being.
Cancer
Trans fats are not only linked to cardiovascular diseases and inflammation but also to cancer. Research has shown that the intake of trans fats may increase the risk of breast, prostate, and colorectal cancer.
Studies have found that high consumption of trans fats may increase the growth of cancer cells and the development of tumors. This is because trans fats can interfere with the normal functioning of cells and lead to mutations in the DNA. These mutations can then increase the risk of cancer development.
Trans fats may also promote inflammation, which is associated with the development and progression of cancer. By consuming a diet high in trans fats, there is an increased production of free radicals and cytokines, which are pro-inflammatory molecules that can damage cells.
It is essential to take adequate measures to reduce the intake of trans fats in your diet. This includes reading nutrition labels, choosing healthy fats, and avoiding processed foods. Ensuring that your diet includes healthy fats, such as those found in nuts, seeds, and fish, may help to reduce the risk of cancer and promote overall health.
Adopting a healthy diet, such as the Mediterranean diet, which is rich in healthy fats, can help to reduce the risk of cancer and other chronic diseases. Thus, it is crucial to limit the consumption of trans fats and include healthy fats in your diet to promote optimal health.
Takeaway: Consuming a high amount of trans fats may increase the risk of developing cancer, including breast, prostate, and colorectal cancers. Adopting a healthy diet that includes healthy fats, such as the Mediterranean diet, can help to reduce the risk of cancer and other chronic diseases. Choosing healthy fats, reading nutrition labels, and avoiding processed foods are essential steps to avoid trans fats.
How to Avoid Trans Fats
When it comes to maintaining a healthy diet, it is important to reduce or eliminate the consumption of trans fats. Trans fats are notorious for their negative impact on heart health and can be found in a variety of processed foods. Fortunately, avoiding trans fats is not as difficult as it may seem. By being mindful of your food choices and opting for healthier fats, you can greatly reduce your trans fat intake. Here are some effective ways to avoid trans fats in your diet:
Read Nutrition Labels
When it comes to avoiding trans fats, one of the most important things you can do is to read nutrition labels carefully. This will help you to identify any trans fats that might be lurking in your food.
When examining nutrition labels, there are a few things you should look for. First, check the ingredient list for any oils that might contain trans fats. These include partially hydrogenated oils, hydrogenated oils, and shortening. If any of these ingredients are listed, there is likely trans fat in the food.
Additionally, nutrition labels will often list the amount of trans fats contained in a serving of the food. Look for the words “partially hydrogenated” in the ingredients list, and aim for foods with less than 0.5 grams of trans fats per serving. It’s important to note that even if a food has 0 grams of trans fats listed, it can still contain up to 0.5 grams per serving and still be labeled as 0 grams. So be sure to check the ingredients list as well.
If reading nutrition labels is confusing or overwhelming, don’t hesitate to speak with a registered dietitian or other healthcare professional. They can help you to understand how to read labels and make healthy choices.
By reading nutrition labels, you can make informed choices about the foods you eat and reduce your intake of harmful trans fats. And remember, opting for a diet rich in healthy fats rather than a diet high in trans fats or saturated fats can have long-term benefits for your health, including reduced risk of heart disease and other chronic conditions.
Choose Healthy Fats
Consuming healthy fats is important for overall health and well-being. Not all fats are created equal, and it’s important to choose the right types of fats to include in a healthy diet.
One type of healthy fat is unsaturated fats, which can be found in foods like avocado, nuts, and fatty fish. These fats have been linked to a lower risk of heart disease and stroke. Studies have shown that replacing saturated fats with unsaturated fats can lead to improved heart health.
Another type of healthy fat is omega-3 fatty acids, which are found in flaxseeds, chia seeds, and fatty fish. These fats have been linked to a reduced risk of heart disease, as well as improved brain function and joint health.
It’s important to include these healthy fats in your diet in moderation. While they are beneficial, they still contain calories and excessive consumption can lead to weight gain. It’s also important to balance these fats with other macronutrients, such as protein and carbohydrates.
In contrast, it’s important to limit or avoid unhealthy fats, such as trans fats. These fats have been linked to a higher risk of heart disease and other health issues. Instead, choose healthy fats like unsaturated and omega-3 fatty acids to promote optimal health.
Avoid Processed Foods
When it comes to avoiding trans fats in your diet, one important step is to avoid processed foods. This is because many of these products contain hydrogenated oils, a major source of trans fats.
To steer clear of foods that may be high in trans fats, it’s important to read labels carefully. Look for keywords such as “partially hydrogenated oil” or “shortening” on the ingredient list. Additionally, choose fresh foods over packaged or pre-made options whenever possible.
Some specific examples of processed foods that are often high in trans fats include:
- Frozen dinners and entrees
- Baked goods such as pastries, cakes, and cookies
- Snack foods like potato chips and crackers
- Margarine and other spreads
- Non-dairy creamers and flavored coffee drinks
- Fast food and other high-fat options
By avoiding these types of products, you can reduce your intake of trans fats and improve your overall health. Instead, focus on a diet that is rich in fresh fruits and vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats like olive oil, avocado, and nuts.
In addition to reducing your intake of trans fats, following a high-fat diet can be an effective way to promote heart health and overall well-being. By focusing on healthy sources of fat and reducing your consumption of processed foods, you can make positive changes to your diet that will impact your health for years to come.
Conclusion
After going through the above information, it’s clear that trans fats should be avoided in the diet at all costs as they have been linked to several health risks. They are artificially created with the purpose of improving the taste and texture of food and increasing its shelf life, but they come at a cost to our health.
Consuming trans fats can lead to increased levels of LDL cholesterol, inflammation, diabetes, and even cancer. It’s important to read nutrition labels carefully on packaged foods and avoid foods that contain partially hydrogenated oils, which are the main source of trans fats. Instead, opt for healthy fats such as monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats found in nuts, seeds, and avocados.
Avoiding processed and fried foods can also help to reduce trans fats intake, as they are often cooked in oils containing trans fats for longer shelf life. Cook at home using healthier alternatives like olive oil, coconut oil or butter, and choose foods that are low in saturated and trans fats.
In conclusion, it’s important to be aware of the role trans fats have in our diet and the harm they can cause to our health. By understanding how to identify and avoid them, we can make better choices for our overall health and wellbeing.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are some common foods high in trans fats?
Common foods high in trans fats include fried foods, baked goods like cakes and cookies, margarine, and packaged snacks.
Can trans fats be found in natural foods?
Trans fats can be found in small amounts in some natural foods like meat and dairy products, but the majority of trans fats in the modern diet come from processed foods.
Are all fats unhealthy?
No, not all fats are unhealthy. Unsaturated fats, like those found in avocados and nuts, can have positive health benefits.
Why are trans fats commonly used in processed foods?
Trans fats are commonly used in processed foods because they can improve the texture and increase the shelf life of these products.
How do trans fats affect heart health?
Trans fats have been linked to an increased risk of heart disease, as they can raise levels of LDL cholesterol and lower levels of HDL cholesterol.
What are some alternative fats to use in cooking?
Some healthier fat options for cooking include olive oil, coconut oil, and avocado oil.
What should you look for on a nutrition label to identify trans fats?
Look for the words “partially hydrogenated” in the ingredients list, as this is an indication that the product contains trans fats.
Can trans fats be completely eliminated from the diet?
While it may be difficult to completely eliminate all trans fats from the diet, making healthy food choices and avoiding processed foods can significantly decrease consumption.
What is the main reason trans fats are considered harmful?
The main reason trans fats are considered harmful is because they can increase the risk of various health conditions, including heart disease, diabetes, and cancer.
Are trans fats banned in all countries?
No, trans fats are not banned in all countries. However, many countries, including the United States, have implemented regulations to limit the use of trans fats in food products.







