It can be challenging for vegetarians and vegans to ensure they are getting all of the necessary macronutrients their bodies require. With so many dietary restrictions, it’s easy to become perplexed about how to maintain a balanced and healthy diet. However, by understanding what macronutrients are and their importance, it is possible to tailor a plant-based diet that nourishes the body. In this article, we will delve into the essential macronutrients for vegetarians and vegans, healthy sources of each, and how to plan a balanced plant-based meal plan.
What are Macronutrients

Macronutrients are the essential nutrients that our bodies require in larger amounts for optimal functioning. These nutrients can be broadly classified into three categories: carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. Each of these macronutrients plays a critical role in providing energy, promoting growth and development, maintaining tissue repair, and supporting overall health. Understanding what macronutrients are and their importance is crucial for maintaining a balanced and healthy plant-based diet. To learn more about macronutrients and their role in our daily diet, check out our article on daily macronutrient intake.
Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates play a crucial role in providing energy to the body. Vegetarians and vegans can choose from a variety of healthy carbohydrate-rich foods that will meet their daily macronutrient intake. It is important to consume complex carbohydrates that provide long-lasting energy and are rich in fiber which improves digestion and overall health.
Here are some examples of healthy carbohydrate-rich foods for vegetarians and vegans:
| Food | Carbohydrate content (per 100g) | Link to relevant article |
|---|---|---|
| Sweet potato | 20.1g | Carbohydrates in the body |
| Brown rice | 23g | How to Increase Your Fiber Intake with Macronutrients |
| Quinoa | 21.3g | The Importance of Plant-Based Macronutrients |
| Wholemeal bread | 40.6g | The Impact of Macronutrients on Energy Levels |
| Lentils | 20.1g | The Role of Protein in Muscle Growth and Repair |
| Beans | 22.5g | Myths and Facts About Macronutrients and Weight Loss |
| Fruits (apples, bananas, oranges) | 12-22g | Health Benefits of Healthy Fats and Oils |
It is important to note that simple carbohydrates such as refined sugar should be consumed in moderation as they can cause spikes in blood sugar levels and lead to health issues. By choosing complex carbohydrates, vegetarians and vegans can maintain a healthy and balanced diet.
Proteins
Proteins are essential macronutrients that play a crucial role in the growth, repair, and maintenance of tissues in the body. They are made up of amino acids, which are often referred to as the building blocks of protein.
Vegetarians and vegans can get their protein from a variety of plant-based sources, including legumes (such as beans, lentils, and chickpeas), nuts and seeds (such as almonds and chia seeds), tofu and tempeh, whole grains (such as quinoa and brown rice), and some vegetables (such as spinach and broccoli). However, the protein content and quality may vary among these sources.
It is important for vegetarians and vegans to consume an adequate amount of protein to ensure they are meeting their daily needs. The amount of protein needed can depend on various factors, such as age, sex, weight, and activity level. Generally speaking, adults need approximately 0.8 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight per day.
When planning a plant-based diet, it is crucial to make sure you are getting enough protein from a variety of sources. Incorporating different combinations of plant-based protein sources (link to daily macronutrient intake) can improve the quality and quantity of protein in your diet. For example, combining legumes with whole grains can create a complete protein source that provides all the essential amino acids.
Plant-based protein supplements, such as pea protein or soy protein powder, can be used to increase protein intake. However, it is important to read labels carefully and choose supplements that are minimally processed and low in added sugars.
Vegetarians and vegans can easily meet their protein needs by including a variety of plant-based protein sources in their diet and being mindful of their daily macronutrient intake.
Fats
Fats are an essential macronutrient that plays a crucial role in maintaining good health. They are a rich source of energy, help to insulate the body and protect vital organs, and are necessary for the absorption of certain vitamins.
There are several types of fats, including saturated, unsaturated, and trans fats. Saturated fats are typically solid at room temperature and are often found in animal products such as meat, cheese, and butter. Eating too much saturated fat can increase cholesterol levels and increase the risk of heart disease.
Unsaturated fats, on the other hand, are liquid at room temperature and are found in plant-based foods such as avocados, nuts, and seeds. These fats can help to lower cholesterol and reduce the risk of heart disease.
Trans fats are artificially created through the process of hydrogenation and can be found in many processed foods such as fried foods, baked goods, and snack foods. Trans fats have been linked to an increased risk of heart disease and should be avoided as much as possible.
It’s important to aim for a healthy balance of fats in your diet. Monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats are particularly beneficial and should make up the majority of your fat intake. Some great sources of these healthy fats for vegetarians and vegans include:
| Food | Fat Content |
|---|---|
| Avocado | 22g per avocado |
| Nuts (such as almonds, cashews, and pistachios) | 13-18g per 1/4 cup serving |
| Seeds (such as chia, flax, and hemp seeds) | 9-12g per 1/4 cup serving |
| Plant-based oils (such as olive, coconut, and sunflower oil) | 14g per tablespoon |
| Soybeans | 18g per cup serving |
It’s important to remember that fats are high in calories and should be consumed in moderation. Aim to get 20-35% of your daily calories from fat, with a focus on mostly unsaturated sources. Including healthy sources of fat in your diet can improve your overall health and reduce your risk of heart disease.
The Importance of Macronutrients for Vegetarians and Vegans
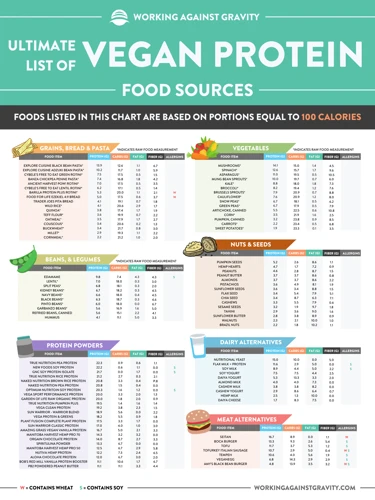
For individuals following a plant-based diet, getting adequate macronutrients is crucial for maintaining optimal health and preventing deficiencies. It can be a concern for vegetarians and vegans as they may not consume animal products that are typically rich in protein, iron, calcium, and vitamin B12. Macronutrients, which include carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, are the primary source of energy for our bodies, and each plays a vital role in maintaining various functions of the body. It’s essential for individuals on a plant-based diet to understand the importance of macronutrients and include the right foods in their diet to meet their daily nutrient requirements. In this section, we’ll explore the significance of macronutrients, specifically protein, iron, calcium, and vitamin B12, and how vegetarians and vegans can ensure they obtain sufficient amounts of these nutrients.
Protein for Vegetarians and Vegans
Protein is an essential macronutrient for the growth, repair, and maintenance of body tissues. While animal products are the most common sources of protein, vegetarians and vegans can still obtain sufficient protein from plant-based sources.
Legumes and Pulses: Legumes and pulses, such as lentils, chickpeas, and beans, are excellent sources of protein for vegetarians and vegans. They also provide fiber, iron, and other essential nutrients.
Nuts and Seeds: Nuts and seeds, like almonds, sunflower seeds, and chia seeds, are also a good source of protein. They can be eaten as a snack or added to meals for extra protein.
Whole Grains: Whole grains, such as quinoa, oats, and brown rice, are another source of plant-based protein. They also provide fiber, B vitamins, and other essential nutrients.
Soy Products: Soy products, like tofu and tempeh, are popular sources of plant-based protein. They are also a good source of calcium and iron.
It is important for vegetarians and vegans to ensure they are consuming enough protein from a variety of sources to meet their daily needs. Combining different sources of protein can also improve its quality and absorption by the body.
Iron for Vegetarians and Vegans
Iron is an essential mineral needed for the production of red blood cells in the body. Vegetarians and vegans, in particular, need to pay close attention to their iron intake as the type of iron found in plant-based foods is not as easily absorbed by the body as the type of iron found in meat. Nevertheless, there are many plant-based sources of iron that can be incorporated into a balanced diet.
The following table outlines some of the best plant-based sources of iron:
| Food | Serving Size | Iron Content (mg) |
|---|---|---|
| Spinach | 1 cup, cooked | 6.4 |
| Lentils | 1 cup, cooked | 6.6 |
| Chickpeas | 1 cup, cooked | 4.7 |
| Black beans | 1 cup, cooked | 3.6 |
| Quinoa | 1 cup, cooked | 2.8 |
It is important to note that the body’s ability to absorb iron from plant-based sources can be enhanced by consuming foods high in vitamin C at the same time. For example, having a glass of orange juice with a spinach salad can increase the amount of iron absorbed by the body. On the other hand, drinking coffee or tea with meals can hinder the absorption of iron.
If you are concerned about your iron intake, it is always a good idea to consult with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian to ensure that you are meeting your daily iron needs.
Calcium for Vegetarians and Vegans
Calcium is an essential mineral that is crucial for building and maintaining strong bones and teeth. While dairy products are often considered the primary source of calcium, vegetarians and vegans can still meet their recommended daily intake through various plant-based sources.
Dairy Alternatives: Non-dairy milks such as soy milk, almond milk, and oat milk are often fortified with calcium and offer similar levels of calcium as regular cow’s milk. Other dairy alternatives such as tofu and vegan cheese also can be good sources of calcium.
Leafy Greens: Dark green leafy vegetables such as kale, collard greens, and broccoli are excellent sources of calcium. They also provide other essential nutrients such as vitamin K and fiber.
Nuts and Seeds: Sesame seeds and almonds are particularly high in calcium, and other nuts and seeds such as chia seeds and Brazil nuts also contain significant amounts of calcium. Incorporating these into the daily diet can boost calcium intake.
Fortified Foods: Many foods are fortified with calcium, including orange juice, breakfast cereals, and even some brands of tofu. Checking food labels can help identify fortified foods and increase calcium intake.
It is essential to maintain adequate calcium intake, especially for premenopausal women, as low calcium intake can increase the risk of osteoporosis. A balanced plant-based diet can provide enough calcium to meet daily needs.
Vitamin B12 for Vegetarians and Vegans
Vitamin B12 is an essential nutrient for the body which is mainly found in animal products. This makes it important for vegetarians and vegans to properly plan their diets to ensure that they get an adequate amount of vitamin B12 from their food or supplements.
Vegetarians who consume dairy products and eggs can meet their daily requirement of vitamin B12 easily. But in the case of vegans, it is a bit more challenging as they need to seek out vitamin B12 fortification or supplements which can be found in plant-based milks, cereals, or nutritional yeast.
A deficiency of vitamin B12 can lead to the following symptoms:
| Symptom | Description |
|---|---|
| Anemia | Vitamin B12 plays a key role in the formation of healthy red blood cells. A deficiency can lead to anemia. |
| Nerve damage | Vitamin B12 deficiency can damage the nerves, resulting in tingling or numbness in the hands or feet. |
| Difficulty with movement | In severe cases, a deficiency can cause difficulty with movement and coordination. |
It is recommended that all vegans and vegetarians get regular blood tests to check their vitamin B12 levels and supplement as necessary. The recommended daily intake for adults is about 2.4 micrograms.
Healthy Sources of Macronutrients for Vegetarians and Vegans

When it comes to obtaining macronutrients, such as carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, from a plant-based diet, it’s important to consider a variety of options. Luckily, there are plenty of healthy and delicious sources of these nutrients that vegetarians and vegans can incorporate into their meals. By mixing and matching plant-based foods, individuals can ensure they are meeting their daily nutritional requirements. Let’s take a look at some of the top sources of macronutrients for a plant-based diet.
Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are one of the three main macronutrients that our body needs to function properly. They provide us with the necessary energy to carry out daily activities. However, not all carbohydrates are created equal.
Simple Carbohydrates: These are broken down quickly by the body and provide immediate energy. However, they lack essential nutrients and can lead to a spike in blood sugar levels. Sources of simple carbohydrates include processed sweets, white bread, and sugary drinks.
Complex Carbohydrates: In contrast, complex carbohydrates are broken down slower by the body, providing a sustained source of energy. They are also rich in fiber, vitamins, and minerals. Sources of complex carbohydrates include whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and legumes.
As a vegetarian or vegan, complex carbohydrates should be the primary source of your energy intake. They not only provide energy, but also other essential nutrients that can be lacking in a plant-based diet.
Healthy sources of complex carbohydrates include:
- Whole grain bread, pasta, and rice
- Quinoa
- Sweet potatoes
- Bananas
- Chickpeas
- Black beans
- Lentils
- Oats
- Berries
It’s important to note that carbohydrates should not be avoided altogether, but rather, incorporated in moderation and with a focus on complex carbohydrates. A balanced diet consisting of a variety of healthy carbohydrates, proteins, and fats can help support optimal health for vegetarians and vegans.
Proteins
Proteins are essential macronutrients that are needed for body tissues to grow and repair. They are also important for maintaining good health and carrying out enzymatic reactions in the body. For vegetarians and vegans, it is important to make sure they are getting adequate amounts of protein from plant-based sources.
Good sources of plant-based protein include:
- Legumes such as lentils, chickpeas, and black beans
- Nuts and seeds such as almonds, peanuts, and chia seeds
- Soy products such as tofu and tempeh
- Whole grains such as quinoa and brown rice
It is important to note that some vegetarian and vegan sources of protein may not contain all the essential amino acids that the body needs. However, by incorporating a variety of plant-based protein sources into a diet, one can ensure adequate intake of all essential amino acids.
Adequate protein intake has numerous benefits, including:
- Building and repairing body tissues such as muscles, bones, and organs
- Maintaining a healthy immune system
- Supporting hormone production and regulation
- Aiding in weight management by promoting feelings of fullness
It is important to make sure that vegetarians and vegans are getting enough protein in a day, based on their individual needs. This can be done by using protein supplements or consuming protein-rich plant-based sources throughout the day.
In addition to protein, it is also important for vegetarians and vegans to make sure they are getting enough iron, calcium, and vitamin B12 in their diets to ensure overall good health.
Fats
Fats are essential macronutrients that are often misunderstood and sometimes avoided by people trying to maintain a healthy diet. However, fats are an important component of a balanced diet, providing energy, aiding in the absorption of certain vitamins, and playing a crucial role in the proper functioning of the body’s cells. For vegetarians and vegans, it can be challenging to get enough healthy fats in their diets, but there are plenty of plant-based options available.
Here are some healthy sources of fats for vegetarians and vegans:
- Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, walnuts, pumpkin seeds, and chia seeds are all high in healthy fats such as monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, which can lower cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of heart disease.
- Avocado: This versatile fruit is high in healthy fats and can be used as a replacement for butter or mayonnaise in many recipes.
- Coconut Oil: Although it is high in saturated fat, coconut oil has been shown to have numerous health benefits, including aiding in weight loss and improving brain function.
- Olive Oil: This heart-healthy oil is a great source of monounsaturated fats, which can help reduce inflammation and lower the risk of heart disease.
- Tofu: Tofu is made from soybeans and is a good source of essential fatty acids, which are important for brain function and maintaining healthy skin and hair.
It’s important to note that not all fats are created equal. Trans fats, found in many processed foods, can raise cholesterol levels and increase the risk of heart disease. It’s best to avoid these types of fats and focus on incorporating healthy fats into your diet.
Additionally, it’s important to be mindful of portion sizes. While healthy fats are beneficial, they are still high in calories, and too much of any type of fat can lead to weight gain over time.
Incorporating a variety of healthy fats into your diet can help improve overall health and reduce the risk of chronic diseases. By incorporating the above listed plant-based options into your meals, you can easily meet your necessary fat intake without compromising the benefits of a plant-based diet.
Planning a Balanced Plant-based Diet
Ensuring a balanced plant-based diet can seem daunting, but with the right knowledge and planning, it can be easily achieved. By considering macronutrient needs and incorporating a variety of healthy food sources, vegetarian and vegan diets can provide all the necessary nutrients for optimal health. Let’s explore how to plan a balanced plant-based diet.
Calculating Macronutrient Needs
Macronutrient needs vary from person to person depending on various factors such as age, gender, weight, height, and activity level. To ensure adequate intake of macronutrients, it is important to calculate individual needs.
Protein: Protein is an essential macronutrient and the daily requirement varies depending on age and body weight. As per the Dietary Reference Intake (DRI), an average adult requires at least 0.8 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight. However, for athletes or individuals who are highly active, the protein requirement may be higher.
Carbohydrates: Carbohydrates are a primary source of energy for the body. The recommended daily intake of carbohydrates for an average adult is around 130 grams. However, individuals who are highly active or involved in strenuous physical activity may require more carbohydrates for energy.
Fats: Fats are an important macronutrient and they are essential for various functions in the body. As per the DRI, an average adult requires at least 20-35% of their daily calorie intake from fats. However, it is important to consume healthy fats such as omega-3 fatty acids and limit the intake of saturated and trans fats.
To calculate macronutrient needs, one can use online calculators or consult a registered dietitian. A dietitian can analyze the individual’s lifestyle, preferences, and goals to recommend a balanced diet.
Once the macronutrient needs are calculated, it is important to plan meals accordingly to ensure a balanced intake of all macronutrients. The following table provides an overview of healthy sources of macronutrients for vegetarians and vegans:
| Macronutrient | Healthy Sources for Vegetarians | Healthy Sources for Vegans |
|---|---|---|
| Protein | Lentils, chickpeas, beans, tofu, tempeh, nuts, seeds, quinoa, seitan | Tofu, tempeh, soy milk, lentils, chickpeas, beans, nuts, seeds, quinoa, seitan, nutritional yeast |
| Carbohydrates | Whole grains, fruits, vegetables, legumes | Whole grains, fruits, vegetables, legumes |
| Fats | Nuts, seeds, avocado, olive oil, coconut oil | Nuts, seeds, avocado, olive oil, coconut oil |
By incorporating a variety of these healthy sources into meals and calculating individual macronutrient needs, individuals can ensure a balanced and nutritious plant-based diet.
Sample Meal Plan for Vegetarians and Vegans
Creating a balanced and nutritious meal plan is essential for vegetarians and vegans to ensure they are meeting their macronutrient needs. Here is a sample meal plan that incorporates healthy sources of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats:
Breakfast:
- Vegan protein smoothie made with almond milk, banana, spinach, and hemp seeds
- Whole grain toast with avocado and sliced tomato
Snack:
- Apple slices with almond butter
Lunch:
- Quinoa and black bean salad with roasted sweet potatoes and bell peppers
- Top with a homemade lemon-tahini dressing made with tahini, lemon juice, olive oil, garlic, and water
Snack:
- Raw veggies such as carrot sticks, celery, and cucumber with hummus
Dinner:
- Lentil and vegetable stir-fry served over brown rice
- Top with sliced avocado and cilantro
This meal plan provides a good balance of macronutrients, including protein from plant-based sources such as quinoa, black beans, and lentils. Complex carbohydrates are included in the form of whole grains and vegetables, while healthy fats are provided by sources like avocado, hemp seeds, and olive oil. Snacks incorporating fruits, vegetables, and nut butters provide an additional source of nutrients and keep hunger at bay between meals.
Remember, this is just a sample meal plan and should be tailored to individual needs and preferences. It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian to ensure a balanced and adequate intake of macronutrients when following a plant-based diet.
Conclusion
In conclusion, it is clear that macronutrients play a crucial role in a balanced diet for both vegetarians and vegans. A proper balance of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats can provide the necessary energy and nutrients to maintain a healthy body, support muscle growth and repair, and aid in weight management.
While obtaining adequate amounts of certain nutrients can be more challenging on a plant-based diet, with proper planning and attention to food choices, it is possible to meet all of your nutrient needs without relying on animal products. Additionally, plant-based sources of macronutrients often come with added benefits, such as fiber and antioxidants, that can further support overall health.
It is essential to remember to include a variety of foods in your diet to ensure you are getting all of the necessary nutrients. This can include a combination of whole grains, legumes, nuts and seeds, fruits and vegetables, and plant-based protein sources such as tofu and tempeh.
Overall, a balanced and well-planned plant-based diet can provide all of the necessary macronutrients for optimal health and well-being. With the right mindset and approach, going vegetarian or vegan can be a rewarding and healthy lifestyle choice.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the importance of macronutrients in a vegetarian or vegan diet?
Macronutrients provide the essential building blocks for a healthy body, ensuring proper functioning and support of bodily systems.
What are some good vegetarian sources of protein?
Some plant-based sources of protein include lentils, legumes, tofu, seitan, quinoa, nuts, and seeds.
What are the benefits of consuming carbohydrates in a vegetarian or vegan diet?
Carbohydrates provide energy, fiber, and essential vitamins and minerals that are necessary for optimal functioning of the body.
What are some healthy plant-based sources of carbohydrates?
Fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes are all excellent sources of carbohydrates in a plant-based diet.
Do vegetarians and vegans have to worry about getting enough iron?
Yes, vegetarians and vegans should pay attention to getting enough iron in their diet as plant-based sources may be less bioavailable. Good sources include dark leafy greens, beans, and fortified cereals.
What are some healthy sources of fats in a plant-based diet?
Healthy plant-based sources of fats include avocado, nuts, seeds, and olive oil.
How can vegetarians and vegans ensure they are getting enough calcium?
Calcium can be obtained from plant-based sources such as fortified plant milks, tofu, dark leafy greens, and calcium-set tofu.
Is it possible to get enough vitamin B12 on a plant-based diet?
It may be difficult for vegetarians and vegans to meet their B12 needs through diet alone. It is important to either consume B12-fortified foods or a B12 supplement.
What are some easy ways to plan a balanced plant-based meal?
One easy way is to include a source of protein, such as beans or tofu, a healthy carbohydrate source, such as whole grains, and a variety of colorful fruits and vegetables.
What are some benefits of following a plant-based diet?
Some potential benefits of a plant-based diet include lower risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease and obesity, improved digestion, and increased energy levels.







