Introduction

Starting a weight management journey can be an overwhelming process, but it is also an important step towards leading a healthier lifestyle. A crucial component of weight management is exercise. Exercise not only helps to shed extra pounds but also contributes to overall health, including reducing the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease and diabetes. However, with so many exercise options, it can be challenging to know where to start. In this article, we will delve into the role of exercise in weight management, exploring the benefits of exercise for weight loss and how to incorporate exercise into a weight management plan.
Why is weight management important?
Maintaining a healthy weight is important for overall health and well-being. Excess weight and obesity increase the risk of numerous health conditions including diabetes, heart disease, stroke, and some cancers. Being overweight can also cause fatigue and negatively impact self-esteem. On the other hand, achieving and maintaining a healthy weight can lead to more energy, improved mood, and decrease in health risks.
There are various reasons why people struggle with managing their weight. One of the most common reasons is poor diet habits, such excessive consumption of high-calorie and unhealthy foods. Portion control and balanced diet are crucial for maintaining a healthy weight. Along with diet, another important factor that could cause weight gain is stress, as it can lead to overeating and making poor food choices.
Fortunately, there are some strategies that can help people with weight management, including exercise, healthy eating habits, and proper sleep. Having support from friends or a weight loss group could be helpful in staying on track with healthy habits.
In order to successfully achieve weight management, one needs to change their lifestyle habits in the long term. It is important to choose a gradual and sustainable approach. Fad diets that promise quick and dramatic weight loss are usually not effective and can be harmful to health. Instead, people should focus on building healthy habits that could be sustained for the long-term, such as regular exercise, healthy eating, and staying hydrated.
If you are trying to manage your weight, take it slow and focus on small changes that you can stick to over time. Check out some 10 tips for weight management to help you get started.
How Exercise Affects Your Weight

When it comes to weight management, exercise plays a vital role in achieving your goals. Regular exercise provides numerous benefits beyond just weight loss, such as improved cardiovascular health, enhanced mood, and increased energy. By incorporating various exercises into your routine, you can burn calories, increase metabolism, build muscle mass, and reduce body fat. In this section, we’ll explore how exercise affects your weight and the various ways it can contribute to your weight management journey.
Exercise Burns Calories
Exercise is a crucial component of weight management, as it helps burn calories. Calories are a unit of energy, and they are stored in the body as fat if they are not expended through physical activity. By burning calories, exercise helps individuals maintain a healthy weight and reduce body fat.
The number of calories burned during exercise depends on the intensity, duration, and type of exercise. The American Heart Association recommends at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise per week for weight management.
Here’s an example of the number of calories burned during one hour of different exercises for a person who weighs 150 pounds:
| Exercise Type | Calories Burned (per hour) |
|---|---|
| Running (6 mph) | 684 |
| Cycling (14-16 mph) | 648 |
| Swimming (laps, freestyle) | 528 |
| Strength Training (moderate) | 360 |
| Yoga | 240 |
While burning calories through exercise is important for weight management, it’s important to also focus on proper nutrition and portion control. Exercise alone is not enough to achieve weight loss goals if individuals are regularly consuming more calories than they are burning. Consider seeking professional help or joining a support group to develop a comprehensive plan for weight management that includes both exercise and a healthy diet.
Increases Metabolism
Regular exercise increases metabolism, which is the rate at which your body burns calories. This means that the more active you are, the more calories you burn even when you are at rest. When you exercise, your muscles require energy to work, and this energy comes from the calories that you consume. However, when you engage in activities such as strength training, your muscles continue to require energy even after your workout is finished, which means that your body continues to burn calories. This process is called excess post-exercise oxygen consumption (EPOC), or the “afterburn effect”.
EPOC is the amount of oxygen required after exercise to restore your body to its pre-exercise state. During EPOC, your metabolism remains elevated, which means that you continue to burn calories long after you are finished working out. Research has shown that the intensity and duration of exercise can affect EPOC. High-intensity activities such as interval training and heavy weight lifting take your body more time to recover, which elevates metabolism for longer periods.
Incorporating strength training into your routine can lead to an increase in muscle mass, which has a positive effect on your metabolism. Muscles require more energy to maintain than fat, so the more muscle you have, the more calories you burn even when you are at rest. According to a study published in the journal Obesity, adding just 11 pounds of muscle can lead to an additional 350 to 450 calories burned per day.
In addition to increasing metabolism, exercise also has other benefits for weight management such as reducing body fat and improving overall health. It is important to note that exercise alone may not be sufficient for weight loss, and dietary changes are also necessary for long-term weight management. However, regular exercise can significantly contribute to achieving and maintaining a healthy weight.
Internal link: Learn more about the importance of diet in weight management here.
Builds Muscle Mass
Building muscle mass is another way that exercise can help with weight management. Muscle is denser than fat, meaning that it takes up less space in the body but weighs more. This is why a person who has a higher percentage of muscle relative to fat may weigh more on the scale, but still appear lean and toned.
To build muscle mass through exercise, it’s important to engage in strength training exercises that target the major muscle groups of the body, such as the chest, back, legs, and arms. These exercises include things like weightlifting, resistance band workouts, and bodyweight exercises like push-ups and squats.
One of the benefits of building muscle mass is that it increases your Resting Metabolic Rate (RMR). This is the number of calories your body burns at rest in order to perform essential functions like breathing and circulating blood. With a higher RMR, your body will burn more calories throughout the day, even when you’re not actively exercising.
However, it’s important to remember that muscle mass DOES NOT increase significantly without a proper diet. The body requires an adequate amount of protein to build muscle, so it’s important to consume enough lean protein sources like chicken, fish, and tofu. Additionally, consuming enough water and staying hydrated is also important for building muscle and supporting weight management efforts.
It’s important to gradually increase the amount of weight that you lift or the amount of resistance that you use in order to continue building muscle mass over time. Engaging in group exercise classes or seeking out a personal trainer can also be helpful for learning proper strength training techniques and avoiding injury.
Reduces Body Fat
Regular exercise can reduce body fat, which is crucial for weight management. When we consume more calories than we burn, the excess energy is stored as body fat. Reducing body fat can be achieved with a combination of regular exercise and a healthy diet. Exercise can help to create a calorie deficit, leading to the burning of stored fat for energy.
One way that exercise reduces body fat is through increased energy expenditure. Physical activity significantly increases the number of calories burned by the body, leading to an overall reduction in body fat. Another way that exercise can help with weight management is by increasing muscle mass. Muscle tissue burns more calories than fat tissue, so as muscle mass increases, so does the body’s metabolic rate.
In addition, cardiovascular exercise can be particularly effective for reducing body fat. Running, cycling, and swimming are all examples of effective cardiovascular exercises. Studies suggest that high-intensity interval training (HIIT) can also be an effective form of exercise for reducing body fat.
It’s important to note that exercise alone may not be sufficient for weight management. It’s necessary to combine regular exercise with a healthy diet for optimal results. Fad diets are not a sustainable or healthy solution for weight management. Instead, focus on consuming a variety of nutrient-dense foods and avoid overconsumption of processed and high-calorie foods.
In conclusion, exercise is an essential factor in weight management. It aids in reducing body fat and increasing muscle mass. When combined with a healthy diet and other healthy lifestyle choices such as getting enough sleep and managing stress, regular exercise forms the foundation for successful weight management over time.
How Much Exercise Is Required for Weight Management?
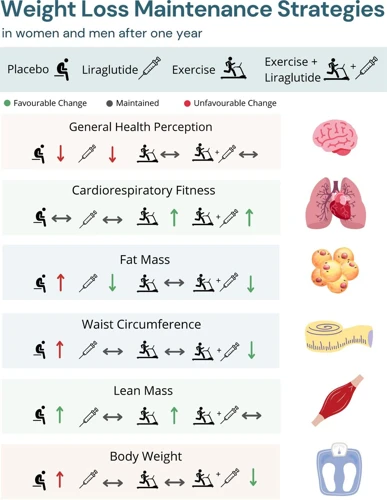
As we understand that exercise plays a significant role in weight management, the next question that arises is, “How Much Exercise Is Required for Weight Management?” It’s essential to find the right balance between exercise and diet to achieve weight management goals. Knowing the amount of exercise required to maintain a healthy weight can help us make informed decisions about our lifestyle choices. Additionally, proper nutrition, adequate sleep, and stress management also play a crucial role in weight management. You can learn more about these topics using the following links: stress and weight management, maintaining weight loss, truth about fad diets and weight management, importance of sleep for weight management, and healthy snacks for weight management.
Aerobic Exercise
Aerobic exercise is one of the most effective forms of exercise for weight management. This type of exercise is also known as cardio exercise or endurance exercise. It’s called aerobic exercise because it requires oxygen to fuel the body’s energy demands during the workout. Here are some benefits of incorporating aerobic exercise into your weight management routine:
- Burns calories: Aerobic exercise burns a lot of calories, which is key to weight loss. The amount of calories burned during aerobic exercise will depend on the intensity, duration, and frequency of the workout.
- Improves cardiovascular health: Aerobic exercise is great for your heart and lungs. Regular cardio workouts can help lower blood pressure, reduce the risk of heart disease, and improve overall cardiovascular health.
- Reduces stress: Aerobic exercise is a great way to relieve stress and anxiety. Studies have shown that regular cardio workouts can help improve mood and reduce symptoms of depression.
- Increases endurance: Aerobic exercise can improve your stamina and endurance. Regular cardio workouts can help you feel less fatigued during daily activities like climbing stairs or carrying groceries.
- Boosts metabolism: Aerobic exercise can increase your metabolism, which can help you burn more calories even when you’re not working out.
Examples of aerobic exercise include:
- Brisk walking or jogging
- Cycling
- Swimming
- Dancing
- Aerobics classes
It’s important to note that the amount of aerobic exercise needed for weight management will vary depending on individual factors such as age, gender, and current fitness level. However, the American Heart Association recommends at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week for overall health benefits and weight management.
Resistance Training
Resistance training is an essential component of weight management. Incorporating resistance training into your weekly exercise routine can help promote muscle growth and increase muscle mass, which in turn can help burn more calories. Resistance training involves using weights, resistance bands or bodyweight to work your muscles to help strengthen and tone your body.
One of the benefits of resistance training is that it can help improve your metabolism, allowing you to burn more calories throughout the day, even when you are at rest. Resistance training has also been shown to help reduce the risk of developing chronic conditions such as diabetes and heart disease.
When starting a resistance training program, it is important to start with low weights and gradually increase the weight as your strength improves over time. Using proper form and technique is also crucial in order to avoid injury and get the maximum benefit from each exercise.
Here are some common resistance training exercises that can be included in your workout routine:
- Squats: This exercise primarily targets the legs, glutes and core muscles. It can be done using bodyweight or with weighted objects such as dumbbells or a barbell.
- Deadlifts: This exercise targets the lower back, legs and glutes. It involves lifting a heavy barbell off the ground and standing up straight before lowering it back down.
- Bench press: This exercise targets the chest, triceps and shoulders. It is done lying down on a bench with a weighted barbell or dumbbells.
- Rows: This exercise targets the back muscles and can be done using dumbbells or a rowing machine.
- Shoulder press: This exercise targets the shoulders and can be done using dumbbells or a barbell.
It is recommended to include resistance training in your workout routine two to three times per week, with at least one day of rest in between sessions to allow your muscles time to recover. Remember to start with lower weights and progress gradually over time to avoid injury and maximize results.
Combining Cardio and Resistance Training
Combining cardiovascular and resistance training can be an effective strategy for weight management. Cardiovascular exercise helps to burn calories, while resistance training strengthens and builds muscle mass.
When it comes to the combination of these two types of exercise, the key is to find the right balance. Too much cardio without enough resistance training can lead to muscle loss, while too much resistance training without enough cardio may not burn enough calories to support weight loss.
One way to balance cardio and resistance training is to alternate between the two. For example, performing cardio exercises one day and resistance training the next. This approach allows for recovery time for each muscle group while still providing a cardiovascular workout.
Another way to incorporate both types of exercise is to do circuit training. This involves performing a series of resistance exercises with short periods of cardio exercise in between each set. For example, performing a set of squats followed by a minute of jumping jacks before moving on to the next set of resistance exercises.
An effective way to ensure proper balance is to use a heart rate monitor during workouts. This can help to determine the appropriate intensity and duration of both cardio and resistance training.
Here is a table outlining the benefits of combining cardiovascular and resistance training:
| Benefits of Cardiovascular Exercise | Benefits of Resistance Training |
|---|---|
| Burns calories to support weight loss | Builds and strengthens muscle mass |
| Improves cardiovascular health | Increases metabolism to burn more calories at rest |
| Reduces risk of chronic diseases | Improves bone density to reduce risk of osteoporosis |
Combining cardiovascular and resistance training can be a great way to support weight management and improve overall health. Finding the right balance and incorporating both types of exercise into a fitness routine can lead to long-lasting results.
Best Types of Exercise for Weight Management

When it comes to weight management, not all exercises are created equal. It’s important to choose the right types of exercise that can effectively help you reach your weight goals. While any physical activity can contribute to weight loss, there are certain types of exercise that have been shown to be particularly effective. In this section, we’ll explore some of the best types of exercise for weight management and what makes them so effective.
Cardiovascular Exercise
When it comes to weight management, cardiovascular exercise is often the first thing that comes to mind. In fact, cardio is a popular method for burning calories and losing weight. This type of exercise is any activity that increases the heart rate and breathing rate, such as running, cycling, swimming or dancing.
Cardiovascular exercise not only burns calories, but it can also improve heart health, reduce the risk of chronic diseases, and increase overall fitness levels. According to the American Heart Association, adults should aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week for overall cardiovascular health.
Here’s a table outlining some examples of cardiovascular exercise:
| Type of Exercise | Intensity Level | Calories Burned per Hour (approx.) |
|---|---|---|
| Running | High | 600-900 |
| Cycling | Moderate to High | 500-1000 |
| Swimming | Moderate to High | 400-700 |
| Dancing | Moderate | 300-500 |
Remember, the intensity level of cardiovascular exercise will vary depending on factors such as age, fitness level, and health status. It’s important to consult a doctor before starting any new exercise program, especially if you have any underlying medical conditions.
Incorporating cardiovascular exercise into your weight management plan can be a great way to improve your overall health and fitness, in addition to shedding those extra pounds. So, lace up those sneakers and hit the pavement or hop on that bike and get moving!
Strength Training
Strength training involves using resistance, such as weights, bands, or bodyweight, to challenge and strengthen your muscles. This type of exercise not only helps with weight management but also has numerous health benefits, including improving bone density, reducing the risk of injury, and increasing overall strength.
Benefits of Strength Training for Weight Management
Incorporating strength training into your exercise routine can have numerous benefits for weight management. Here are a few:
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Increase Muscle Mass | Strength training can help increase muscle mass, which in turn increases your metabolism, allowing you to burn more calories throughout the day. |
| Burns Calories | Strength training burns calories during the exercise, and the increased muscle mass from it raises your metabolism, allowing you to burn more calories even when you’re not working out. |
| Improves Body Composition | Strength training can help reduce body fat percentage and improve overall body composition, creating a leaner physique. |
| Increases Caloric Expenditure | Strength training causes your body to burn calories during the exercise, but it also leads to an afterburn effect, where your body continues to burn calories at a higher rate than normal to repair and recover muscles. |
| Develops Stronger Muscles | Strength training helps to build stronger muscles, which can improve overall physical performance and reduce the risk of injury in everyday life. |
How to Incorporate Strength Training into Your Routine
To incorporate strength training in your routine, begin with exercises that target the major muscle groups, including the chest, back, shoulders, legs, and arms. Using resistance bands or weights can increase the intensity and challenge your muscles. Aim for two to three sessions of strength training per week, allowing for adequate rest and recovery between sessions.
Conclusion
Strength training is a crucial component of any exercise program, especially for weight management. Incorporating it into your routine can help increase muscle mass, burn calories, and promote a leaner physique. Start gradually and seek guidance from a fitness professional if you’re new to strength training.
HIIT
High-intensity interval training (HIIT) is another effective form of exercise for weight management. It involves short bursts of intense activity followed by lower-intensity recovery periods. This type of exercise has gained popularity due to its effectiveness in burning calories in a shorter amount of time than traditional steady-state cardio.
Benefits of HIIT
– Burns more calories in less time: HIIT workouts can burn a lot of calories in a shorter amount of time compared to steady-state cardio.
– Increases metabolism: The intense nature of HIIT can increase the body’s metabolism for hours after the workout, leading to more calories burned at rest.
– Improves cardiovascular health: HIIT is a form of cardiovascular exercise that can improve heart health and decrease the risk of chronic diseases like heart disease and type 2 diabetes.
– Requires little to no equipment: HIIT workouts can be done with just bodyweight exercises, making them convenient for at-home or on-the-go workouts.
How to Incorporate HIIT Into Your Routine
– Start with a warm-up: It’s important to warm up before any exercise, especially high-intensity workouts. A 5-10 minute warm-up of light cardio or dynamic stretching can help prevent injury.
– Choose exercises wisely: HIIT workouts usually involve a mix of bodyweight exercises like squats, lunges, and push-ups, as well as high-intensity cardio like jump rope or burpees.
– Find your work-to-rest ratio: The work-to-rest ratio is the amount of time spent performing high-intensity exercise compared to the recovery period. A common ratio is 30 seconds of work followed by 30 seconds of rest, but this can be adjusted to fit individual needs and fitness levels.
– Gradually increase intensity: As with any exercise program, it’s important to gradually increase the intensity of HIIT workouts to avoid injury and improve performance over time.
Mistakes to Avoid
– Doing too much too soon: HIIT can be very demanding on the body, so it’s important to start with shorter workouts and gradually increase intensity.
– Not allowing for proper recovery: HIIT workouts require adequate rest periods to allow the body to recover and build strength. Overtraining can lead to injury and burnout.
– Not modifying exercises for individual needs: Not all exercises may be appropriate for every individual. It’s important to modify exercises to fit individual fitness levels and any injuries or limitations.
Incorporating HIIT into your exercise routine can be a great way to increase calorie burn and improve overall fitness. However, it’s important to start slowly and gradually increase intensity while also allowing for proper rest and recovery. As with any exercise program, it’s always a good idea to consult with a healthcare professional before starting.
Tips for Starting an Exercise Program
Getting started with an exercise program can be a daunting task, especially if you’re new to the fitness world or haven’t exercised in a while. But don’t worry, we’ve got some tips to help you ease into it and make lasting changes for weight management. With these tips, you can establish a sustainable exercise program that suits your needs and lifestyle. Let’s dive in!
Gradual Progression
Starting an exercise program can be challenging, but it’s important to remember to start gradually and progress at a pace that suits your fitness level. Gradual progression is key to prevent injury and ensure long-term sustainability.
Gradual Progression Tips:
| Start with low-impact exercises: | Low-impact exercises such as walking, cycling, and swimming are great options for beginners. These exercises are less stressful on the joints and can help build a strong foundation for more intense workouts later on. |
| Gradually increase intensity: | As your body adapts to exercise, gradually increase the intensity of your workouts. This can be done by increasing the duration or intensity of your exercises or by adding resistance to your workouts. |
| Don’t skip warm-ups and cool-downs: | Before beginning any workout, take the time to warm up your muscles with some dynamic stretching or light cardio. When you’re finished, cool down with some static stretching to help prevent injury and reduce muscle soreness. |
| Listen to your body: | Pay attention to how your body feels during and after exercise. If you experience pain or discomfort, slow down or modify your workout. Pushing through pain can lead to injury and setbacks. |
Keep in mind: the key to long-term success is consistency, so it’s important to make exercise a regular part of your routine. By gradually increasing the intensity of your workouts and being mindful of your body’s signals, you can create a sustainable exercise program that works for you.
Set Goals
When starting an exercise program, it’s important to set goals in order to measure progress and stay motivated. Setting goals can help you tailor your workouts to your specific needs and track your achievements. Here are some tips for setting effective exercise goals:
- Be specific: Instead of setting a general goal like “lose weight,” make it more specific like “lose 5 pounds in 4 weeks.”
- Make it measurable: Use a tool like a scale or measuring tape to track progress towards your goal.
- Set realistic goals: Don’t set yourself up for failure by setting goals that are too difficult to achieve. Be realistic about your current fitness level and abilities.
- Set short-term and long-term goals: Set small goals that can be achieved in a few weeks or months, as well as long-term goals that may take several months or even a year to achieve.
- Write down your goals: Writing down your goals can help you stay accountable and motivated. Put them in a place where you can see them regularly.
- Re-evaluate and adjust: If you find that you’re not making progress towards your goals, don’t be afraid to adjust them or set new ones.
By setting goals for your exercise program, you can stay focused and motivated on your weight management journey. Just remember to be specific, realistic, and measurable, and don’t be afraid to adjust your goals as needed.
Find Something You Enjoy
An important factor to consider when starting an exercise program for weight management is to find something you enjoy. This is crucial because it increases the likelihood of sticking with the program long-term.
There are many different types of exercises to choose from, ranging from cardio to strength training to HIIT. The key is to find something that you actually look forward to doing. This can involve experimenting with different activities until you find the right fit.
Some examples of exercises that may be enjoyable for weight management include:
| Exercise Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Group Exercise Classes | Classes such as yoga, cycling, or dance can be a fun way to exercise while socializing with others. |
| Outdoor Activities | Going hiking, swimming, or kayaking can be a great way to get exercise while enjoying the outdoors. |
| Sports | Joining a local sports team, such as basketball or soccer, can provide the opportunity to exercise while being part of a team and competing against others. |
| Personal Trainer | Working with a personal trainer can help you create a personalized exercise plan that meets your fitness goals while providing motivation and accountability. |
Finding something you enjoy can make a huge difference in your adherence to an exercise program. Exercise shouldn’t feel like a chore or punishment, but rather an enjoyable and rewarding part of your life. When you enjoy exercising, it becomes a sustainable habit that can positively impact your weight management and overall health.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
As you embark on your weight management journey, it’s important to keep in mind the potential pitfalls and mistakes that can hinder your progress. Mistakes are a natural part of any new endeavor, but by recognizing and avoiding them, you can stay on track towards achieving your goals. In this section, we’ll explore some common missteps that people make when starting an exercise program for weight management, and how to avoid them. By being mindful of these mistakes and taking a proactive approach, you can stay focused and committed to your healthy lifestyle changes.
Only Focusing on Cardio
One common mistake that people make when it comes to exercising for weight management is solely focusing on cardiovascular exercise. While cardio is an important component of a well-rounded exercise routine, it shouldn’t be the only form of exercise you do. Here are some reasons why:
- Cardio burns calories while you’re doing it, but once you stop, the calorie burn stops as well. Resistance training, on the other hand, helps build muscle mass which increases your overall metabolism, meaning you continue to burn calories even after your workout session.
- Cardio can also lead to muscle loss if not done properly. When you perform cardio for long periods of time, your body can start breaking down muscle tissue to use as fuel. This can sabotage your weight loss efforts because muscle burns more calories than fat, even when you’re at rest.
- Cardio can also increase your cravings for food, especially carbohydrates. This is because cardio can lower your blood sugar levels, making you feel hungry and leading you to eat more than you should.
To avoid this mistake, it’s important to incorporate resistance training and other forms of exercise into your routine. Not only will it help you burn more calories and preserve muscle mass, but it can also help prevent boredom with your workout routine. A good rule of thumb is to aim for a combination of cardio and resistance training at least three to four times a week.
Forgetting About Diet
Many people believe that if they exercise regularly, they can eat whatever they want and still maintain a healthy weight. However, this is not entirely true. Diet plays a crucial role in weight management, and neglecting it can sabotage your efforts to lose weight. Exercise alone cannot compensate for a poor diet.
A balanced diet that provides your body with the necessary nutrients, vitamins, and minerals is essential for weight management. A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean protein, and healthy fats can help you control your calorie intake and maintain a healthy weight.
On the other hand, a diet that is high in processed foods, sugar, and saturated fats can cause weight gain and put you at risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, and high blood pressure. Even if you exercise regularly, consuming a diet that is high in calories and low in nutrients may lead to weight gain.
To ensure that you are getting the proper nutrition, it is important to track your calorie intake and keep an eye on your portion sizes. Use an app or a food diary to monitor your daily calorie intake, and make sure you are consuming a healthy balance of macronutrients – protein, carbohydrates, and healthy fats.
It is also important to plan your meals ahead of time and avoid skipping meals or going too long without eating. Skipping meals can cause your metabolism to slow down, making it harder for you to burn calories efficiently. Eating frequent, small meals throughout the day can help boost your metabolism and keep you feeling full and satisfied.
Remember, weight management is a combination of both diet and exercise. Neglecting one of these aspects can hinder your progress and make it difficult to achieve your goals. Make sure to prioritize a healthy, balanced diet alongside your exercise routine.
Overtraining
Overtraining can be a common mistake when starting an exercise program. While consistent exercise is necessary for weight management, it is important to avoid overtraining. Overtraining occurs when one exercises too much without enough rest and recovery time. This can lead to physical and emotional exhaustion.
Signs of overtraining include fatigue, decreased performance, and increased risk of injury. It is important to listen to your body and take rest days. Rest days allow the body to recover and rebuild muscles, which can actually lead to better physical performance overall.
It is recommended to have at least one or two rest days per week. Incorporating lighter workouts such as yoga or stretching on rest days can also be beneficial. Additionally, mixing up your routine with different types of exercises, such as cardio and resistance training, can also prevent overtraining by giving certain muscles a break on alternating days.
Remember, the key to successful weight management is consistency, but it is important not to push yourself too hard. Rest and recovery are just as important as exercise itself.
Not Seeking Professional Help
One of the common mistakes people make when starting an exercise program for weight management is not seeking professional help. While exercising on your own can be beneficial, seeking the guidance of a professional can help you to exercise safely and effectively.
Why seek professional help?
There are several reasons why seeking professional help is essential when beginning an exercise program for weight management, including:
| Reasons to seek professional help |
|---|
| Personalized plans: A professional can create a personalized exercise and nutrition plan that is tailored to your individual needs and goals. |
| Reduced risk of injury: A professional can show you the proper way to perform exercises, reducing your risk of injury. |
| Increased effectiveness: A professional can help to ensure that you are performing exercises that will be most effective in helping you achieve your weight management goals. |
| Monitoring progress: A professional can monitor your progress and make adjustments to your plan as needed to ensure that you continue to see results. |
Who can provide professional help?
There are several types of professionals who can provide help when starting an exercise program, including:
| Types of professionals |
|---|
| Personal trainer: A personal trainer can create a personalized exercise plan for you and provide guidance on proper exercise technique. |
| Dietitian: A dietitian can create a personalized nutrition plan for you to enhance your weight management efforts. |
| Doctor: A doctor can evaluate your health and provide guidance on exercise programs that will be safe and effective for you. |
Seeking professional help when starting an exercise program for weight management can help to ensure that you exercise safely and effectively, reducing your risk of injury and increasing the effectiveness of your efforts.
The Bottom Line
It is clear that exercise plays a crucial role in weight management. Regular physical activity can help one burn calories, increase metabolism, build muscle mass, and reduce body fat. However, it is important to keep in mind that the amount and type of exercise needed for weight management will vary from person to person depending on factors such as age, gender, and current fitness level.
For aerobic exercise, it is recommended to aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity activity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity activity per week. Resistance training, on the other hand, should be done at least two days a week, targeting all major muscle groups. Combining the two can be highly effective for weight management.
Cardiovascular exercise, strength training, and HIIT are all great options for weight management. Individuals should choose the type of exercise that they enjoy, as this can help them stick to their routine and make long-term lifestyle changes.
When starting an exercise program, it is important to progress gradually, set goals, and seek professional guidance if needed. Common mistakes to avoid include only focusing on cardio, forgetting about diet, overtraining, and not seeking professional help when necessary.
The benefits of exercise for weight management are numerous and well-documented. By incorporating regular physical activity into one’s routine and adopting healthy eating habits, individuals can achieve and maintain a healthy weight while improving overall health and wellbeing. Remember, the key to success is consistency and making lifestyle changes that can be maintained in the long-term.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is weight management?
Weight management refers to the methods and strategies used to maintain a healthy weight through proper diet, exercise, and lifestyle habits.
Can exercise alone help with weight loss?
While exercise can help with weight loss, it should be combined with a healthy diet for optimal results.
How does exercise affect metabolism?
Exercise can increase metabolism by boosting the number of calories burned at rest.
How much exercise should I do to manage my weight?
It is recommended to get at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity exercise per week for weight management.
What is the best type of exercise for weight management?
A combination of cardiovascular exercise, strength training, and interval training is best for weight management.
What is aerobic exercise?
Aerobic exercise is any activity that increases heart rate and breathing for an extended period of time, such as running, cycling, or swimming.
What is resistance training?
Resistance training is any exercise that involves working against resistance, such as weightlifting, to build strength and muscle mass.
What is HIIT?
HIIT, or high-intensity interval training, is a type of workout that involves short bursts of intense exercise followed by periods of rest or low-intensity exercise.
How can I avoid overtraining?
Listen to your body, vary your workouts, and make sure to take rest days to avoid overtraining.
Why is it important to seek professional help for exercise?
Seeking professional help, such as a personal trainer or physical therapist, can help you create a safe and effective exercise plan and prevent injuries.







