Have you ever experienced digestive issues or irregular bowel movements? Are you looking for a natural solution to maintain good digestion? Look no further than fiber! This often overlooked nutrient plays a crucial role in keeping our digestive system working effectively. In this article, we’ll explore what fiber is, its benefits for good digestion, and the top fiber-rich foods to add to your diet. So sit back, relax, and get ready to learn how fiber can transform your digestive health!
What is Fiber?
The mystery of what exactly fiber is can leave many wondering. When it comes to nutrition and digestion, understanding the importance of fiber is crucial for maintaining a healthy diet. Fiber, also known as roughage or bulk, refers to the indigestible part of plant foods that moves through the digestive system, absorbing water along the way and easing bowel movements. In this article, we will explore the different types of fiber, the recommended daily intake, and the impact fiber has on our digestion. Whether you’re looking to improve your gut health or incorporate more fiber-rich foods into your diet, we’ve got you covered.
The Two Types of Fiber
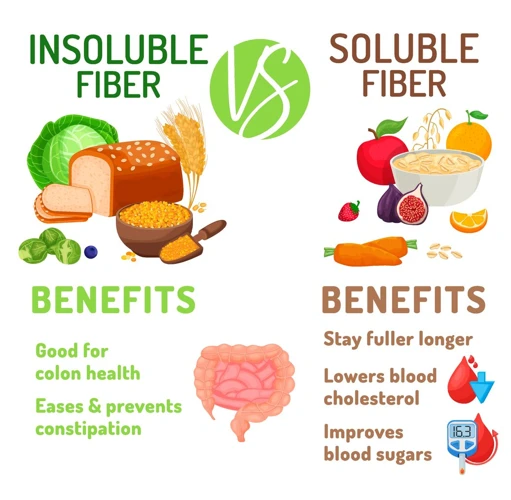
Fiber is an important nutrient that plays a crucial role in maintaining good digestion. There are two main types of fiber: soluble and insoluble.
Soluble fiber dissolves in water and forms a gel-like substance in the intestines, which helps to slow down the digestive process. This type of fiber is found in foods such as oats, beans, and some fruits and vegetables. Soluble fiber is known to help lower cholesterol levels in the blood, as well as regulate blood sugar levels.
Insoluble fiber, on the other hand, does not dissolve in water and helps to add bulk to stool, making it easier to pass. This type of fiber is found in foods such as whole grains, nuts, seeds, and most vegetables. Insoluble fiber is known to promote regular bowel movements and prevent constipation.
It’s important to consume both types of fiber in your diet for optimal digestive health. While some foods contain both types of fiber, others may contain more of one type than the other. By incorporating a variety of fiber-rich foods into your diet, you can ensure that you’re getting the benefits of both types of fiber.
If you’re experiencing digestive problems, increasing your fiber intake can be one way to improve your symptoms. However, it’s important to note that increasing your fiber intake too quickly can actually worsen digestive issues such as bloating and gas. Gradually increasing fiber intake and staying hydrated can help to prevent these issues.
Eating certain foods, such as probiotic-rich foods, whole foods, and foods high in fiber, can naturally aid digestion and promote gut health. Additionally, incorporating practices such as yoga and stress management techniques into your daily routine can also help to improve digestion.
Recommended Daily Intake of Fiber
Fiber is an essential nutrient that helps our digestive system to function properly. It is necessary to consume an adequate amount of fiber each day to maintain good digestive health. The recommended daily intake of fiber varies depending on age and gender. The following table shows the recommended daily intake of fiber for different age groups and genders:
| Age (Years) | Male (Grams per Day) | Female (Grams per Day) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Children | 1-3 | 19 | 19 |
| 4-8 | 25 | 25 | |
| Adolescents | 9-13 | 31 | 26 |
| 14-18 | 38 | 26 | |
| Adults | 19-50 | 38 | 25 |
| 51+ | 30 | 21 |
As we can see, males generally require more fiber than females. Adolescents also require more fiber than children and adults. It is important to note that these recommended values may vary based on an individual’s lifestyle, underlying health conditions, and certain medications they may be taking. The recommended fiber intake may increase during pregnancy or lactation. Check with a healthcare provider if you are uncertain about your recommended daily intake of fiber.
By consuming a well-balanced diet that includes adequate amounts of fiber, one can ensure good digestive health. The next section will explore the numerous benefits of fiber for good digestion, including its effect on constipation, colon cancer, blood sugar levels, and weight management.
Benefits of Fiber for Good Digestion

When it comes to promoting good digestion and overall health, fiber is an essential nutrient that should not be overlooked. Fiber plays an important role in maintaining digestive health and has numerous benefits that can help prevent common digestive issues and illnesses. Consisting of plant-based foods that our bodies can’t digest or absorb, fiber is essential for maintaining bowel regularity, preventing constipation, and even reducing the risk of colon cancer. Adding a variety of high-fiber foods to your daily diet can lead to a multitude of health benefits.
Prevents Constipation
Fiber is important for good digestion for various reasons, one of which is that it prevents constipation. Constipation is a common digestive problem that causes difficulty in bowel movements and straining. It occurs when the stool moves too slowly through the digestive system and becomes hard and dry, making it difficult to pass.
The good news is that increasing fiber intake can help prevent and alleviate constipation. Fiber adds bulk to the stool, making it easier to pass through the digestive tract. It also softens the stool by absorbing water, which helps to prevent constipation.
To further illustrate this point, here is a table of fiber-rich foods that can aid in the prevention of constipation:
| Fiber-Rich Foods | Fiber Content (per 1 cup/serving) |
|---|---|
| Broccoli | 5.1 grams |
| Raspberries | 8.0 grams |
| Lentils | 15.6 grams |
| Chickpeas | 12.5 grams |
| Avocado | 10.0 grams |
Other fiber-rich foods that can also help prevent constipation include whole grains, nuts, seeds, and fruits such as apples, pears, and bananas.
It’s also important to note that increasing fiber intake should be done gradually and with sufficient hydration to avoid potential digestive discomfort. Drinking enough water throughout the day is crucial for fiber to function properly and prevent constipation.
It’s worth noting that if you are experiencing chronic constipation or other digestive problems, it’s always best to consult with a healthcare professional. They can help identify the underlying cause of your digestive issues and suggest solutions or treatments that are tailored to your needs.
If you would like to learn more about other ways to aid digestion and maintain good gut health, check out our article on probiotics and their food sources.
Protects Against Colon Cancer
Fiber not only promotes regular bowel movements but also helps protect against colon cancer. The colon is the last part of the digestive system, where waste material is stored before being eliminated from the body. When food hangs around in the colon for too long, it may lead to the development of polyps, which could eventually turn cancerous.
Research has shown that a high-fiber diet can reduce the risk of developing colon cancer. This is because fiber helps speed up the passage of food through the digestive system, reducing the time that potentially harmful substances are in contact with the lining of the colon.
If you want to reduce the risk of developing colon cancer and other digestive problems, it’s essential to make fiber-rich foods a regular part of your diet. Here are some top fiber-rich foods that you can add to your meals:
- Legumes such as beans, lentils, and peas are excellent sources of fiber that also provide other essential nutrients.
- Beans, like black beans, pinto beans, and kidney beans, are an excellent source of both soluble and insoluble fiber.
- Berries such as raspberries, blueberries, and strawberries are rich in both fiber and antioxidants that help reduce the risk of various types of cancer.
- Whole grains, like brown rice, quinoa, and whole-wheat pasta, are an excellent source of dietary fiber and provide a range of essential vitamins and minerals.
- Nuts and seeds, such as chia seeds and almonds, are an excellent source of fiber, healthy fats, and protein.
- Vegetables like broccoli, cauliflower, and brussels sprouts are a great source of fiber and also contain various vitamins and minerals.
- Fruits such as apples, pears, and oranges are rich in insoluble fiber and can also help promote healthy digestion.
Incorporating these fiber-rich foods into your diet can help you protect your digestive system from disease and keep things moving smoothly. However, keep in mind that increasing fiber intake should be done gradually to avoid discomfort or digestive issues. Also, it’s essential to stay well hydrated to avoid constipation when consuming foods high in fiber.
If you’re looking for other ways to improve digestion, you can explore options such as 10 ways to aid digestion after overeating, foods to avoid for digestive problems, or even incorporating yoga and breathing exercises to promote gut health. Stress can also negatively affect digestion, so finding ways to manage stress levels can be an integral part of maintaining good digestive health, alongside consuming adequate fiber. And don’t forget to have a look at our article on healthy smoothies for digestion for some creative ways to add more fiber to your diet.
Helps Control Blood Sugar Levels
One of the lesser-known benefits of fiber is its ability to help control blood sugar levels. When we eat carbohydrates, they are broken down into sugar molecules in our body. These sugar molecules then enter our bloodstream, causing our blood sugar levels to rise. However, fiber can help slow down the absorption of sugar into our bloodstream, which can help prevent blood sugar spikes and crashes.
How does this work? Soluble fiber, which dissolves in water, forms a gel-like substance in our gut. This substance slows down the passage of food through our digestive system, allowing for a slower and more gradual release of sugar into our bloodstream. This can be especially beneficial for people with diabetes or those at risk of developing the disease.
Some of the top high-fiber foods for controlling blood sugar levels include:
- Legumes: This includes beans, lentils, and peas. They are not only high in fiber, but also protein, which can also help slow down the absorption of sugar.
- Berries: Berries are an excellent source of fiber and also contain antioxidants, which can help protect against inflammation and disease.
- Whole grains: Whole grains like brown rice, quinoa, and oats are high in fiber and also have a lower glycemic index, meaning they won’t cause a large spike in blood sugar levels.
- Nuts and seeds: Nuts and seeds are not only high in fiber, but also healthy fats and protein, which can help slow down digestion and prevent blood sugar spikes.
- Vegetables: Vegetables like broccoli, spinach, and Brussels sprouts are high in fiber and also rich in other important nutrients like vitamins and minerals.
If you’re looking to better control your blood sugar levels, incorporating more fiber-rich foods into your diet can be a great place to start. Just be sure to start slowly and gradually increase your intake, as too much fiber too quickly can cause digestive discomfort. It’s also important to choose whole foods over processed foods, read food labels to ensure you’re getting enough fiber, and stay hydrated to help fiber move through your digestive system smoothly.
If you’re experiencing digestive issues related to stress, be sure to check out our article on stress and digestion for more tips on how to support your gut health.
Supports Weight Management
Fiber is an important nutrient that is beneficial for weight management. It aids in weight loss by helping you feel full for longer periods of time, which can prevent overeating and snacking between meals.
Here are some ways fiber supports weight management:
- Fiber takes up space in your stomach and slows down the digestive process, making you feel full for longer and reducing the likelihood of overeating. This can lead to a reduction in calorie intake over time.
- Fiber-rich foods often require more chewing, which can also help to slow down your eating speed and assist with portion control.
- High-fiber foods like fruits and vegetables are often low in calories and nutrient-dense, meaning you can eat more of them without consuming excess calories.
- Fiber can also help to stabilize blood sugar levels, reducing cravings for sugary foods that can contribute to weight gain.
Incorporating high-fiber foods into your diet can be a helpful tool for maintaining a healthy weight. However, it’s important to note that increasing fiber intake should be done gradually and in conjunction with a balanced diet and regular exercise regimen.
Top Fiber-Rich Foods to Add to Your Diet
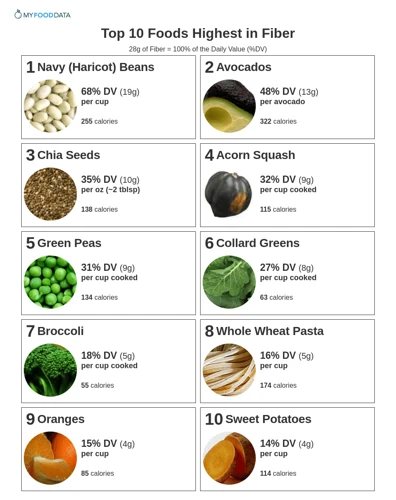
When it comes to achieving optimal digestive health, incorporating fiber-rich foods into your daily diet can make a significant difference. These foods not only aid in digestion but can also provide numerous other health benefits, such as reducing the risk of certain diseases and supporting weight management. In this section, we’ll explore some top foods that are high in fiber and easy to incorporate into your meals. By adding these options to your grocery list and meals, you’ll be making a positive impact on your digestive and overall health.
Legumes
Legumes are a great source of fiber as well as other essential nutrients like protein and iron. Including legumes in your diet can also help decrease the risk of chronic diseases such as diabetes, heart disease, and certain types of cancer. Here are some of the top legumes to consider adding to your diet:
| Legume | Fiber per 1/2 cup (cooked) | Other Nutrients |
|---|---|---|
| Lentils | 8 grams | Protein, iron, folate, potassium |
| Chickpeas | 6 grams | Protein, iron, folate |
| Black beans | 8 grams | Protein, iron, folate, potassium |
| Lima beans | 6 grams | Protein, iron, folate, potassium |
| Green peas | 4 grams | Protein, vitamin C, vitamin K |
These legumes can be easily added to soups, stews, salads, and curries. They can also be used to make dips and spreads like hummus, or as a meat substitute in vegetarian dishes. Including legumes in your diet is a great way to increase your daily fiber intake and reap the many health benefits they offer.
Beans
Beans are a fantastic source of fiber that can help to keep your digestive system healthy. They are also packed with other nutrients like protein, iron, and folate. There are many types of beans to choose from, so it’s easy to find a variety that you enjoy. Here are some of the top fiber-rich beans to add to your diet:
- Black Beans: These beans have 15 grams of fiber per cup, making them an excellent choice for boosting your fiber intake. They are also loaded with antioxidants and protein.
- Lentils: Lentils are a great source of both soluble and insoluble fiber, with 16 grams of fiber per cup. They are also rich in iron and protein, making them a great meat alternative.
- Split Peas: Split peas are an excellent source of soluble fiber, with 16 grams per cup. They are also low in fat and high in protein, making them a healthy addition to any meal.
- Chickpeas: Also known as garbanzo beans, chickpeas are a versatile option that can be added to salads, soups, and stews. They have 12.5 grams of fiber per cup and are also a good source of protein and iron.
Adding beans to your diet is easy and affordable. You can find them canned or dried at most grocery stores, and they can be added to a variety of dishes like chili, stir-fry, and burritos. So why not try adding some fiber-rich beans to your next meal? Your digestive system will thank you!
Berries
Berries, such as strawberries, blueberries, raspberries, and blackberries, are not only delicious but also an excellent source of fiber. These small, juicy fruits are packed with nutrients that contribute to better digestion and overall health.
Strawberries: One cup of strawberries contains 3 grams of fiber. They are also high in vitamin C, which boosts the immune system.
Blueberries: One cup of blueberries contains 4 grams of fiber. They are also rich in antioxidants, which help protect the body against damage from free radicals.
Raspberries: One cup of raspberries contains 8 grams of fiber. They are also a good source of vitamin C and manganese.
Blackberries: One cup of blackberries contains 8 grams of fiber. They are also high in vitamin C and vitamin K.
Berries are incredibly versatile and can be enjoyed in many different ways. They can be eaten as a snack, added to smoothies, used in baking, or added to oatmeal or yogurt for breakfast. Choose fresh or frozen berries without added sugar for the most health benefits.
Adding berries to your diet is a simple and delicious way to increase your fiber intake. Plus, they are low in calories and high in nutrients, making them a great addition to any healthy diet.
Whole Grains
Whole grains are an excellent source of fiber, and they should be included in your daily diet for good digestion. They offer several health benefits and provide essential nutrients that are beneficial for overall health.
Here is a table of some top whole grains rich in fiber:
| Whole Grains | Fiber Content (per 100g serving) |
|---|---|
| Oats | 10.6g |
| Brown Rice | 3.5g |
| Quinoa | 2.8g |
| Barley | 2g |
| Bulgur | 4.1g |
| Wheat Berries | 12.6g |
Oats are one of the most popular grains and are available in several forms such as rolled, quick or steel-cut. They are a great source of soluble fiber, which slows down the digestion process and helps in maintaining stable blood sugar levels. Brown rice is another excellent source of fiber and can be consumed in several forms, including as a side dish or in a salad.
Quinoa is a unique grain that is rich in both fiber and protein, and it’s equally beneficial for vegetarians and non-vegetarians. It is a great gluten-free option and can be used to replace rice or pasta in several dishes.
Barley is another fiber-rich whole grain that can be used to make soups or stews, adding a nutty flavor to the dishes. It is also an excellent source of selenium, which is an important nutrient for the immune system.
Bulgur is a common ingredient in Mediterranean and Middle Eastern cuisines and is used in dishes such as tabbouleh or kibbeh. It’s a great source of fiber and contains essential minerals such as iron and magnesium.
Wheat berries are unprocessed whole wheat kernels and are an excellent source of fiber, protein, and other essential nutrients. They can be used in salads or as a side dish, and they provide a unique chewy texture to the dishes.
Incorporating these whole grains into your daily diet can help in maintaining good digestion and overall health.
Nuts and Seeds
Nuts and seeds are not only delicious but also packed with fiber. They are a great addition to any diet and can help improve digestion. Here are some of the top nuts and seeds to add to your diet:
- Chia seeds: Chia seeds are a great source of fiber, with 10 grams per ounce. They are also high in omega-3 fatty acids, which can help reduce inflammation and improve heart health.
- Flaxseeds: Flaxseeds are another great source of fiber, with 8 grams per ounce. They are also high in lignans, which have been shown to have anti-cancer properties.
- Almonds: Almonds are a good source of fiber, with 3.5 grams per ounce. They are also high in vitamin E, which is important for skin health.
- Pistachios: Pistachios are a good source of fiber, with 2.9 grams per ounce. They are also high in protein and healthy fats, which can help keep you feeling full and satisfied.
- Walnuts: Walnuts are a good source of fiber, with 2 grams per ounce. They are also high in omega-3 fatty acids, which can help reduce inflammation and improve brain health.
Adding nuts and seeds to your diet is easy. You can sprinkle them on top of your morning oatmeal or yogurt, add them to your lunchtime salad, or snack on them in between meals. Just be sure to watch your portion sizes, as nuts and seeds are high in calories. A small handful, about 1 ounce, is typically a good serving size.
Vegetables
Vegetables are an excellent source of fiber that should be included in a healthy and balanced diet. They come in a wide range of colors, textures, and flavors, making it easy to incorporate them into your meals. Here are some of the top fiber-rich vegetables to add to your diet:
| Vegetable | Serving Size (1 cup) | Fiber Content |
| Artichokes | One medium | 6.9 grams |
| Broccoli | Chopped, raw | 2.4 grams |
| Brussels Sprouts | Chopped, boiled | 4.1 grams |
| Carrots | Chopped, raw | 3.6 grams |
| Cauliflower | Chopped, raw | 2 grams |
| Green Peas | Boiled | 8.8 grams |
| Kale | Chopped, raw | 2.6 grams |
| Spinach | Chopped, raw | 0.7 grams |
Adding a variety of vegetables to your diet is an easy way to get more fiber. Whether you enjoy them raw, steamed, or roasted, vegetables provide essential nutrients and help keep your digestive system running smoothly. So, next time you’re planning your meals, make sure to include a few of these fiber-rich veggies on your plate.
Fruits
One of the best and most delicious sources of fiber is fruit. With an array of colors and flavors, fruits are not only satisfying to the taste buds but also provide a plethora of nutrients that are critical for overall health. Here are some of the fiber-rich fruits to add to your diet:
- Apples: Apples are an excellent source of soluble fiber, particularly in their skin. Soluble fiber helps to reduce blood cholesterol levels and regulate blood sugar levels. Also, apples contain a type of insoluble fiber known as pectin, which helps to support healthy digestion.
- Pears: Pears are also high in soluble fiber, which can help lower cholesterol and maintain bowel regularity. Additionally, they contain sorbitol, a natural sugar alcohol that acts as a mild laxative and helps to prevent constipation.
- Raspberries: Raspberries are a great source of both soluble and insoluble fiber, making them an excellent choice for maintaining digestive health. They also contain antioxidants, which can protect the body against damage from free radicals.
- Bananas: Bananas are a good source of dietary fiber that helps to promote regularity and support digestive health. They also contain resistant starch, a type of carbohydrate that can help to feed the good bacteria in the gut.
- Avocado: While technically a fruit, avocados are an excellent source of fiber, particularly insoluble fiber. Additionally, they are rich in healthy monounsaturated fats, which can help to lower cholesterol and reduce inflammation in the body.
By incorporating these fiber-rich fruits into your diet, you can not only satisfy your sweet tooth but also support good digestive health. However, it’s important to remember that fruits should be consumed in moderation as they are also a source of natural sugars. Strive for at least 2-3 servings of fruit per day and choose a variety of colors to ensure a diverse range of nutrients.
How to Increase Fiber Intake
If you have recently discovered the benefits of fiber for good digestion, you may be wondering how to increase your fiber intake. Fortunately, making small changes to your diet can make a big impact over time. In this section, we will explore some practical tips and strategies to help you incorporate more fiber-rich foods into your diet. By following these simple steps, you can enjoy the benefits of improved digestion and overall health.
Start Slowly and Gradually Increase Intake
When it comes to increasing fiber intake in your diet, it’s essential to start slowly and gradually increase your intake. This is important because sudden increases in fiber intake can lead to discomfort, bloating, and gas. It’s best to make small changes and give your body time to adjust to the new diet.
Here are some tips to follow while gradually increasing your fiber intake:
- Add one high-fiber food at a time: Adding legumes or whole grains to your meal can be a good start. You can also add a small serving of fruits or vegetables to your meals gradually.
- Track your fiber intake: It’s essential to keep track of your fiber intake and ensure you’re gradually moving towards the recommended daily intake.
- Drink plenty of water: High fiber intake requires water to help digestion. Drinking plenty of fluids can help prevent constipation and improve bowel movements.
- Listen to your body: It’s important to pay attention to how your body responds to new high-fiber foods so you can adjust accordingly.
By gradually increasing your fiber intake, you can help your body adjust to new foods and reduce the chances of digestive problems. Over time, your body will get used to eating high-fiber foods, which will help you achieve your recommended daily intake of fiber for optimal digestive health.
Choose Whole Foods over Processed Foods
When it comes to increasing your fiber intake, it’s important to choose whole foods over processed foods. Whole foods are foods that are in their natural state, with minimal processing or refinement. These foods tend to be higher in fiber and other nutrients, making them a better choice for overall health.
Processed foods, on the other hand, have often been stripped of their natural fiber content during processing. They are also frequently high in added sugars, fats, and calories, which can have negative implications for digestion and overall health when consumed in excess.
To help illustrate the importance of choosing whole foods over processed foods, we’ve compiled a list of some common examples of each:
| Whole Foods | Processed Foods |
|---|---|
| Whole fruits | Fruit juice |
| Vegetables | Canned vegetables with added salt or sugar |
| Whole grains | Refined grains like white bread, white rice, and pasta |
| Legumes | Canned, seasoned beans |
| Nuts and seeds | Candied or salted nuts, sweetened nut butter spreads |
As you can see, whole foods tend to be simple, unprocessed, and closer to their natural state. Choosing whole foods over processed ones can help you increase your fiber intake and benefit from a wider range of nutrients, without the added sugars and calories commonly found in processed foods.
Additionally, whole foods tend to be more filling and satisfying than processed foods, which can help you maintain a healthy weight and avoid overeating. Incorporating more whole foods into your diet can be a simple yet effective way to increase your fiber intake and promote good digestion.
Read Food Labels
When trying to increase your fiber intake, it is important to read food labels carefully. This will help you identify foods that are high in fiber and those that are not. Here are some tips on how to read food labels to identify high fiber foods:
- Look for High Fiber Content: When reading food labels, look for the total amount of fiber per serving. Aim for foods that have at least 3 grams of fiber per serving.
- Check Serving Size: Be sure to check the serving size listed on the label. The amount of fiber listed is based on the serving size, so make sure you are comparing similar servings when looking at different products.
- Identify Sources of Fiber: Look at the list of ingredients to identify sources of fiber. Foods that are high in fiber will typically list whole grains, fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds as ingredients.
- Beware of Added Sugars: Many processed foods that are high in fiber also contain added sugars. Be sure to check the ingredient list for added sugars, such as high fructose corn syrup, cane sugar, or molasses.
- Choose Foods with Minimal Processing: Foods that are minimally processed are often higher in fiber than heavily processed foods. Choose whole foods, such as fresh fruits and vegetables, whole grains, and legumes, over highly processed products like chips and snack bars.
By reading food labels and choosing foods that are high in fiber, you can improve your digestive health and overall well-being. Remember to aim for at least 25 grams of fiber per day for women and 38 grams for men. Start by incorporating high fiber foods into your diet gradually and increase your intake over time.
Stay Hydrated
Drinking enough water is crucial for good digestion, and it is especially important when consuming a diet high in fiber. Fiber absorbs water as it moves through the digestive system, which helps to soften stools and prevent constipation. It is important to stay well hydrated so that fiber can do its job properly.
How much water should you drink?
There is no single answer to this question since the amount of water a person needs can vary depending on their age, gender, weight, activity level, and other factors. However, a common recommendation is to drink at least eight glasses of water per day, which is equivalent to about two liters.
Other sources of hydration
While water is the best way to stay hydrated, other beverages and foods can also contribute to your daily fluid intake. Some examples include:
| Beverages | Approximate Fluid Content (per 8 oz. serving) |
|---|---|
| Water | 8 ounces |
| Tea (herbal or non-herbal) | 8 ounces |
| Coffee | 8 ounces |
| Milk (cow’s or plant-based) | 8 ounces |
| Juice (100% fruit juice) | 8 ounces |
In addition to beverages, many fruits and vegetables have high water content, which can also contribute to your daily fluid intake. Examples include watermelon, cucumber, celery, and tomatoes.
The bottom line
Staying well hydrated is important for good digestion, and it is especially crucial when consuming a diet high in fiber. Aim to drink at least eight glasses of water per day, and consider other sources of hydration such as herbal tea, milk, and high-water-content fruits and vegetables.
Conclusion
In conclusion, it’s clear that fiber plays a crucial role in maintaining good digestion and overall health. There are two types of fiber, soluble and insoluble, and both should be included in our daily diet. The recommended daily intake of fiber is around 25-30 grams, but many people fail to reach this goal.
The benefits of consuming adequate amounts of fiber cannot be overstated. Fiber keeps our digestive system functioning properly, preventing constipation, protecting against colon cancer, and helping to control blood sugar levels. Additionally, fiber supports weight management by keeping us feeling full longer and reducing overall calorie intake.
To increase fiber intake, it’s essential to incorporate fiber-rich foods into our diet. This includes legumes, beans, berries, whole grains, nuts and seeds, vegetables, and fruits. When making diet changes, it’s essential to start gradually and choose whole foods over processed ones. Reading food labels and staying hydrated can also be helpful when increasing fiber intake.
By increasing fiber intake, you can reap the numerous benefits of this essential nutrient and improve your digestive health. Don’t hesitate to start incorporating fiber-rich foods into your diet today. Your body will thank you for it!
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between soluble and insoluble fiber?
Soluble fiber dissolves in water and forms a gel-like substance in the digestive tract, while insoluble fiber adds bulk to stool and helps food pass through the digestive system.
How does fiber prevent constipation?
Fiber increases stool bulk and softness, making it easier to pass through the digestive tract. It also helps regulate bowel movements by stimulating the muscles in the intestines.
What role does fiber play in preventing colon cancer?
Insoluble fiber in particular helps prevent colon cancer by promoting regular bowel movements and reducing the time that waste spends in the digestive tract.
Can fiber help with weight loss?
Yes, fiber can aid in weight management by increasing satiety and reducing overall calorie intake. Soluble fiber in particular has been shown to reduce belly fat.
What are some examples of legumes?
Legumes include foods such as lentils, chickpeas, black beans, and peanuts.
How much fiber should I aim to consume each day?
The recommended daily intake of fiber is 25 grams for women and 38 grams for men.
How can I tell if a food is high in fiber?
One way to identify high fiber foods is to check the nutrition label for the amount of dietary fiber per serving. Foods with 5 grams or more of fiber per serving are considered high in fiber.
Should I consume fiber supplements instead of whole foods?
It is recommended to consume fiber from whole food sources rather than relying solely on supplements, as whole foods contain other beneficial nutrients and promote overall health.
Can too much fiber be harmful?
Consuming excessive amounts of fiber can lead to bloating, gas, and diarrhea. It is important to gradually increase fiber intake and stay hydrated to prevent these symptoms.
What are some easy ways to add more fiber to my diet?
Addition of things like oatmeal and fruit to breakfast or opting for whole grain breads and pasta are simple ways to add more fiber to your diet. Eating more raw vegetables and other healthy snacks such as nuts and seeds can also be helpful.







