When it comes to maintaining a healthy diet, there are many conflicting opinions on how much fat we should consume. Some diet plans promote a low-fat lifestyle, while others emphasize the benefits of healthy fats. With so many different opinions, it can be hard to know which approach to take. In this article, we will explore the different types of fat, recommended daily intake guidelines from reputable sources, and the various health benefits and risks associated with fat consumption. By the end of this article, you will have a better understanding of the role fat plays in a healthy diet and be able to make more informed choices about the types and amounts of fat you consume.
Types of Fat
Understanding the different types of fat is crucial when it comes to making informed and healthy dietary choices. Not all fats are created equal, and some can have negative effects on our health while others are essential for our wellbeing. While some types of fat, such as monounsaturated and omega-3 fatty acids, are known to have numerous health benefits, others, like trans fats, are associated with an increased risk of heart disease and other health issues. In this section, we will explore the various types of fat and their impact on our bodies. For more detailed information on the health effects of saturated fats, check out our article “Saturated Fats: Separating Health from Hype.”
Saturated Fat
Saturated fats are typically solid at room temperature and come mainly from animal sources. They are commonly found in high-fat dairy products, fatty meat, and processed meats. The American Heart Association recommends limiting the intake of saturated fats to less than 6% of daily caloric intake. Research has shown a strong correlation between consuming high amounts of saturated fat and an increased risk of heart disease and stroke.
It’s essential to choose healthier sources of fat, such as monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats. These types of fats are commonly found in plant-based foods like nuts, seeds, and avocados. They also play a crucial role in reducing the bad cholesterol levels in the body, which reduces the risk of heart disease.
It’s important to note that not all saturated fats are created equal. Some types of saturated fats, such as those found in coconut oil, have been shown to have some health benefits. However, more research is needed to understand the full extent of these benefits.
Choosing healthy fat alternatives is crucial when it comes to protecting your heart health. These alternatives include using extra virgin olive oil, avocado, and nuts instead of butter or margarine. The Mediterranean diet is an excellent example of a diet rich in healthy fats that can offer several health benefits. Several studies have shown that the Mediterranean diet may have protective effects against chronic diseases such as heart disease and type 2 diabetes.
While it’s important to limit the consumption of saturated fats, it’s equally essential to choose healthy fat sources that can provide a range of health benefits. By making small changes to your diet and choosing healthy fat alternatives, you can reduce your risk of heart disease and enjoy better overall health.
Unsaturated Fat
Unsaturated fats are considered to be healthy and are a recommended part of a balanced diet. These fats are usually in a liquid form at room temperature and are predominantly found in vegetable oils, nuts, seeds, and fish.
Monounsaturated fats are a type of unsaturated fat that have only one double bond in their chemical structure. Eating foods high in monounsaturated fats has been linked to a reduced risk of heart disease and lower levels of LDL (bad) cholesterol. Some examples of foods high in monounsaturated fats include avocado, olive oil, and nuts like almonds and cashews. For more options, check out our article on 10 healthy monounsaturated fats.
Polyunsaturated fats have more than one double bond in their chemical structure. These fats are essential because they provide the body with essential fatty acids that the body cannot produce itself. Polyunsaturated fats can be found in foods like salmon, flaxseeds, soybean oil, and some nuts. For more information on the importance of polyunsaturated fats in the diet, check out our article on the importance of polyunsaturated fats in the diet.
Omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids are two types of polyunsaturated fats that have been linked to numerous health benefits. Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fatty fish like salmon and tuna, have been shown to reduce inflammation and the risk of heart disease. You can read more about the benefits of omega-3 fatty acids in our article on the benefits of omega-3 fatty acids.
Healthier alternatives to saturated fats include unsaturated fats. Substituting saturated fats with unsaturated fats has been shown to improve overall health and reduce the risk of heart disease. You can read about some of these healthier alternatives in our article on healthier fat alternatives to butter and margarine.
Incorporating more unsaturated fats into your diet can be a healthy choice. One popular diet that emphasizes the consumption of healthy fats like unsaturated fats is the Mediterranean diet. You can read more about how a high-fat diet can be healthy in our article on the Mediterranean diet and healthy fats.
How Much Fat Should You Eat Per Day?
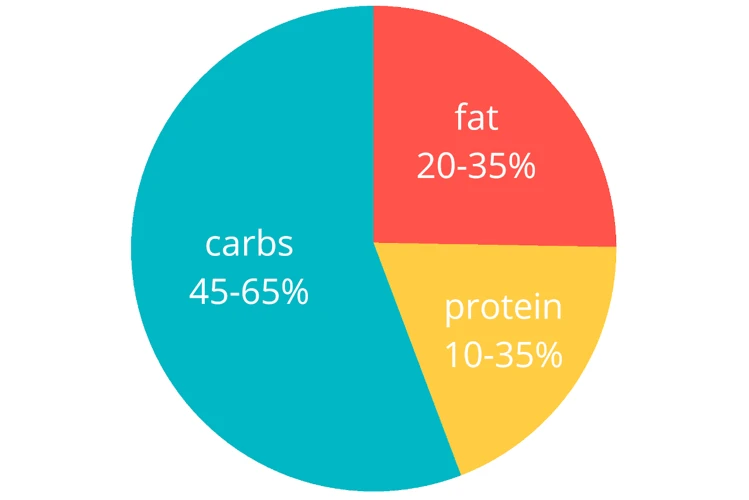
Determining the appropriate amount of fat to consume each day can be perplexing. While some types of fat provide health benefits, others can increase the risk of heart disease and other health issues. Fortunately, there are guidelines that suggest recommended daily intake of fat, and customized intake options based on individual factors. Before calculating your personal intake, understanding the different types of fat is important. This knowledge can help make informed decisions about what types of fat to consume and in what amounts. To learn more about the types of fats and the guidelines for daily intake, read the following sections. Additionally, understanding the benefits of healthy fats and the risks of unhealthy fats can further clarify the importance of monitoring one’s fat intake.
The American Heart Association Guidelines
The American Heart Association guidelines recommend limiting your daily intake of saturated fats to no more than 5-6% of your daily calorie intake. For an average adult consuming 2000 calories per day, this means restricting the saturated fat intake to 11-13 grams per day. Saturated fats are mostly found in animal products such as meat, dairy, and eggs. The AHA also advocates replacing trans fats with healthy fats. Trans fats are usually found in processed foods and baked goods.
The American Heart Association also recommends consuming healthy fats, like those found in nuts, seeds, and fish. These unsaturated fats can have health benefits when consumed in moderation. The AHA suggests that 25-35% of your daily calorie intake should come from unsaturated fats.
While the American Heart Association is a reliable source for nutrition information, it’s important to note that these guidelines may vary depending on your unique health needs. Consult with a registered dietitian or your healthcare provider for personalized recommendations. It’s important to know that a high-fat diet can be healthy if the majority of fats come from unsaturated sources, like avocados, nuts, and olive oil. Research has shown that diets high in healthy fats are associated with reduced risk of heart disease and stroke, while diets high in unhealthy fats can increase the risk. So, it’s essential to be mindful of the types of fat consumed in your diet. For more information about the role of trans fats in your diet, check out our guide to trans fats and their impact on health. The quality and quantity of fats in the diet can significantly impact heart health, making it crucial to be mindful of fat intake.
The Institute of Medicine Guidelines
According to The Institute of Medicine Guidelines, adults should consume 20-35% of their daily calorie intake from dietary fats. This means that if a person consumes 2000 calories per day, they should consume between 44 and 77 grams of fat per day. However, these recommendations vary based on age, sex, and physical activity level.
The Institute of Medicine also recommends limiting intake of saturated fats to less than 10% of daily calorie intake. This is because high intake of saturated fats can increase LDL cholesterol levels and increase the risk of heart disease. Additionally, consuming trans fats should be avoided as much as possible as they have been linked to an increased risk of heart disease and other health issues.
It’s important to note that not all fats are created equal, and some types of fat are actually beneficial for our health. Rather than solely focusing on limiting fat intake, it’s important to make choices that prioritize consuming healthy fats while limiting unhealthy ones.
For more information on the role of dietary fats in heart health, check out our article on dietary fats and heart health.
Customized Fat Intake
Customized Fat Intake
While the American Heart Association and Institute of Medicine have provided general guidelines for fat intake, individual needs may vary depending on factors such as age, gender, activity level, and health status. That’s why customized fat intake may be a better approach for some people.
To determine your customized fat intake, you need to calculate your daily caloric needs first. Then, you can allocate a certain percentage of those calories to fat. As a general rule, it’s recommended that fat should make up 20-35% of your daily caloric intake.
Here’s an example of how to calculate your customized fat intake:
Step 1: Calculate your daily caloric needs based on your age, gender, and activity level. For example, a 30-year-old sedentary female may need around 1,800 calories per day.
Step 2: Determine the percentage of calories you want to allocate to fat. Let’s assume you want to aim for 30% fat intake.
Step 3: Convert the percentage to grams of fat. To do this, multiply your daily caloric intake by the percentage of calories you want to come from fat, and then divide by 9 (since fat contains 9 calories per gram).
Using the example above, 30% of 1,800 calories is 540 calories (0.3 x 1,800). To convert that to grams of fat, divide 540 by 9, which equals 60 grams of fat per day.
Remember that this is just a general guideline and your customized fat intake may need to be adjusted based on your individual needs and health goals. It’s also important to choose healthy sources of fat, such as those high in unsaturated fats, to promote optimal health.
To help you keep track of your customized fat intake, consider using a food diary or app that helps you log and monitor your daily macronutrient intake. By being mindful of your fat intake and making healthy food choices, you can support your overall health and well-being.
| Step | Calculation | Example |
| Step 1 | Determine daily caloric needs based on age, gender, and activity level | A sedentary 30-year-old female needs around 1,800 calories per day |
| Step 2 | Determine percentage of calories to allocate to fat | Aim for 30% fat intake |
| Step 3 | Convert percentage to grams of fat | For 30% fat intake, that would be 60 grams of fat per day for a person consuming 1,800 calories |
Measuring Your Fat Intake
It can be difficult to determine how much fat you are consuming each day simply by eyeballing your meals. However, there are methods to measure your fat intake more accurately.
One way is to use a food scale to weigh the portions of fatty foods that you consume. This will give you a more accurate idea of how many grams of fat you are eating. You could also use measuring cups to portion out the appropriate amount of liquid fats, such as olive oil or avocado oil.
Another method to measure your fat intake is to keep a food diary in which you record the types and amounts of fats you consume each day. You can also use online resources or mobile apps that help you keep track of your nutrition intake.
It’s important to note that your recommended fat intake may vary based on a variety of factors, including your age, gender, weight, and physical activity level. Additionally, your recommended fat intake may change if you have certain health conditions such as high cholesterol or heart disease.
Regardless of how you measure your fat intake, it’s essential to pay attention to the types of fats you are consuming. Aim to consume mainly heart-healthy fats, such as mono- and polyunsaturated fats, and limit your intake of saturated and trans fats.
The Benefits of Healthy Fats

As contradictory as it may sound, consuming certain types of fats can actually be beneficial for your health. Healthy fats, unlike their unhealthy counterparts, can provide numerous advantages to our body systems. Including these fats in your diet can lead to better heart health, improved brain function, and a stronger immune system, among other things. Let’s take a deeper dive into the benefits of healthy fats and how they can nourish your body.
Lowering Risk of Heart Disease and Stroke
Adding healthy fats to your diet can have numerous benefits, including the potential to lower your risk of heart disease and stroke. Research shows that eating foods high in unsaturated fats, such as fatty fish, avocado, nuts, and seeds, can help improve cholesterol levels, lower blood pressure, and reduce inflammation in the body.
Additionally, a diet high in healthy fats can help lower the risk of developing heart disease and stroke by reducing the buildup of plaque in the arteries. This plaque buildup is often caused by a diet high in saturated and trans fats, which can be found in processed and fried foods.
Saturated and trans fats can raise your LDL, or “bad” cholesterol levels, which can increase your risk of heart disease and stroke. On the other hand, incorporating healthy fats into your diet can help increase your HDL, or “good” cholesterol levels, which can help protect your heart.
It’s important to note, however, that incorporating healthy fats into your diet should be done in moderation, as they are still high in calories. It’s recommended to replace saturated and trans fats with healthier, unsaturated fats rather than adding them on top of an already unhealthy diet.
Better Absorption of Vitamins
Healthy fats play a crucial role in the absorption of vitamins by the body. Vitamins, such as A, D, E, and K, are fat-soluble, which means they need fat to be properly absorbed and utilized by the body. When you consume healthy fats like those found in avocado and nuts and seeds, you provide your body with the necessary nutrients to help absorb vitamins and improve overall health.
On the other hand, consuming unhealthy fats, such as those found in fast foods and processed snacks, can have the opposite effect on vitamin absorption. Not only do these fats lack the nutrients needed for vitamin absorption, but they can also interfere with the absorption process altogether.
To ensure your body properly absorbs vitamins, it’s important to include foods high in healthy fats in your diet. Try incorporating salmon and other fatty fish, which are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, and extra virgin olive oil, which is high in monounsaturated fats, into your meals. Additionally, snacking on peanut butter or incorporating nuts and seeds into your meals can provide a boost of healthy fats to help with vitamin absorption.
Improved Brain Function
Consuming healthy fats can lead to numerous health benefits, including improved brain function. The brain is made up of nearly 60% fat, so it is important to include healthy fats in your diet. These types of fats help to provide the brain with the necessary nutrients it needs to function properly.
Here are some of the ways that healthy fats can improve brain function:
- Better Memory and Cognitive Function: Research has linked diets high in healthy fats with improved memory and cognitive function. Omega-3 fatty acids, in particular, have been shown to improve memory and reduce the risk of Alzheimer’s disease.
- Improved Mood: Healthy fats can help to improve mood and reduce symptoms of depression. Omega-3 fatty acids have been shown to reduce inflammation in the brain, which can lead to improved mood and a decreased risk of depression.
- Reduced Risk of Brain Disorders: Some research suggests that diets high in healthy fats may reduce the risk of developing brain disorders such as Parkinson’s and multiple sclerosis.
- Improved Learning: Studies have shown that consuming healthy fats can improve learning and information processing. Omega-3 fatty acids in particular have been linked to improved learning and attention span.
Including foods high in healthy fats, like salmon, avocado, nuts, and olive oil, in your diet can lead to improved brain function and overall health. It is important to make healthy food choices and include a variety of foods in your diet to ensure that you are getting all the necessary nutrients your body needs to function properly.
Foods High in Healthy Fats
When it comes to incorporating healthy fats into your diet, it can be hard to know where to start. However, with so many delicious and nutritious options available, you’re sure to find something you love. From fatty fish to nuts and seeds, these foods are not only satisfying, but also provide numerous health benefits. So, let’s explore some of the top foods high in healthy fats that you can start incorporating into your diet today.
Salmon and Other Fatty Fish
Fish is an excellent source of healthy fat, and fish that are rich in omega-3 fatty acids include salmon, sardines, herring, and mackerel. These fatty fish contain a type of omega-3 called EPA and DHA. Consuming these types of omega-3s can help reduce inflammation in the body and lower the risk of heart disease.
Below is a table showcasing the nutritional information for a 3.5-ounce (100-gram) serving of some of the most popular fatty fish:
| Fatty Fish | Calories | Protein (g) | Fat (g) | Omega-3 (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Salmon (Atlantic, Farmed) | 206 | 22 | 13 | 2.3 |
| Sardines (Pacific, Canned in Oil) | 208 | 24 | 11 | 1.5 |
| Herring (Atlantic, Pickled) | 262 | 18 | 20 | 1.7 |
| Mackerel (Atlantic, Cooked) | 305 | 20 | 25 | 1.8 |
As shown in the table, salmon provides a good source of protein along with a healthy dose of omega-3s. Canned sardines are another budget-friendly option for getting your daily dose of healthy fats while remaining low in calories.
When consuming fish, it is important to be mindful of the mercury content. Large, predatory fish such as tilefish and swordfish have higher levels of mercury, and it is recommended to limit their consumption. Pregnant women and children are particularly vulnerable to the effects of mercury and should avoid these types of fish altogether.
Incorporating fatty fish into your diet at least two times a week can be a great way to increase your intake of healthy fats and reap the associated health benefits.
Avocado
Avocados are packed with healthy unsaturated fats that our bodies need. In fact, avocados are one of the richest sources of healthy fats available. Not only that, but they are also rich in a variety of nutrients, including fiber, potassium, and vitamins C, K, and B6. Adding avocado to your diet can bring multiple health benefits.
Consider incorporating avocados into your diet by following these ideas:
- Sliced on toast: Mash some avocado onto a slice of whole-grain toast and sprinkle with salt, pepper, and red pepper flakes for a delicious and satisfying breakfast or snack.
- In a smoothie: Add half an avocado to your morning smoothie for added creaminess and a boost of healthy fats.
- In a salad: Add sliced avocado to your favorite salad for a satisfying and nourishing meal.
- As a dip: Make guacamole by mashing avocado with diced tomato, onion, and lime juice for a delicious dip for carrots, celery, or whole-grain tortilla chips.
- In a wrap: Add sliced avocado to your favorite wrap or sandwich for added creaminess and nourishment.
It’s important to note that while avocados are high in healthy fats, they are also high in calories, so it’s important to consume them in moderation as part of a balanced diet. Incorporating them in a variety of ways can help increase their nutritional value and keep your meals interesting.
Nuts and Seeds
Nuts and seeds are an excellent source of healthy fats. Almonds, for example, are a great source of vitamin E, magnesium, and fiber. Walnuts are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which have been shown to improve heart health. Chia seeds are packed with antioxidants and omega-3s, and can be easily added to smoothies, yogurt, or oatmeal. Pumpkin seeds are an excellent source of zinc, which is important for a healthy immune system. Other healthy nuts and seeds include flaxseeds, hemp seeds, sunflower seeds, and pecans.
It’s important to note that while nuts and seeds are a healthy source of fat, they are also high in calories. It’s easy to overdo it on these tasty snacks, so be sure to enjoy them in moderation. A small handful of nuts or seeds (about 1/4 cup) per day is a good serving size to aim for. Try incorporating them into your meals as a topping for salads or yogurt, or as a crunchy snack on their own.
Extra Virgin Olive Oil
Extra virgin olive oil is a flavorful and healthy source of fat that has been used for centuries as a staple in Mediterranean diets. This type of oil is made from freshly pressed olives, without any chemical treatments or heat, making it the purest and most nutrient-dense form of olive oil available.
One of the key benefits of extra virgin olive oil is its high content of monounsaturated fatty acids, which are essential for maintaining good heart health. These types of fats help to lower bad cholesterol levels, reducing the risk of heart disease and stroke. Additionally, extra virgin olive oil contains antioxidant compounds that help to protect your cells from damage caused by free radicals.
Here is a table showcasing the nutritional information of one tablespoon (15 ml) of extra virgin olive oil:
| Nutrient | Amount |
|---|---|
| Calories | 120 |
| Total fat | 14 g |
| Saturated fat | 2g |
| Monounsaturated fat | 10 g |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 2 g |
| Vitamin E | 13% of the Daily Value (DV) |
As you can see, extra virgin olive oil is a calorie-dense food, providing 120 calories per tablespoon. However, the majority of these calories come from healthy fats, with only a small amount of saturated fat. Additionally, one tablespoon of extra virgin olive oil provides 13% of the Daily Value (DV) for vitamin E, a potent antioxidant that helps to protect your cells from oxidative damage.
Incorporating extra virgin olive oil into your diet in moderation can provide numerous health benefits. It can be used as a dressing for salads or as a cooking oil, and its rich flavor can add depth and complexity to many dishes. Just remember to use it sparingly, as even healthy fats should be consumed in moderation as part of a balanced diet.
Peanut Butter
Peanut butter is a delicious and easy source of healthy fat. It’s a great addition to a sandwich or as a dip for fruits and vegetables. Not all peanut butters are created equal, however, and it’s important to choose a high-quality option.
One of the best things about peanut butter is its high content of monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, which are considered healthy fats. These healthy fats can help improve cholesterol levels, reduce inflammation, and even lower the risk of heart disease. Peanut butter is also a good source of protein and fiber.
When choosing a peanut butter, look for options that are made with 100% peanuts and no added sugars or oils. Avoid brands that contain hydrogenated oils, which can increase the risk of heart disease.
Here’s a table comparing the nutritional information for two popular brands of peanut butter:
| Peanut Butter Brand | Calories per Serving (2 tbsp) | Total Fat per Serving (g) | Saturated Fat per Serving (g) | Added Sugars per Serving (g) | Protein per Serving (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brand A (100% peanuts) | 190 | 16 | 3 | 0 | 7 |
| Brand B (with added oil and sugar) | 210 | 19 | 3.5 | 2 | 6 |
As you can see, the 100% peanut option (brand A) has fewer calories and less added sugars, while still providing a good amount of healthy fats and protein. It’s also important to pay attention to serving size, as it can be easy to overindulge in peanut butter due to its delicious taste.
Peanut butter can be a healthy and tasty addition to your diet as long as you choose an option that’s made with 100% peanuts and no added sugars or oils. Be mindful of serving size and enjoy it in moderation.
Foods High in Unhealthy Fats
When it comes to maintaining a healthy diet, it’s just as important to know what foods to avoid as it is to know what foods to incorporate. Unfortunately, there are plenty of options out there that are high in unhealthy fats, which can contribute to a range of health issues when consumed in excess. From fast foods to processed snacks and desserts, it can be all too easy to fall into the trap of eating foods that offer little nutritional value but plenty of calories from harmful fats. In this section, we’ll explore some of the worst offenders when it comes to unhealthy fats, so that you can make informed choices about your diet.
Fast Foods
Fast food is a popular and convenient choice for many people, but it is important to be aware of the high levels of unhealthy fats found in these foods. Fast foods are typically high in saturated and trans fats, which can increase your risk of developing heart disease and other health problems. Here are some common fast food items and their fat content:
| Fast Food Item | Grams of Saturated Fat | Grams of Trans Fat |
|---|---|---|
| Cheeseburger | 8 | 1.5 |
| French fries | 4 | 0 |
| Fried chicken | 3.5 | 0 |
| Milkshake | 5 | 0 |
As you can see, just one fast food meal can easily exceed your daily recommended intake of saturated and trans fats. It is important to limit your intake of fast foods and opt for healthier options whenever possible. Choose grilled or baked options instead of fried, and look for salads and vegetable-based sides instead of french fries. By making these small changes, you can reduce your intake of unhealthy fats and improve your overall health.
Processed Snacks and Desserts
When it comes to processed snacks and desserts, it’s important to pay attention to the type of fat they contain. Many of these products are high in saturated and trans fats, which can increase your risk of heart disease and other health problems.
Here are some examples of processed snacks and desserts that are high in unhealthy fats:
- Commercially-made cookies, cakes, and pastries
- Potato chips and other fried snack foods
- Candy bars and other sugary sweets
- Processed snack crackers
- Granola and energy bars that contain high amounts of added sugar and fats
While it’s okay to indulge in these treats occasionally, it’s important to consume them in moderation and balance them out with healthier options. For example, instead of reaching for a candy bar as a snack, try having a piece of fruit or a handful of nuts instead. And instead of eating processed crackers, try a slice of whole grain bread with avocado or hummus spread on top for a more nutritious snack. Remember, a healthier diet is all about making small changes over time to create lasting habits that will benefit your health in the long run.
Butter and Other Solid Fats
Solid fats, such as butter and margarine, can be a major source of unhealthy fats in your diet. These fats are typically high in saturated and trans fats, which can raise your cholesterol levels and increase your risk for heart disease. It’s important to limit your intake of these fats and opt for healthier options instead.
| Food | Unhealthy Fat Content |
|---|---|
| Butter | High in saturated fat |
| Margarine | May contain trans fat |
| Lard | High in saturated fat |
| Shortening | High in trans fat |
Instead of using butter and other solid fats in your cooking and baking, try using healthier options like olive oil, coconut oil or avocado oil. You can also choose spreads and margarines that are low in trans and saturated fats. Reading nutrition labels can help you make informed choices about the amount and type of fat in the foods you eat. By making these healthier choices, you can help lower your risk for heart disease and improve your overall health.
Conclusion
As we come to the end of this detailed article about how much fat you should eat per day, it’s important to reflect on the information we’ve covered. It can be perplexing to navigate the world of dietary recommendations, but understanding the different types of fats and their potential impact on your health is crucial. By making conscious and informed choices about the types of fats we consume and the quantity in which we consume them, we can prioritize our health and wellbeing. Let’s explore some key takeaways from our discussion about fat intake.
Calculate Your Fat Intake and Make Healthy Food Choices
To maintain a healthy diet and meet your daily fat needs, it is important to measure your fat intake and make healthy food choices. Calculating your daily fat intake can be done by using either the American Heart Association or the Institute of Medicine guidelines, or by customizing your own fat intake plan.
The American Heart Association Guidelines: this guideline suggests that adults should consume no more than 25 to 35% of calories from fat, with saturated fat making up no more than 7% of total calorie intake. For example, if you consume 2,000 calories a day, your daily fat intake should be between 56 to 77 grams with saturated fat intake no more than 16 grams.
The Institute of Medicine Guidelines: this guideline recommends that adults should consume between 20 to 35% of their daily calories from fat, with saturated fat making up no more than 10% of total calorie intake. If you follow a 2,000 calorie diet, your daily fat intake should be between 44 to 77 grams with saturated fat intake no more than 22 grams.
Customized Fat Intake: to determine your customized fat intake, it is important to consider your age, sex, weight, and activity level. As with any dietary changes, consult with your doctor or a registered dietitian before making any changes.
Once you have determined your daily fat intake, it is important to make healthy food choices. Foods high in healthy fats include fatty fish like salmon, avocado, nuts and seeds, extra virgin olive oil, and peanut butter. Foods high in unhealthy fats include fast foods, processed snacks and desserts, and butter and other solid fats.
By measuring your fat intake and making healthy food choices, you can maintain a well-balanced diet and lower your risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease and stroke. Remember to consult with a healthcare professional before making any drastic changes to your diet.
| Guidelines | Daily Fat Intake | Daily Saturated Fat Intake |
|---|---|---|
| American Heart Association | 25-35% of daily calories | No more than 7% of daily calories |
| Institute of Medicine | 20-35% of daily calories | No more than 10% of daily calories |
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the differences between saturated and unsaturated fats?
Saturated fats are typically solid at room temperature and are primarily found in animal products, while unsaturated fats are usually liquid and are found in plant-based oils and some fish.
How much saturated fat should I consume per day?
The American Heart Association recommends limiting saturated fat intake to no more than 5-6% of daily calories, which equates to about 13 grams for an average adult.
What are some good sources of unsaturated fats?
Some good sources of unsaturated fats include nuts, seeds, avocado, olive oil, fatty fish, and vegetable oils like canola and sunflower.
How can I measure my fat intake?
You can measure your fat intake by tracking your food intake using a food diary or app, checking nutrition labels on packaged foods, and measuring out oils and other fats when cooking and preparing meals.
How can healthy fats benefit my health?
Healthy fats can lower your risk of heart disease and stroke, improve brain function, and aid in the absorption of vitamins and other nutrients.
What are some good sources of healthy fats?
Some good sources of healthy fats include salmon, avocado, nuts and seeds, olive oil, and peanut butter.
What are some common sources of unhealthy fats?
Common sources of unhealthy fats include fast food, processed snacks and desserts, butter and other solid fats, and fatty meats like bacon and sausage.
How much fat should I consume if I want to lose weight?
Your fat intake for weight loss will depend on your individual calorie needs and nutritional goals, but generally it’s recommended to aim for a moderate intake of healthy fats.
Can I consume fat if I have high cholesterol?
If you have high cholesterol levels, it’s important to limit your intake of saturated and trans fats, but you can still consume healthy fats like those found in fatty fish, nuts, and seeds.
What are some tips for making healthier food choices for fat intake?
Some tips for making healthier food choices for fat intake include opting for lean meats and plant-based protein sources, choosing oils and spreads made from healthy fats, and limiting processed and packaged foods that are high in unhealthy fats.