It’s no secret that our diet plays a crucial role in our overall health, and there are few things more important to our well-being than heart health. One aspect of our diet that has been the subject of much debate and confusion is dietary fats. While we know that some fats are good for us and others are not, there seems to be a lot of conflicting information out there that can be overwhelming. The Connection Between Dietary Fats and Heart Health: Exploring the Facts aims to provide a clear and detailed examination of the different types of dietary fats, their effects on heart health, and tips for incorporating healthy fats into your diet. Whether you’re a health enthusiast or just looking to make some positive changes to your diet, this article will provide valuable insights into the world of dietary fats and help you make informed decisions about what you put into your body.
Types of Dietary Fats
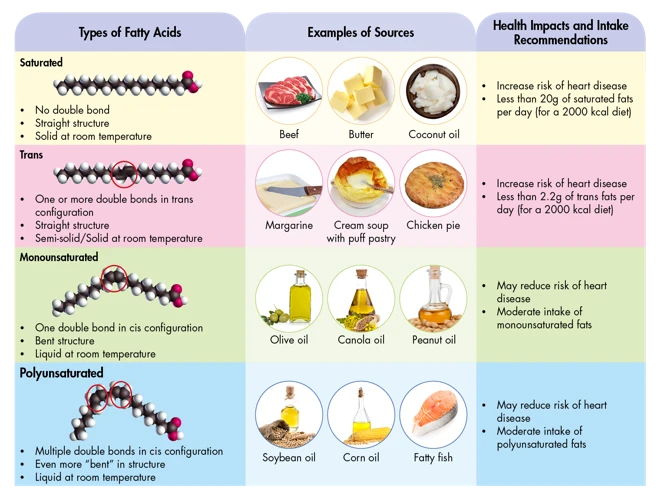
It’s important to understand the different types of dietary fats that exist and how they can affect our health. Some fats are considered healthy and necessary for optimal bodily function, while others can be harmful and contribute to chronic diseases like heart disease. In this section, we will explore saturated fats, trans fats, monounsaturated fats, polyunsaturated fats, and omega-3 fatty acids and how they impact our health. Understanding the differences between these types of fats can help us make informed decisions about our diets and promote overall health and wellbeing. To learn more about the health impacts of specific types of fats, check out our articles on saturated fats, trans fats, monounsaturated fats, polyunsaturated fats, and omega-3 fatty acids.
Saturated Fats
Saturated fats are typically solid at room temperature and are mainly found in animal products such as meat and dairy products. They are also found in some plant sources like coconut oil and palm oil.
While saturated fats have been demonized in the past for causing heart disease, recent studies have challenged this belief. However, it is still recommended to limit saturated fat intake and replace it with healthier alternatives to promote heart health.
Saturated fats have a tendency to increase the levels of LDL (low-density lipoprotein) or “bad” cholesterol in the blood, which can lead to the formation of plaque in the arteries, increasing the risk of heart disease. It is recommended to limit the intake of saturated fats to less than 10% of total daily calorie intake (according to the American Heart Association).
Some sources of saturated fats, like fatty cuts of meat and full-fat dairy products, can also be high in calories and increase the risk of obesity and other health problems. However, there are some healthier sources of saturated fats like eggs and dark chocolate, which can be incorporated into a balanced diet in moderation.
To summarize, while saturated fats are not as harmful as previously believed, it is still recommended to limit the intake of saturated fats and replace them with healthier alternatives like those found in the Mediterranean diet. It is recommended to limit saturated fat intake to less than 10% of total daily calorie intake.
Trans Fats
Trans fats are another type of dietary fat that can have negative effects on heart health. They are a type of unsaturated fat that is typically found in processed foods, fried foods, and baked goods.
What are trans fats?
Trans fats are formed when liquid vegetable oils are partially hydrogenated, which means that hydrogen atoms are added to the unsaturated fats. This process makes the fats more solid, and they are often used in food products to improve their texture, flavor, and shelf life. However, trans fats are not only unhealthy but also taste differently. They are often used in less healthy fast food meals and other processed food items.
Why are trans fats unhealthy?
Unlike other fats, trans fats raise LDL cholesterol levels (sometimes called “bad” cholesterol) and lower HDL cholesterol (“good” cholesterol) levels. This leads to an increase in the risk of heart disease, stroke, and type 2 diabetes. In general, it is recommended that people limit their trans fat consumption as much as possible.
To avoid trans fats, it is important to look at food labels and choose foods that are labeled as trans fat-free. You should also avoid fast food restaurants, which may use trans fats in frying food because they are cheaper and have longer shelf life. Trans fats can be listed on the ingredient list as “partially hydrogenated oils.”, but if they contain less than 0.5 grams of trans fat per serving, the food label can legally read “0 grams trans fat.”
Conclusion:
Trans fats are unhealthy and can have negative effects on heart health. It is important to limit consumption of foods containing trans fats by reading food labels and avoiding fast food restaurants. Choosing healthy fats such as monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats is a better choice to keep a healthy diet with no more than recommended /fat-eat-per-day/. A /high-fat-diet-healthy/ should be made of healthy fats that can be found in a variety of foods, including nuts, seeds, avocados, fatty fish, and healthy oils.
Monounsaturated Fats
Monounsaturated fats are an important part of a healthy diet. They are a type of unsaturated fat that can be found in a variety of foods, including oils, nuts, and seeds. Unlike saturated fats, which are solid at room temperature, monounsaturated fats are typically liquid at room temperature.
Benefits of Monounsaturated Fats
– They can help improve cholesterol levels by lowering LDL (bad) cholesterol and increasing HDL (good) cholesterol.
– They may help reduce inflammation in the body, which can lower the risk of certain chronic diseases.
– They can help improve insulin sensitivity and control blood sugar levels.
– They may help protect against heart disease and stroke.
Sources of Monounsaturated Fats
– Olive oil: Olive oil is a great source of monounsaturated fat, and is often used in Mediterranean diets for its health benefits.
– Avocado: Avocado is another great source of monounsaturated fat, as well as fiber and potassium.
– Nuts: Almonds, cashews, and peanuts are all high in monounsaturated fat, making them a great snack option.
– Seeds: Sunflower seeds, pumpkin seeds, and sesame seeds are all good sources of monounsaturated fat.
How to Incorporate Monounsaturated Fats into Your Diet
– Use olive oil as your main cooking oil.
– Add avocado to your salads, sandwiches, or smoothies.
– Snack on a handful of nuts, such as almonds or cashews, instead of reaching for a processed snack.
– Sprinkle seeds, such as sunflower or pumpkin, on top of your salads or yogurt.
By including monounsaturated fats in your diet, you can reap the numerous health benefits they provide. Adding sources of monounsaturated fats to your meals and snacks is a delicious and easy way to promote heart health.
Polyunsaturated Fats
Polyunsaturated fats are an essential part of a healthy diet. These types of fats are found in a variety of healthy foods, including:
- Salmon: Salmon is a fatty fish that is rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which are a type of polyunsaturated fat.
- Chia seeds: Chia seeds are a great source of polyunsaturated fats, including omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids.
- Flaxseed: Flaxseed is another good source of omega-3 fatty acids, as well as other polyunsaturated fats.
- Walnuts: Walnuts are a delicious and nutritious snack that is rich in polyunsaturated fats.
Polyunsaturated fats are important because they can help to improve cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of heart disease. In particular, omega-3 fatty acids have been shown to have numerous health benefits, including:
- Reducing inflammation: Omega-3 fatty acids have anti-inflammatory properties, which can help to reduce inflammation in the body and lower the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, cancer, and arthritis.
- Lowering triglycerides: Omega-3 fatty acids can help to lower triglyceride levels, which are a type of fat found in the blood. High levels of triglycerides are associated with an increased risk of heart disease.
- Lowering blood pressure: Some studies suggest that omega-3 fatty acids can lower blood pressure, which is another important factor in reducing the risk of heart disease.
In addition to omega-3 fatty acids, polyunsaturated fats also include omega-6 fatty acids. While omega-6 fatty acids are also important for health, it’s important to maintain a healthy balance between omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids. Most people in the Western diet consume too much omega-6 fatty acids and not enough omega-3 fatty acids, which can contribute to a number of health problems. It is important to incorporate foods that are high in omega-3 fatty acids like salmon and chia seeds in our diet.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 fatty acids are a type of polyunsaturated fat that are essential for good health1. They play an important role in many bodily functions, including brain function and reducing inflammation2.
Sources of omega-3 fatty acids include:
- Fatty Fish: Examples include salmon, tuna, and sardines.
- Flaxseed: This can be consumed ground or as an oil.
- Chia Seeds: These can be added to smoothies or used as a topping for yogurt or oatmeal.
- Walnuts: These can be eaten raw as a snack, or used in baking and cooking.
Studies have shown that omega-3 fatty acids can have a positive effect on heart health. They can lower levels of triglycerides, and reduce the risk of abnormal heart rhythms3. Omega-3 fatty acids may help lower blood pressure and reduce inflammation4.
It is recommended that adults consume at least two servings of fatty fish per week to obtain sufficient amounts of omega-3 fatty acids5. For those who do not consume fish, supplements can be taken under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
It is important to note that while omega-3 fatty acids are beneficial for heart health, they should not be consumed in excess as they can have blood-thinning effects and interact with certain medications6.
Incorporating omega-3 fatty acids into the diet is important for reducing the risk of heart disease and improving overall health.
Effects of Dietary Fats on Heart Health
The impact of dietary fats on heart health has been a topic of great concern among health professionals and individuals alike. The type and amount of fat consumed can have a significant effect on various aspects of cardiovascular health, including cholesterol levels, inflammation, and blood pressure. Understanding these effects is crucial in making informed dietary choices to maintain a healthy heart. Let’s delve deeper into the impact of different types of dietary fats on heart health.
Increase in Cholesterol Levels
Consuming a diet high in saturated and trans fats can lead to an increase in cholesterol levels in the body. These fats can raise the levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, commonly referred to as “bad” cholesterol. LDL cholesterol builds up in the walls of arteries and can lead to the development of atherosclerosis, a condition where plaque accumulates inside the arteries, narrowing them and restricting blood flow.
Individuals with high cholesterol levels are at increased risk of developing heart disease and stroke. A diet high in saturated fats, found in animal products such as meat, butter, and cheese, can contribute to elevated cholesterol levels. Additionally, consuming trans fats, which are commonly found in processed foods like baked goods and fried foods, can increase LDL cholesterol and decrease high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, or “good” cholesterol, in the body.
However, not all fats have the same effect on cholesterol levels. Monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats can actually help to decrease LDL cholesterol levels in the body. Foods high in these healthy fats include nuts, seeds, avocados, and fatty fish, like salmon and tuna. Incorporating these foods into the diet in appropriate amounts can help to maintain healthy cholesterol levels and promote heart health.
Inflammation
When it comes to heart health, inflammation is one of the most significant factors that can contribute to the development of heart disease. Inflammation is a natural response of the body’s immune system to fighting infections or injuries. However, when inflammation is chronic, it can lead to a variety of health problems, including heart disease.
What Causes Inflammation?
There are several factors that can contribute to inflammation, including poor diet, lack of exercise, smoking, and stress. An unhealthy diet that is high in saturated and trans fats can cause inflammation in the body, leading to the buildup of plaque in the arteries and an increased risk of heart disease. On the other hand, a healthy diet that is rich in monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats can help to reduce inflammation in the body.
How Dietary Fats Affect Inflammation
Different types of dietary fats can have different effects on inflammation in the body. Saturated fats and trans fats, which are commonly found in processed foods and fried foods, can increase inflammation in the body. In contrast, monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, which are found in foods like fish, nuts, and seeds, can help to reduce inflammation.
One type of polyunsaturated fat that has been found to be especially effective at reducing inflammation is omega-3 fatty acids. Omega-3s are found in fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and tuna, as well as in walnuts, flaxseed, and chia seeds. Studies have shown that omega-3s can help to reduce inflammation in the body and lower the risk of heart disease.
The Bottom Line on Inflammation and Dietary Fats
While inflammation is a natural and necessary process in the body’s immune system, chronic inflammation can lead to a host of health problems, including heart disease. By choosing healthy dietary fats like monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, and limiting intake of saturated and trans fats, you can help to reduce inflammation in your body and lower your risk of heart disease. Incorporating omega-3-rich foods like fatty fish and nuts into your diet can also be beneficial for reducing inflammation and improving heart health.
| Type of Fat | Effect on Inflammation | Food Sources |
|---|---|---|
| Saturated Fat | Increases inflammation | Butter, cheese, red meat |
| Trans Fat | Increases inflammation | Processed foods, fried foods |
| Monounsaturated Fat | Reduces inflammation | Olive oil, avocados, almonds |
| Polyunsaturated Fat | Reduces inflammation | Fatty fish, nuts, seeds |
| Omega-3 Fatty Acids | Especially effective at reducing inflammation | Fatty fish, walnuts, flaxseed, chia seeds |
Increase in Blood Pressure
Consuming diets high in saturated and trans fats can have negative effects on heart health, including increasing blood pressure. High blood pressure, also known as hypertension, is a condition where the force of blood against the walls of the arteries is consistently too high. This can cause the heart to work harder than it should, and over time, can lead to serious health problems such as heart attack and stroke.
Saturated and trans fats can lead to an increase in blood pressure by promoting the buildup of plaque in the arteries, also known as atherosclerosis. This narrowing of the arteries restricts blood flow and increases blood pressure.
Research has shown that replacing saturated and trans fats with healthier fats such as monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats can lead to a reduction in blood pressure levels. For example, a study published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition found that replacing saturated fats with polyunsaturated fats led to a reduction in both systolic and diastolic blood pressure levels.
In addition to replacing unhealthy fats with healthier alternatives, it’s important to also reduce overall intake of fat in order to maintain a healthy weight. Being overweight or obese can also contribute to high blood pressure.
If you have high blood pressure or a family history of hypertension, it’s important to work with your healthcare provider to create a plan that incorporates heart-healthy dietary changes along with other lifestyle modifications such as exercise and stress management.
Risk of Heart Disease
Heart disease is a serious condition that can lead to life-threatening complications. The consumption of high amounts of saturated and trans fats is strongly linked to an increased risk of heart disease. Saturated and trans fats are solid at room temperature and can raise levels of LDL (bad) cholesterol, which can build up in the arteries and lead to blockages. This can increase the risk of developing heart disease, including coronary artery disease, heart attacks, and strokes.
In addition to increasing cholesterol levels, the consumption of unhealthy fats can also cause inflammation in the body. Chronic inflammation is thought to play a role in the development of heart disease, as it can damage the lining of the arteries and contribute to the formation of plaques.
Unhealthy fats can also increase blood pressure, which can further contribute to the development of heart disease. High blood pressure can damage the arteries and increase the risk of developing a host of cardiovascular problems.
To reduce the risk of developing heart disease, it is important to limit the consumption of unhealthy fats and to choose healthier options instead. By choosing healthy fats, such as monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, and limiting saturated and trans fats, individuals can improve their heart health and reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease.
Benefits of Healthy Fats for Heart Health

When it comes to maintaining a healthy heart, choosing the right types of dietary fats can make a significant difference. Studies have shown that consuming healthy fats can have numerous benefits for heart health, such as improving cholesterol levels, reducing inflammation, lowering blood pressure, and reducing the risk of heart disease. However, not all fats are created equal, and some types can have negative effects on heart health. It’s important to understand which types of fats are beneficial and how to incorporate them into your diet in a healthy way.
Improved Cholesterol Levels
When it comes to heart health, one of the key factors is keeping cholesterol levels within a healthy range. Healthy fats, such as monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, can play a role in improving cholesterol levels.
Research has shown that these healthy fats can help increase levels of high-density lipoprotein (HDL), commonly referred to as “good” cholesterol, while decreasing levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL), often called “bad” cholesterol. LDL cholesterol can build up in artery walls, leading to blockages and an increased risk of heart disease.
In fact, a study published in the Journal of the American Medical Association found that replacing just 5% of saturated fat intake with polyunsaturated fat intake resulted in a nearly 10% decrease in the risk of heart disease.
Additionally, one specific type of polyunsaturated fat, omega-3 fatty acids, has been shown to have an even greater impact on cholesterol levels. Omega-3s can help lower triglycerides, another type of fat in the blood that can increase the risk of heart disease, while also increasing HDL cholesterol.
Sources of healthy fats that can help improve cholesterol levels include:
- Fatty fish such as salmon, tuna, and mackerel (high in omega-3 fatty acids)
- Nuts and seeds such as almonds, walnuts, and chia seeds (high in monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats)
- Avocado (high in monounsaturated fat)
- Oils such as olive, canola, and sunflower (high in monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats)
Incorporating these foods into your diet can help improve your cholesterol levels and reduce your risk of heart disease. However, it’s still important to consume these foods in moderation, as they are still high in calories.
Reduced Inflammation
One of the benefits of consuming healthy fats is a reduction in inflammation throughout the body. Chronic inflammation has been linked to a range of health issues, including heart disease. Let’s take a look at how different types of dietary fats can affect inflammation:
| Fat Type | Inflammatory or Anti-Inflammatory? |
|---|---|
| Saturated Fats | Inflammatory: Consuming too much saturated fat has been shown to increase inflammation in the body. |
| Trans Fats | Inflammatory: Trans fats not only increase inflammation but also lower the levels of anti-inflammatory compounds in the body. |
| Monounsaturated Fats | Anti-Inflammatory: Consuming monounsaturated fats has been linked to lower levels of inflammatory markers in the body. |
| Polyunsaturated Fats | Anti-Inflammatory: Polyunsaturated fats, like omega-3 fatty acids, have been found to have powerful anti-inflammatory effects. |
| Omega-3 Fatty Acids | Anti-Inflammatory: Omega-3 fatty acids are particularly effective at reducing inflammation and have been linked to a range of health benefits. |
As we can see, consuming healthy fats like monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats and omega-3 fatty acids can help to lower levels of inflammation in the body, potentially reducing the risk of chronic diseases like heart disease. It’s important to note that while saturated and trans fats may contribute to inflammation, they should not be completely eliminated from the diet. Rather, they should be consumed in moderation as part of a balanced diet that includes plenty of healthy fats.
Lowered Blood Pressure
Another benefit of incorporating healthy fats into your diet is lowered blood pressure. High blood pressure is a major risk factor for heart disease and stroke, and consuming the right types of fats may help to lower blood pressure levels.
Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fatty fish such as salmon and tuna, have been shown to have a blood pressure-lowering effect. A study published in the American Journal of Hypertension found that consuming omega-3s for six weeks resulted in a 4.51 mmHg reduction in systolic blood pressure and a 3.05 mmHg reduction in diastolic blood pressure.
Monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, found in foods such as nuts, seeds, and certain oils, may also help to reduce blood pressure. A study published in the Journal of Hypertension found that replacing saturated fat in the diet with either monounsaturated or polyunsaturated fat resulted in a decrease in blood pressure levels.
To easily incorporate these healthy fats into your diet, consider adding foods such as avocado, olive oil, and nuts to your meals. Check out the following table for some examples of foods high in healthy fats:
| Food | Healthy Fat Content |
|---|---|
| Salmon | Omega-3 fatty acids |
| Avocado | Monounsaturated fats |
| Walnuts | Polyunsaturated fats |
| Flaxseed oil | Omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids |
By incorporating these foods and healthy fats into your diet, you can help to lower your blood pressure levels and reduce your risk of heart disease and stroke.
Reduced Risk of Heart Disease
When we consume healthy fats, our risk of heart disease is reduced. This is because healthy fats, such as monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, can help lower our levels of LDL (low-density lipoprotein) cholesterol, commonly known as “bad” cholesterol. Consuming healthy fats can help increase our levels of HDL (high-density lipoprotein) cholesterol, also known as “good” cholesterol.
Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fatty fish such as salmon and sardines, have also been shown to have a protective effect on the heart. Studies have found that consuming omega-3s can lower our risk of arrhythmias, which are irregular heartbeats, as well as decrease our risk of atherosclerosis, which is the buildup of plaque in the arteries.
Consuming olive oil, which is a source of monounsaturated fat, has also been associated with a lower risk of heart disease. One study found that individuals who consumed olive oil as their primary source of fat had a 30% lower risk of developing cardiovascular disease compared to those who consumed a typical Western diet high in saturated and trans fats.
Consuming nuts and seeds, which are a source of both monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, has also been shown to be beneficial for heart health. One study found that individuals who consumed nuts at least five times a week had a 35% lower risk of coronary heart disease compared to those who rarely consumed nuts. Additionally, consuming seeds such as flax and chia seeds, which are rich in alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), a type of omega-3 fatty acid, has also been associated with a lower risk of heart disease.
Incorporating healthy fats into our diet can help reduce our risk of heart disease by improving our cholesterol levels and decreasing inflammation. It is important to choose a variety of healthy fats and consume them in moderation as part of a balanced diet.
Tips for Incorporating Healthy Fats into Your Diet

As we have discussed, incorporating healthy fats into your diet can have numerous benefits for heart health. However, it can be challenging to know which fats to choose and how to consume them in moderation. Here are some helpful tips on how to incorporate healthy fats into your diet without overdoing it on the saturated and trans fats. By making these small changes in your diet, you can improve your heart health and reduce your risk of heart disease.
Choose Healthy Fats
When it comes to choosing healthy fats for your diet, it’s important to know what options are available to you. Monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats are generally considered healthy fats, as they can help improve cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of heart disease. These can be found in a variety of foods, including:
| Foods with Monounsaturated Fats | Foods with Polyunsaturated Fats |
|---|---|
| Avocado | Fatty fish (salmon, tuna, mackerel) |
| Nuts (almonds, cashews, peanuts) | Flaxseeds |
| Olive oil | Chia seeds |
| Canola oil | Soybeans |
| Peanut oil | Walnuts |
However, it’s important to note that even these healthy fats should be consumed in moderation, as excess calories from any source can lead to weight gain and increased risk of heart disease. Aim to incorporate these healthy fats into your meals in small amounts on a regular basis, rather than relying on them as the primary source of fat in your diet.
On the other hand, saturated and trans fats should be limited in your diet as much as possible, as they can increase cholesterol levels and the risk of heart disease. These fats are commonly found in processed foods, fried foods, and high-fat meats. Instead of consuming these types of fats, try to focus on incorporating healthy options into your meals.
Choosing healthy fats can have a positive impact on your heart health when consumed as part of a balanced diet. By incorporating a variety of options in moderation and limiting unhealthy choices, you can improve your cholesterol levels, reduce inflammation, and lower your risk of heart disease.
Limit Saturated and Trans Fat Intake
When it comes to incorporating healthy dietary fats into your diet, it’s also important to limit your intake of saturated and trans fats. These types of fats have been linked to negative effects on heart health such as increased cholesterol levels and inflammation.
Saturated fats are primarily found in animal products such as meat and dairy. Limit your intake of these types of foods by choosing leaner cuts of meat and opting for low-fat or fat-free dairy products.
Trans fats, on the other hand, can be found in many processed foods such as baked goods, fried foods, and snack items. These fats are created through a process called hydrogenation, which turns liquid oils into solid fats that can improve the texture and shelf life of certain foods. However, trans fats have been shown to increase levels of LDL (bad) cholesterol and decrease levels of HDL (good) cholesterol, making them particularly harmful for heart health.
To reduce your intake of saturated and trans fats, consider the following tips:
- Choose lean cuts of meat and remove visible fat before cooking.
- Opt for low-fat or fat-free dairy products such as skim milk or Greek yogurt.
- Limit your intake of processed foods and opt for whole, natural foods instead.
- Read food labels carefully and avoid products that contain partially hydrogenated oils – a major source of trans fats.
- Use alternative cooking methods such as baking, grilling, or sautéing instead of frying.
By limiting your intake of saturated and trans fats and choosing healthy fats instead, you can improve your heart health and lower your risk of heart disease.
Use Healthy Cooking Oils
When it comes to incorporating healthy fats into your diet, it’s important to not only choose the right sources but also to be mindful of how you cook your food. Using healthy cooking oils is a simple but effective way to boost your intake of heart-healthy fats.
Healthy Cooking Oils
When it comes to healthy cooking oils, options like olive oil, avocado oil, and coconut oil are great choices. Not only do these oils contain healthy fats, but they also have other beneficial properties. For example, olive oil is high in antioxidants, while avocado oil is rich in vitamin E.
Here is a table summarizing the benefits and uses of some healthy cooking oils:
| Oil | Benefit | Best Use |
|---|---|---|
| Olive oil | High in antioxidants | Salad dressings, sautéing, roasting |
| Avocado oil | Rich in vitamin E | High-heat cooking, salad dressings |
| Coconut oil | Contains medium-chain triglycerides, which are easily metabolized by the body | Baking, sautéing, stir-frying, smoothies |
It’s worth noting that while these oils are healthy choices, they should still be used in moderation. All oils are high in calories, and excessive consumption can lead to weight gain and other health issues.
Conclusion
Using healthy cooking oils is a simple but effective way to incorporate heart-healthy fats into your diet. Options like olive oil, avocado oil, and coconut oil offer not only healthy fats but also other beneficial properties. Remember to use these oils in moderation and to always choose high-quality, unrefined versions whenever possible.
Choose Fat-Rich Foods in Moderation
When it comes to incorporating fat-rich foods into your diet, it’s important to do so in moderation. While fats can provide many health benefits, consuming too much of them can lead to negative health effects. Here are some tips for choosing fat-rich foods in moderation:
| Food | Serving Size | Healthy Fat Content | Calories per Serving |
| Avocado | 1/4 of an avocado | 4.5 grams of monounsaturated fat | 80 calories |
| Nuts (almonds, walnuts, etc.) | 1 oz. (about 1/4 cup) | 5-8 grams of healthy fats (monounsaturated and polyunsaturated) | 160-200 calories |
| Olive Oil | 1 Tbsp. | 14 grams of monounsaturated fat | 120 calories |
| Dark Chocolate | 1 oz. | 5 grams of monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats | 170 calories |
As you can see from the table, there are many fat-rich foods that can be incorporated into a healthy, balanced diet. However, it’s important to pay attention to serving sizes and calorie intake in order to avoid consuming too much fat, as well as excess calories. By incorporating healthy fats in moderation alongside a balanced diet, you can reap the many health benefits they offer without the negative consequences of consuming too much.
The Bottom Line
The connection between dietary fats and heart health is complex and multifaceted. While some types of dietary fats can increase the risk of heart disease, others can actually improve heart health. It’s important to focus on incorporating healthy fats, such as monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, into your diet while limiting intake of saturated and trans fats. Additionally, choosing healthy cooking oils and consuming fat-rich foods in moderation can also contribute to a heart-healthy diet.
It’s essential to pay attention to the types and amounts of fats you consume to maintain heart health. By following a balanced diet that includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, as well as healthy fats, you can decrease your risk of heart disease and promote overall wellness.
Remember, small changes in diet can lead to big improvements in heart health. Consult with a healthcare provider or registered dietitian to develop an individualized plan that works for you and your health goals. Don’t forget to combine a healthy diet with regular exercise for optimal heart health.
Keep in mind that the information in this article is intended for informational purposes only and should not be used as a substitute for professional medical advice or treatment. Always consult your healthcare provider before making changes to your diet or starting a new exercise regimen.
References
References play a crucial role in supporting the claims made in an article or research paper. They provide readers with further information about the topic and allow them to investigate and verify the information presented. In this article, we have compiled references from various credible sources such as scientific articles and research papers to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the information provided.
Some of the references used in this article include:
1. American Heart Association. (2020). Know Your Fats. Retrieved from https://www.heart.org/
This source provides valuable information on the different types of dietary fats, their effects on heart health, and tips for adopting a heart-healthy diet. It is a reliable source of information as it is authored by the American Heart Association, a well-established authority in heart health.
2. Harvard Health Publishing. (2020). The truth about fats: the good, the bad, and the in-between. Retrieved from https://www.health.harvard.edu/staying-healthy/the-truth-about-fats-bad-and-good
This article by Harvard Medical School explains the different types of fats and their effects on heart health. It also provides evidence-based information on the benefits of consuming healthy fats and tips for incorporating them into a diet.
3. Mozaffarian, D., & Ludwig, D. S. (2015). The 2015 US Dietary Guidelines: Lifting the Ban on Total Dietary Fat. Retrieved from https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/2297711
This research paper discusses the effects of dietary fats on heart health and provides evidence to challenge the previous guidelines that advocated for a low-fat diet. It argues that total dietary fat is not the sole determinant of cardiovascular risk, and that the type of fat consumed is an important consideration.
4. Schwingshackl, L., & Hoffmann, G. (2014). Monounsaturated fatty acids, olive oil and health status: a systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies. Retrieved from https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25161045/
This systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies provide evidence to support the consumption of monounsaturated fats from sources such as olive oil for their beneficial effects on heart health. The research also highlights the need for a balanced intake of fats for optimal health.
By referencing reliable sources and research studies, this article aims to provide readers with comprehensive and accurate information about the connection between dietary fats and heart health.
Frequently Asked Questions
What types of dietary fats are there?
There are four main types of dietary fats: saturated fats, trans fats, monounsaturated fats, and polyunsaturated fats.
What are saturated fats?
Saturated fats are typically solid at room temperature and are found in animal products such as meat and dairy, as well as in some plant-based oils such as coconut and palm oil.
What are trans fats?
Trans fats are artificially produced through the process of hydrogenation and are found in many processed foods such as cookies and fried foods.
What are monounsaturated fats?
Monounsaturated fats are typically liquid at room temperature and can be found in foods such as avocados, nuts, and olive oil.
What are polyunsaturated fats?
Polyunsaturated fats are typically liquid at room temperature and can be found in foods such as fish, nuts, and seeds.
What are omega-3 fatty acids?
Omega-3 fatty acids are a type of polyunsaturated fat that are highly beneficial for heart health and can be found in fish, nuts, and seeds.
How do dietary fats affect heart health?
Dietary fats can affect heart health by increasing cholesterol levels, causing inflammation, increasing blood pressure, and contributing to the risk of heart disease.
What are the benefits of consuming healthy fats for heart health?
Consuming healthy fats can lead to improved cholesterol levels, reduced inflammation, lowered blood pressure, and a reduced risk of heart disease.
What are some tips for incorporating healthy fats into your diet?
Some tips for incorporating healthy fats into your diet include choosing healthy fats, limiting saturated and trans fat intake, using healthy cooking oils, and choosing fat-rich foods in moderation.
What are some healthy cooking oils to use?
Some healthy cooking oils include olive oil, canola oil, and avocado oil.
What should I keep in mind when choosing fat-rich foods?
When choosing fat-rich foods, it is important to keep portion sizes in mind and choose nutrient-dense options such as nuts and seeds over processed foods.







